Part:BBa_K1033906
tsPurple, purple chromoprotein
This chromoprotein (also known as TinselPurple) naturally exhibits strong purple color when expressed.
Usage and Biology
This part is useful as a reporter.
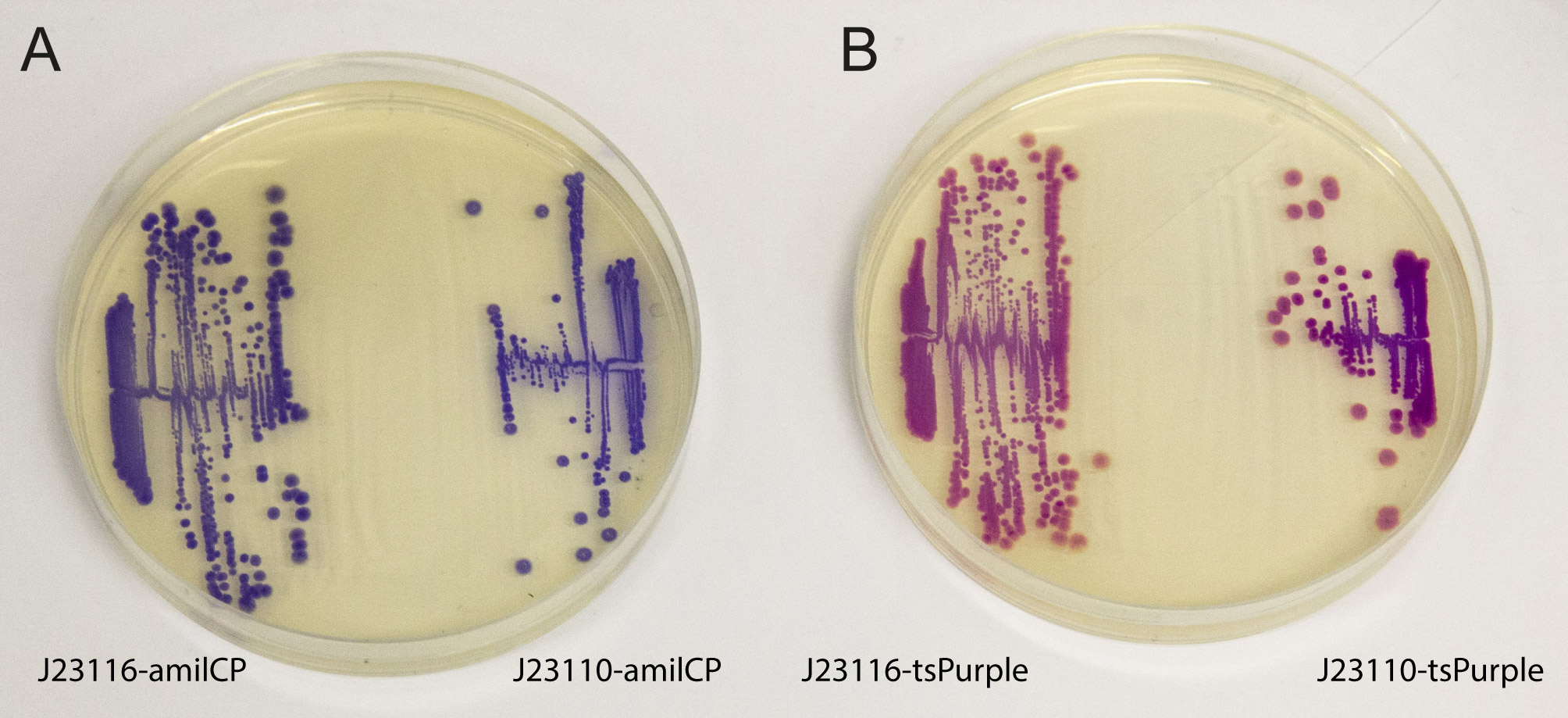
iGEM2013 Uppsala: The images above show E coli constitutively expressing the chromoproteins amilCP BBa_K592009 and tsPurple BBa_K1033906 from the high copy plasmid pSB1C3 from the promoters J23116 and J23110.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Structure and SWISS MODEL Homology Modelling Report
(The following information is the contribution of SVCE_Chennai)
The following sections give a detailed information on this chromoprotein done by its in silico analysis.
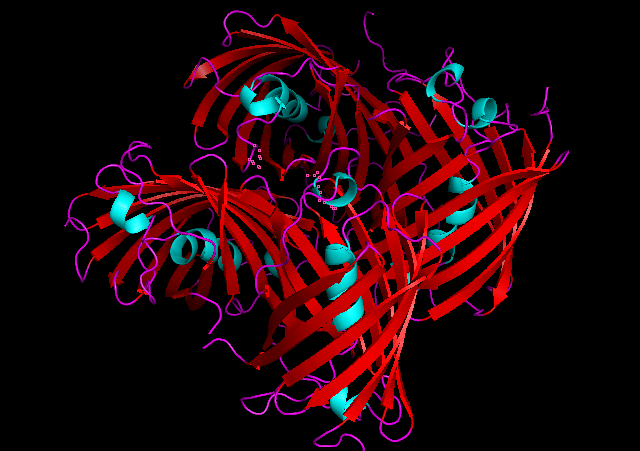
3D Structure
Cartoon representation of tsPurple.
