Coding
mN1c
Part:BBa_K2549006
Designed by: Rongrong Du Group: iGEM18_Fudan (2018-10-02)
mouse Notch1 core
This part is the mouse Notch1 minimal regulatory region[1]. It was used as the transmembrane core domain of the SynNotch. However, original reported design has a high background activation in transfected 293T cells. We have put a lot of effect in optimizing this critical transmembrane domain for Notch receptor.
Sequence and Features
Assembly Compatibility:
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal SapI.rc site found at 592
Biology
Significance of Notch signaling
synNotch with α-CD19 against CD19 antigen works extremely well in Morsut L et al 2016
Please refer the original article for more details.
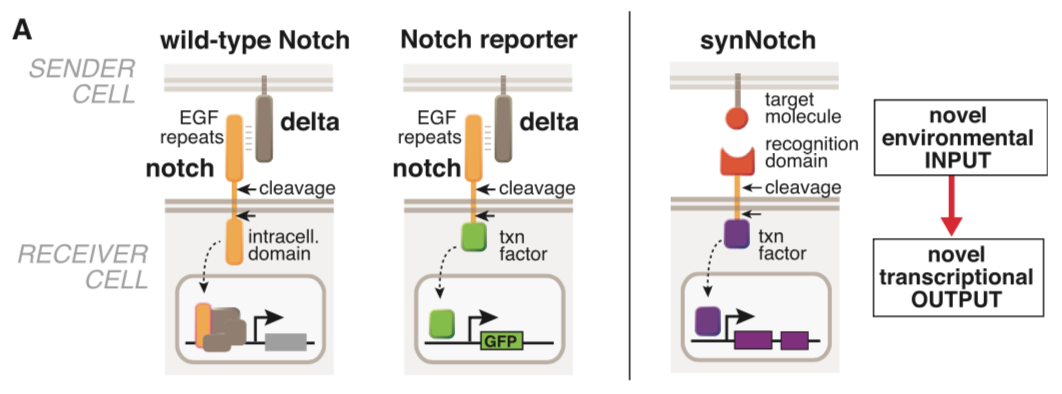
Morsut L at al stated: Conceptual design of synNotch receptor systems. Left: wild-type Notch has a large extra-cellular domain that binds to its ligand, Delta, expressed on opposing partner cells, and an intracellular transcriptional regulatory domain that is released by ligand-induced cleavage. Arrows indicate the multiple proteolytic cleavage sites. Middle: Notch reporters have been built in which the intracellular domain is replaced by an orthogonal transcription factor. Right: in synNotch receptors, both the extracellular and intracellular domains have been completely replaced, leaving only the small central regulatory region of Notch. Both novel inputs and outputs can be defined by using the synNotch architecture.
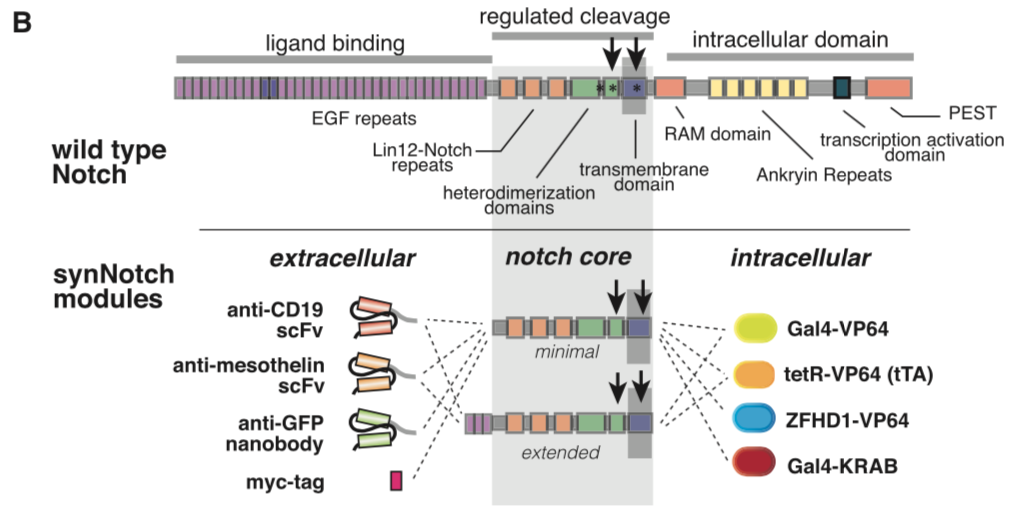
Morsut L at al stated: Modularity of the synNotch platform: the input and output domains from Notch can be swapped with diverse domains. On the extracellular side, diverse recognition domains can be used (antibody based, or peptide tags are shown), and on the intracellular side, diverse effector can be used (transcriptional activators with different DBDs are shown, as well as a transcriptional repressor).

Morsut L at al stated: SynNotch receptors can be used to detect endogenous disease antigens and induce the expression of a reporter gene. Mouse fibroblasts (L929 line) expressing anti-CD19/tTA synNotch are cultivated with K562 sender cells expressing Delta, CD19, or CD19 in the presence of the gamma-secretase inhibitor DAPT. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) plots of the resulting GFP reporter intensity in receiver cells are shown. Inset shows an image of MDCK cells expressing the anti-CD19/GFP synNotch, when co-cultivated for 24 hr with MDCK sender cells expressing CD19 (constitutively labeled with tagBFP). Only receiver cells in contact with (blue) sender cells activate the reporter and turn green.

