Part:BBa_K2984019
L1c-Psad-YFP-RbcS2, Expression of YFP through light-inducible promoter
This Level 1 Construct is designed for comparison of locus dependent expression through fluorescence intensity measuerments. The Construct consist of the Psad promoter an coding sequence for the yellow fluorescent protein and the Rbcs2 terminator. The promoter is inducible by light.
Sequence and Features
- 10INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]Illegal PstI site found at 1046
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal PstI site found at 1046
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 4
- 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal PstI site found at 1046
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal PstI site found at 1046
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 1523 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Usage and Biology
This construct is designed for the expression of the yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) mVenus in C. reinhardtii. It is composed of the PsaD promoter, which stems from the photosystem one complex, the mVenus coding sequence and the terminator Rbcs2, taken from the Rubisco gene. This construct will make C. reinhardtii glow under a fluorescence microscope.
The YFP mVenus has an excitation peak at 515 nm and an emission peak at 528 nm (Kremers et al. 2006). With this construct we focused on the characterization of the light induction of PsaD.
Characterization
The first qualitative characterization we made was to check the mVenus fluorescence of C. reinhardtii that had been transformed with this construct under a fluorescence microscope.

After seeing fluorescence under the microscope, we proceeded to measure the fluorescence intensity of our clone under a plate reader (Fig. 2). Measuring the fluorescence intensity of YFP in C. reinhardtii can be quite challenging, due to the strong interaction of the algae with light (photo systems, chlorophyll, pigments and light antennae). You can find more information about how to measure this part on the measurements siteof the Humboldt Berlin team 2019.
For the measurement we prepared YFP expressing clones and WT algae, to compare the fluorescence of both probes. This is imperative due to the strong autofluorescence of the algae. Additionally, we made sure to have the same optical density (cell concentration) in both YFP and WT probes. We did a sequential dilution in three steps with the probes and measured the fluorescence intensity for each probe. We excited at 490 nm and measured the emission at 528 nm. We were able to show that the fluorescence intensity of the YFP expressing clones was always above the autofluorescence of the wild type, as can be seen in Fig. 2.
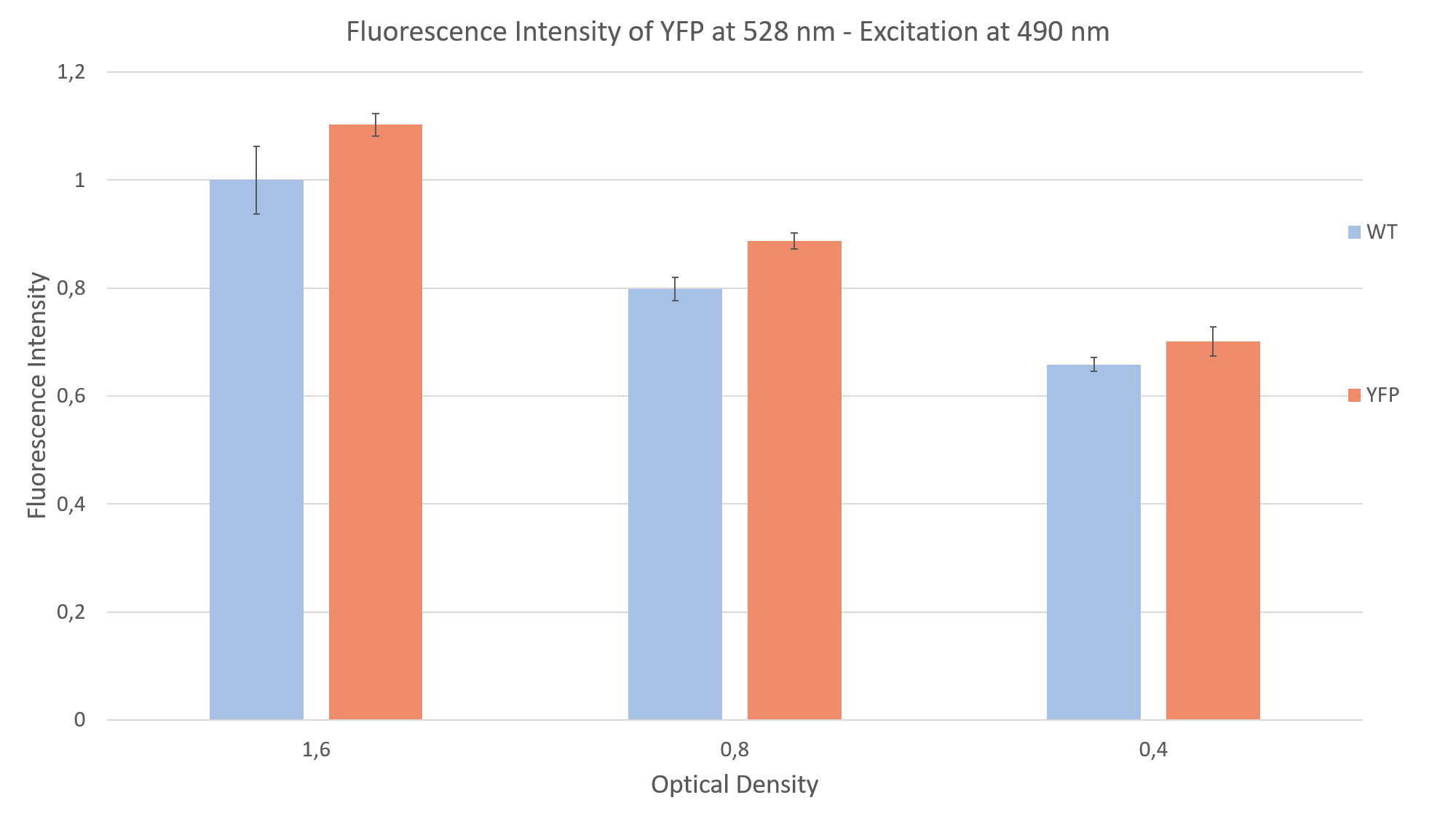
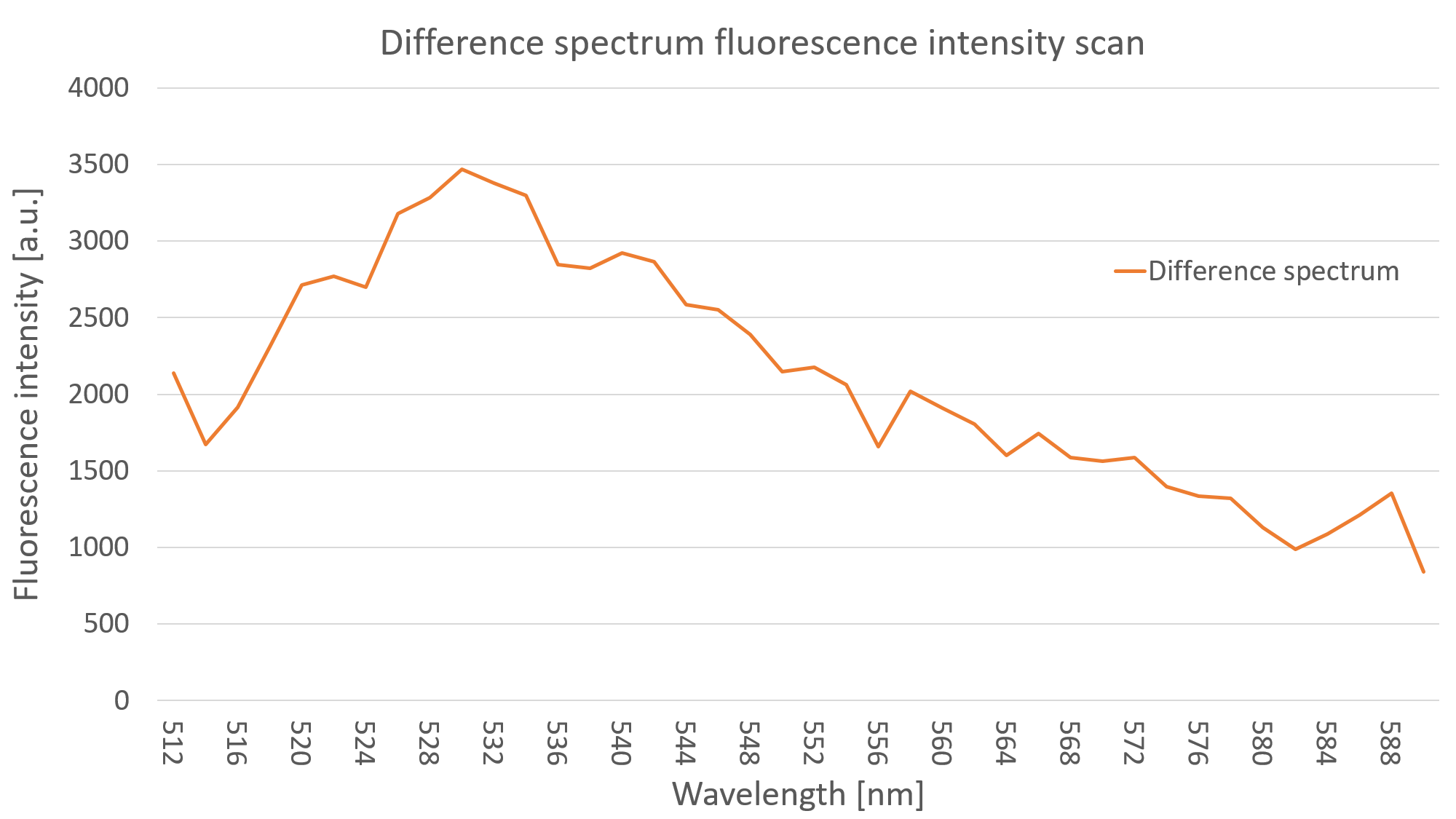

References
- Kremers, G. J., Goedhart, J., van Munster, E. B., & Gadella, T. W. (2006). Cyan and yellow super fluorescent proteins with improved brightness, protein folding, and FRET Förster radius. Biochemistry, 45(21), 6570-6580.
| chassis | C. reinhardtii |
| emission | 528 nm |
| excitation | 515 nm |
