Part:BBa_T2028
Chitin binding internal domain
This is a chitin binding domain (CBD) designed to be at between protein domains. Chitin binding domains are a type of affinity tag that can be used to purify proteins.
Usage and Biology
The chitin binding domain tag is used for protein purification using a chitin column. CBD can be placed on either the N- or C-terminus of proteins and is usually used in conjunction with a self-splicing intein tag. Purification of a CBD-tagged protein is a one-step purification process that yields very pure protein with low miligram yields. The primary disadvantage is that the purification must be done in the absence of thiol-containing reducing agents until the elution step. However, the matrix is compatible with high salt and nonionic detergents.
Proof of the ChBD function
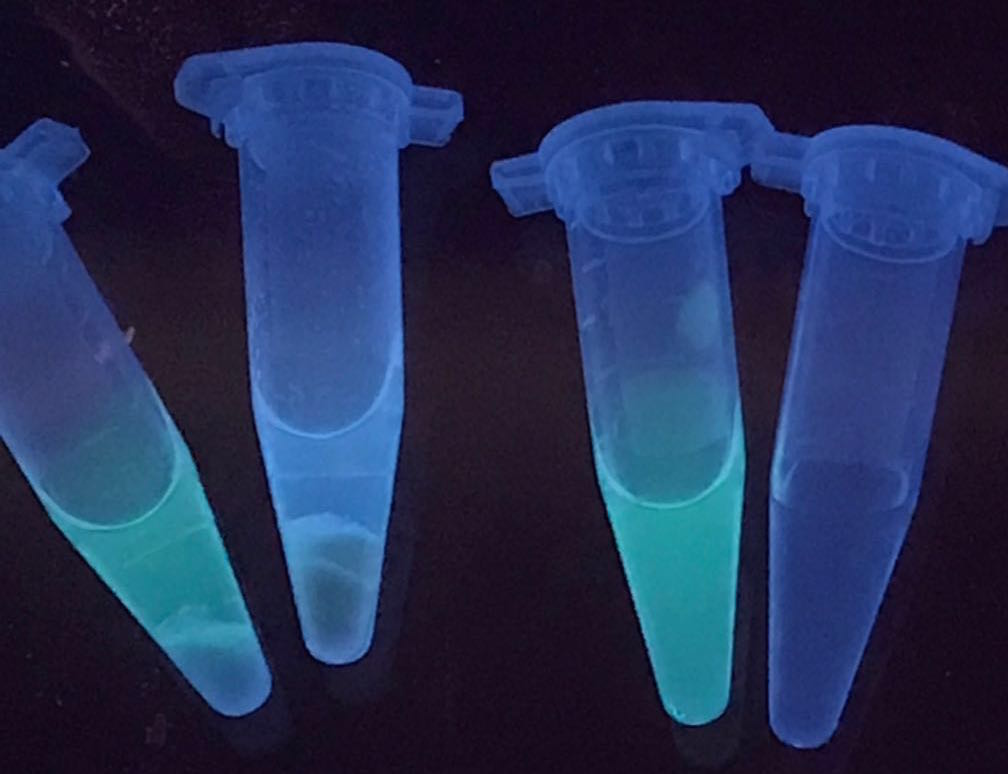
The resulted solution after expression is mixed with chitin powder. Also, the solution with GFP-ChBD but without chitin, solution with the presence of GFP and chitin, and water in comparison, are presented.
Tube 3 contains GFP-ChBD, with a significant green color in the solution. After adding chitin powder inside the tube, the color in the solution disappears and shows on the chitin powder, as presented in tube 2. It proves that the ChBD successfully binds the GFP onto the chitin powder. In contrast, the color of the solution is not changed when adding chitin powder into the GFP solution without ChBD. As a result, the ChBD is well functioned.
[Fig.1. ChBD function: tube1, GFP and chitin; tube2, GFP-ChBD and chitin; tube3, GFP-ChBD; tube4, water]
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
//proteindomain/internal/special
| protein | molecular weight: 5692.36, pI: 7.85, grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY): -0.396 |