Part:BBa_K1675002
glsA, glutaminase1
GlsA encodes an acid-activated glutaminase, which is sufficient for an acid resistance system, and it is able to catalyze a reaction converting glutamate to glutamine and releasing the free gaseous ammonia. The free gaseous ammonia will consume the proton and increase the intracellular pH (Fig.1). The robust glutaminase activity only exists at pH 6.0 or lower. The highest activity is obtained at pH 4.0, followed by pH 5.0 and 6.0. In contrast, GlsA is not activated at pH 7.0 and 8.0. The dependence on pH makes it an effective tool to respond when necessary.
Fig.1 The mechanism of GlsA
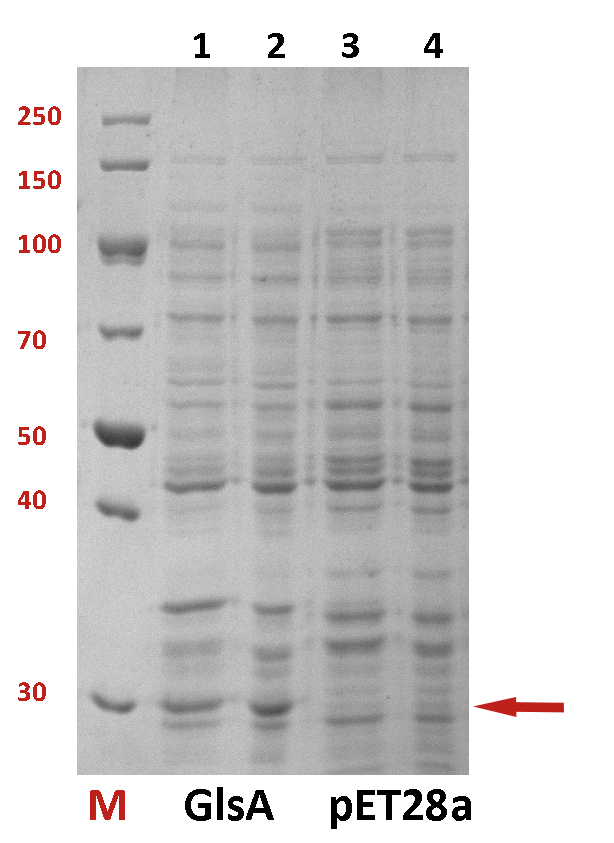
The difference between the testing group and the control group is not evident. We employed a strong promoter T7 to check whether the protein has been expressed. The functional gene GlsA was constructed on plasmid pET28a and the plasmid was transformed into BL21(DE3). 0.5% IPTG was added to induce the expression of the protein. The following is the picture of SDS-PAGE (Fig.2). It shows that our target protein has been expressed successfully.
Fig.2 The SDS-PAGE of GlsA and pET28a
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
| biology | E.coli K-12 |
| protein | glutaminase1 |