Part:BBa_K2933102
His+Linker a+Sumo+Linker b+SPG-1
This part encodes the fusion protein of His-Sumo tag and SPG-1 to promote the expression and purification of target protein(SPG-1).
Sequence and Features
- 10INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]Illegal EcoRI site found at 256
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal EcoRI site found at 256
Illegal NheI site found at 33 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal EcoRI site found at 256
Illegal BglII site found at 145
Illegal BamHI site found at 344 - 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal EcoRI site found at 256
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal EcoRI site found at 256
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Usage and Biology
This composite part is made up with five basic parts, the His tag, the Sumo tag, three cutting sites(NdeI, NheI and BamHI) and our target protein SPG-1. It encodes a protein which is SPG-1 fused with His-Sumo tag. The fusion protein is about 42.2kD. In order to gain the highly purified target protein, we add His-Sumo tag in N-terminal of SPG-1 and combine the three parts with these three cutting sites. The fusion protein can be cut off at the cutting site BamHI. It is convenient for us to purify our target protein.
Molecular cloning
First, we used the vector pET28B-Sumo to construct our expression plasmid. And then we converted the plasmid constructed to E. coli DH5α to expand the plasmid largely.
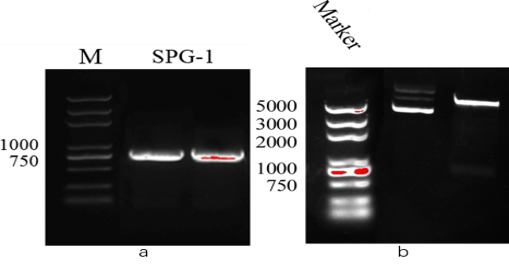
Figure 1. a: The PCR result of SPG. b: The verification results by enzyme digestion.
After verification, it was determined that the construction is successful. We converted the plasmid to E. coli BL21(DE3) for expression and purification.
Expression and purification
Pre-expression:
The bacteria were cultured in 5mL LB liquid medium with ampicillin(100 μg/mL final concentration) in 37℃ overnight.
Massive expressing:
After taking samples, we transfered them into 1L LB medium and add antibiotic to 100 μg/mL final concentration. Grow them up in 37°C shaking incubator. Grow until an OD 600 nm of 0.8 to 1.2 (roughly 3-4 hours). Induce the culture to express protein by adding 1 mM IPTG (isopropylthiogalactoside, MW 238 g/mol). Put the liter flasks in 16°C shaking incubator for 16h.
Affinity Chromatography:
We used the Ni Agarose to purify the target protein. The Ni Agarose can combine specifically with the Ni-Sumo tag fused with target protein.
- First, wash the column with water for 10 minutes. Change to Ni-binding buffer for another 10 minutes and balance the Ni column.
- Second, add the protein solution to the column, let it flow naturally and bind to the column.
- Third, add Ni-Washing buffer several times and let it flow. Take 5ul of wash solution and test with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. Stop washing when it doesn’t turn blue.
- Forth, add Ni-Elution buffer several times. Check as above.
- Fifth, collect the eluted proteins for further operation.
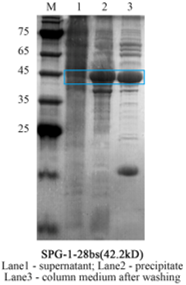
Figure 2. The result of SDS-page.
Anion exchange column:
According to the predicted pI of the protein and the pH of the ion-exchange column buffer, firstly select the appropriate ion exchange column (anion exchange column or cation exchange column). The pH of buffer should deviate from the isoelectric point of the protein. Since the isoelectric point of our protein is 9.42 in theory, we choose buffer pH of 7.4 and use anion exchange column for purification.
The protein is concentrated with a 10KD concentration tube, and then the exchange buffer is used to exchange the protein to the ion-exchange liquid A. Finally, it is concentrated to less than 5ml by centrifuging at 4℃ and 3400rpm for 10 minutes in a high-speed centrifuge to remove insoluble substances and bubbles.
