Part:BBa_K1616023:Experience
Applications of BBa_K1616023
Liquid culture of bacteria transformed with BBa_K325909, BBa_K115900 and BBa_K1616023
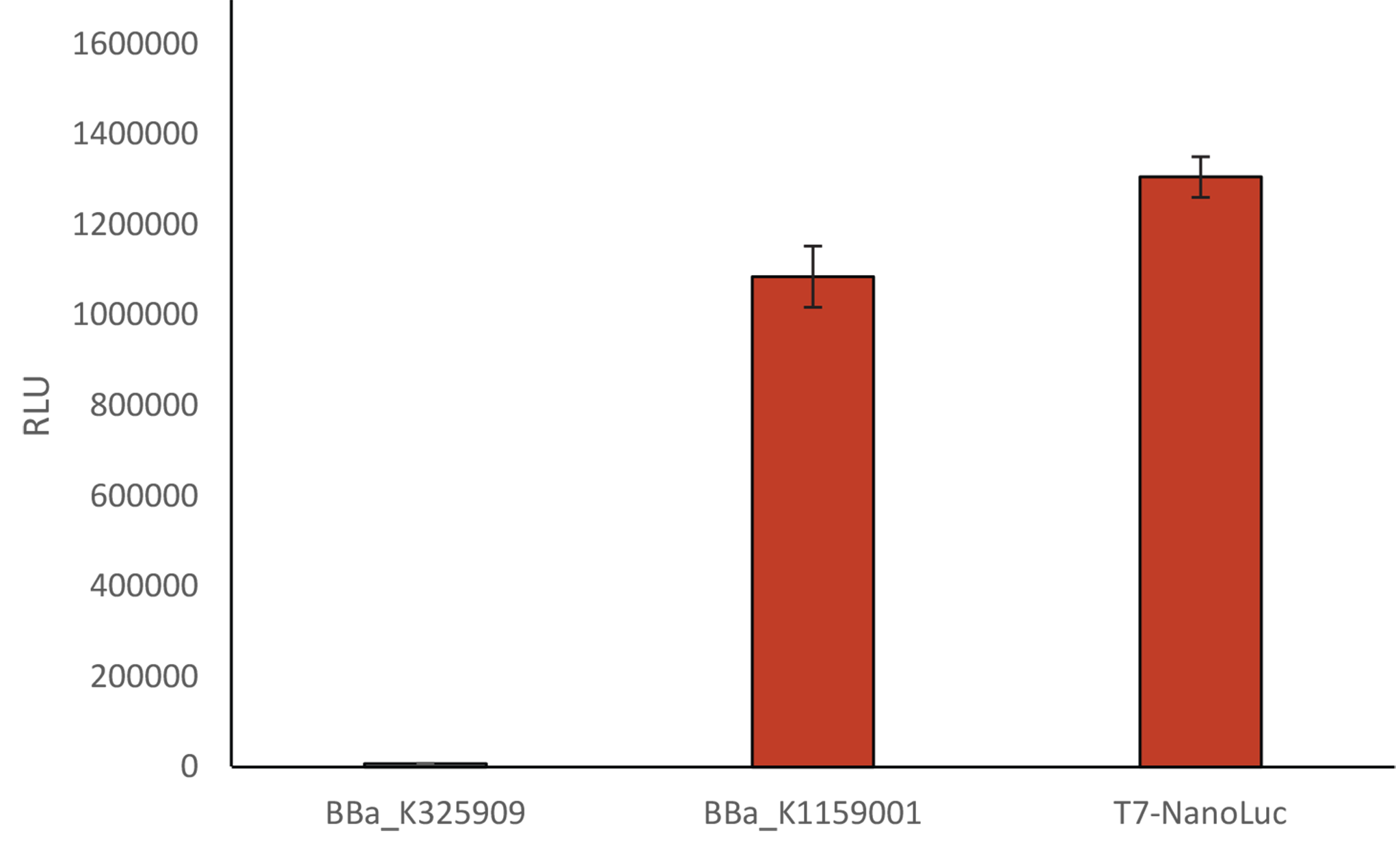
Light intensity has been measured 5 hours after induction with arabinose or IPTG depending on the Biobrick, when DO 600 was between 0,6 and 0,8. BBa_K325909 already has the substrate synthesis within its sequence, therefore we only had to measure the kinetic during 5h of induction and took the maximum value. For the others, we added NanoGlow substrate from Promega (ratio 1:1), measured kinetics over 120 min and took the maximum value.
We worked in BL21(DE3) bacteria for our plasmid “T7 Nanoluc”. Thus, addition of IPTG activates the induction of the Plac promoter and then expression of T7 RNA polymerase is possible. It results in different light intensities proportional to the concentration of IPTG: the more IPTG you have, the brighter!
We compared our new T7 Nanoluc to the first Luxbrick created by Cambridge in 2010 (BBa_K325909), and to BBa_K1159001. T7 NanoLuc showed a 1,2 times brighter light intensity (RLU) than BBa_K1159001 and a light intensity approximately 140 times brighter than BBa_K325909.
User Reviews
UNIQ7435a13c7d82f445-partinfo-00000003-QINU UNIQ7435a13c7d82f445-partinfo-00000004-QINU