Morsut L at al stated: Stimulation of mouse fibroblasts expressing anti-GFP synNotch with ligands in different formats. Anti-GFP synNotch receiver cells are stimulated for 1 hr with GFP either in soluble form, presented on a K562 sender-cell, or cis-presented on the receiver cell itself. The receiver cells show activation only when the ligand is present on an opposing surface and if they do not express the ligand in cis. The FACS data are recorded at 24 hr after the beginning of stimulation. FACS histograms include at least 10,000 cells for each condition.

Morsut L at al stated: Mouse fibroblasts (L929 line) with anti-CD19 synNotch with a transcriptional repressor intracellular domain (Gal4-KRAB) are co-cultivated with K562 sender cells. The receiver cells constitutively express GFP downstream of a SV40/UAS combined promoter. FACS plot of receiver cells is shown, in presence of K562 sender cells with or without CD19 expression, as indicated in figure.

Morsut L at al stated: Primary hippocampal neurons were dissociated from E18 rat embryos and are nucleofected to express an anti-CD19 synNotch receptor/GFP reporter. Neurons were plated on a glass-bottom 35 mm culture dish coated with poly-D-lysine and laminin.Sender cells (K562s) are added to the culture 2 hr after neuron plating. Images are taken from live cells at day 4 after plating. On the right, representative images for neurons that are co-cultured with plain K562 cells (upper panel) or with CD19+ K562 sender cells (bottom panel) are shown. Neurons co-cultured with ligand-presenting sender cells strongly induce GFP expression.

Morsut L at al stated: Jurkat T clonal cell line engineered to stably express an anti-CD19/GFP synNotch receptor system. Data on the right show fluorescence of clonal Jurkat cell population upon stimulation with CD19+ or CD19- sender cells (K562s) at t = 24 hr. T cells are activated only when they encounter cells with the cognate ligand. FACS histograms include at least 10,000 cells for each condition.
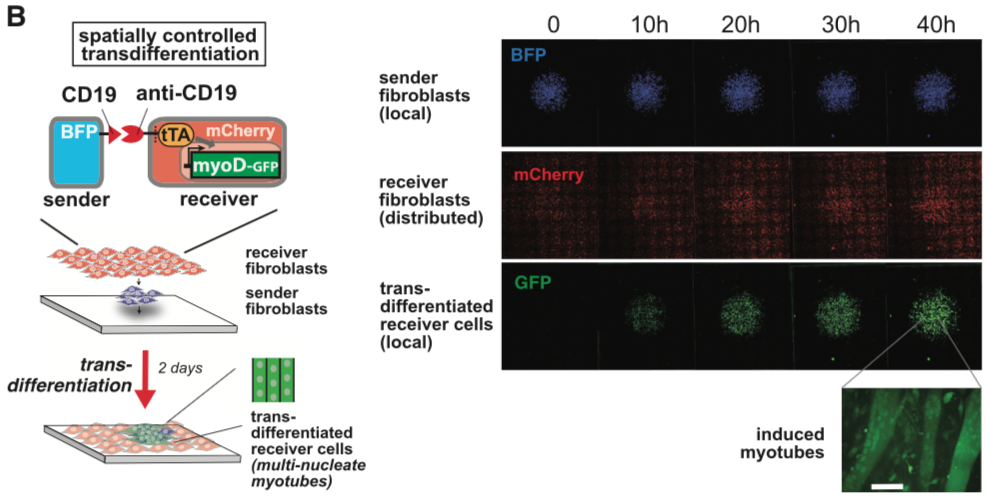
Morsut L at al stated: SynNotch activation of a MyoD in fibroblasts induces transdifferentiation in a spatially controlled manner. C3H mouse fibroblasts are engineered as follows: sender cells express extra-cellular CD19 linked to a transmembrane domain, plus a tagBFP marker; receiver cells express the anti-CD19 synNotch with tTA intracellular domain, along with a TRE/myoD cassette and a constitutive mCherry marker. Sender fibroblasts (blue) are plated first in a limited region of the plate and allowed to adhere to the plate; after 1 hr, the receiver cells (red) are plated to uniformly cover the entire glass plate. Images show a large area of the co-culture and are still frames from a movie that span the first 48 hr after co-plating sSee also Movie S1). GFP channel shows the induction of MyoD-GFP in received cells in a region that overlaps with the blue channel (sender cells). Receiver cells away from sender cells remain uninduced and provide an internal control for the experiment. A higher magnification of the field for the green channel is shown, showing the induction of multinucleate myotubes. Scale bar, 50 um.

Morsut L at al stated: SynNotch and wild-type Notch activate orthogonal signaling pathways. L929 mouse fibroblasts receivers are engineered to express (1) the wild-type Notch receptor with a tTA intracellular domain and a TRE/GFP reporter and (2) a synNotch receptor with anti-CD19 extracellular domain, Gal4-VP64 intracellular domain, and a UAS/tagBFP reporter. The graph on the right shows the clonal population of receiver cells fluorescence signal for the BFP and the GFP reporters in different conditions: black, untreated; blue, stimulated with CD19 expressing senders; orange, stimulated with delta senders; and red, stimulated with sender cells expressing both CD19 and delta. Sender cells are mouse L929 fibroblasts. See Figure S5A for quantification.
References
- ↑ Engineering Customized Cell Sensing and Response Behaviors Using Synthetic Notch Receptors. Morsut L, Roybal KT, Xiong X, ..., Thomson M, Lim WA. Cell, 2016 Feb;164(4):780-91 PMID: 26830878; DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.01.012
[edit]
Categories
Parameters
//cds/membrane
| None |