Balance the selected column with liquid A. Through the AKTApure protein purification system, the samples are loaded to the column at a flow rate of 0.5ml/min, and continue washing for 5min. Gradually increase the content of liquid B in the column, change the salt concentration and then change the interaction between the sample and the column, and collect the corresponding eluent according to the position of the peak. Use SDS-PAGE to check the result.
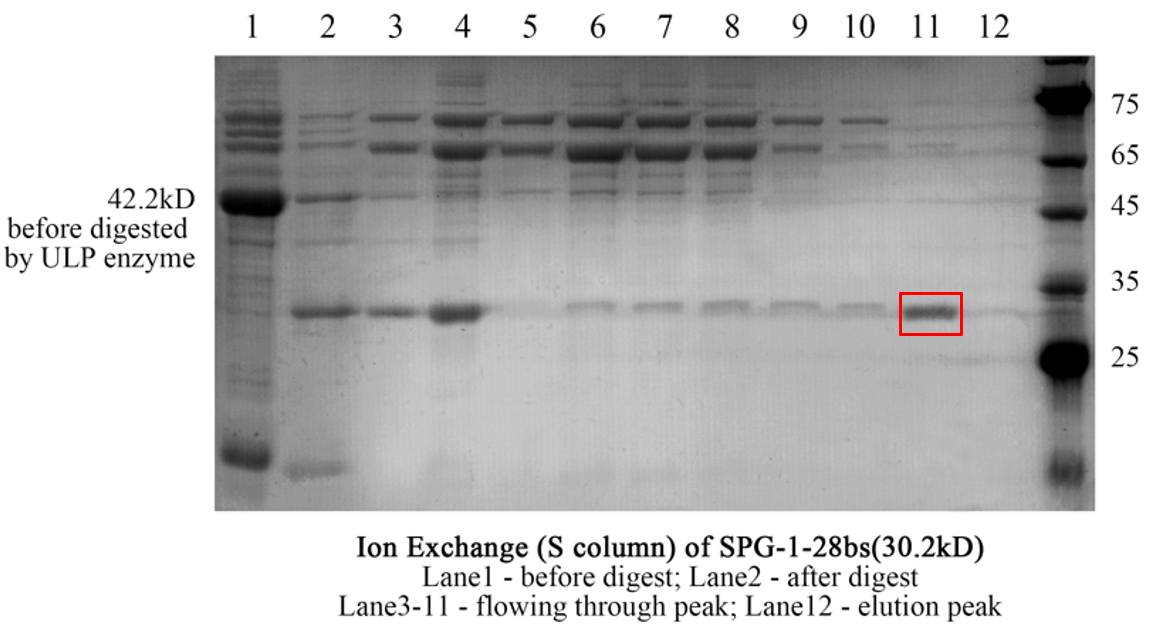
Figure 3. The result of SDS-page of superdex75 S column.
Gel filtration chromatography:
The collected protein samples are concentrated in a 10 KD concentrating tube at a speed of 3400 rpm and concentrated for a certain time until the sample volume is 500 μl. At the same time, the superdex 200 column is equilibrated with a buffer to balance 1.2 column volumes. The sample is then loaded and 1.5 cylinders are eluted isocratically with buffer. Determine the state of protein aggregation based on the peak position and collect protein samples based on the results of running the gel.

Figure 4. (a) The result of gel filtration used the superdex75 column with the AKTA system, which shows that the target protein is monomeric. (b) The result of SDS-PAGE. And the target protein is about 30.2kD.
References
[1]The Soil Microbiota Harbors a Diversity of Carbapenem-Hydrolyzing β-Lactamases of Potential Clinical Relevance. Gudeta DD, Bortolaia V, Amos G, Wellington EM, Brandt KK, Poirel L, Nielsen JB, Westh H, Guardabassi L. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Oct 19;60(1):151-60.| None |