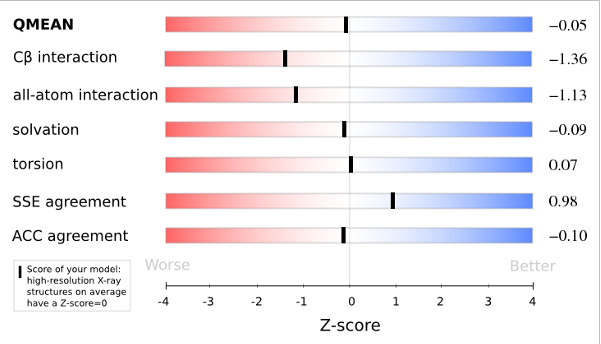
QMEANnorm = 0.02
Cβ = -0.91
All Atom = 0.52
Solvation = -1.19
Torsion = 0.32
The best match during structure prediction.
| Template | Seq. Identity | Oligo-state | Found by | Method | Resolution | Seq Similarity | Range | Coverage | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4ohs.1.A | 86.61 | homotetramer | HHblits | X-Ray | 2.19Å | 0.58 | 2 - 222 | 0.98 | FAR-RED FLUORESCENT PROTEIN AQ143 |
What about Ligands?
| Ligand | Added to Model | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CL | ✕ - Not biologically relevant. | CHLORIDE ION |
| CL | ✕ - Not biologically relevant. | CHLORIDE ION |
| CL | ✕ - Not biologically relevant. | CHLORIDE ION |
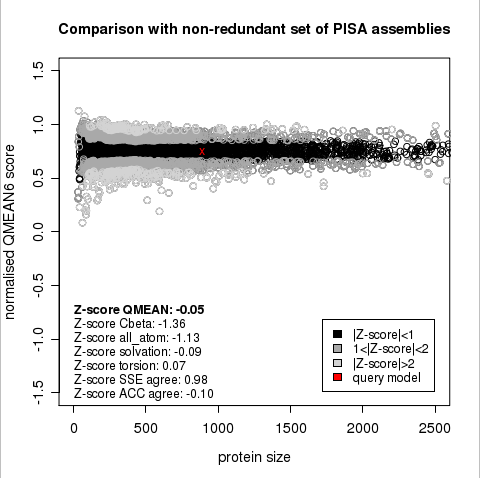
Plot 1
The area built by the circles colored in different shades of grey in the plot on the left hand side represent the QMEAN scores of the reference structures from the PDB. The model's QMEAN score is compared to the scores obtain for experimental structures of similar size (model size +/- 10%) and a Z-score is calculated. A Z-score (or standard score) is a score which is normalised to mean 0 and standard deviation 1. Thus the QMEAN Z-score directly indicates how many standard deviations the model's QMEAN score differs from expected values for experimental structures. In analogy, Z-scores are calculated for all four statistical potential terms as well as the agreement terms being part of the QMEAN score.
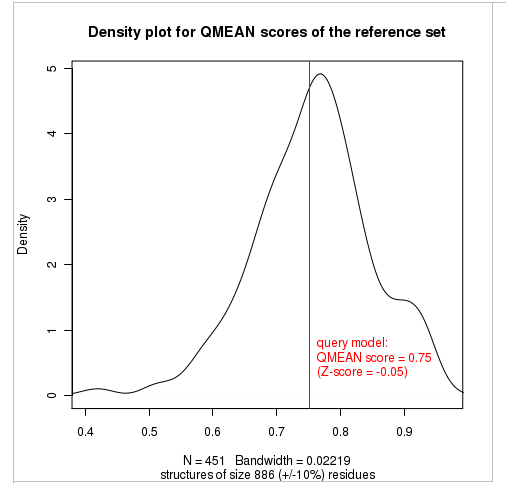
Plot 2
The plot in the middle shows the density plot (based on the QMEAN score) of all reference models used in the Z-score calculation. The location of the query model with respect to the background distribution is marked in red. This plot basically is a "projection" of the first plot for the given protein size. The number of reference models used in the calculation is shown at the bottom of the plot.
Plot 3
The analysis of these Z-scores of the individual terms can help identifying the geometrical features responsible for an observed large negative QMEAN Z-score. Models of low quality are expected to have strongly negative Z-scores for QMEAN but also for most of the contributing terms. Large negative values correspond to red regions in the color gradient. "Good structures" are expected to have all sliders in the light red to blue region.”
//collections/chromoprotein/uppsala
//function/reporter/pigment
| color | Purple |