Part:BBa_K1689007
dCas9-C-luc
dCas9-C-luc fusion protein ORF
A catalytically dead Cas9 (dCas9), when co-expressed with a guide RNA, forms a DNA recognition complex which can binds any sequence [1]. Firefly luciferase, widely used as a reporter, is split into two fragments, namely N-luc and C-luc [2]. Each fragment by itself is inactive; when two fragments are reassembled, the enzymatic activity of the original protein would be reconstituted, providing easily measurable readout.
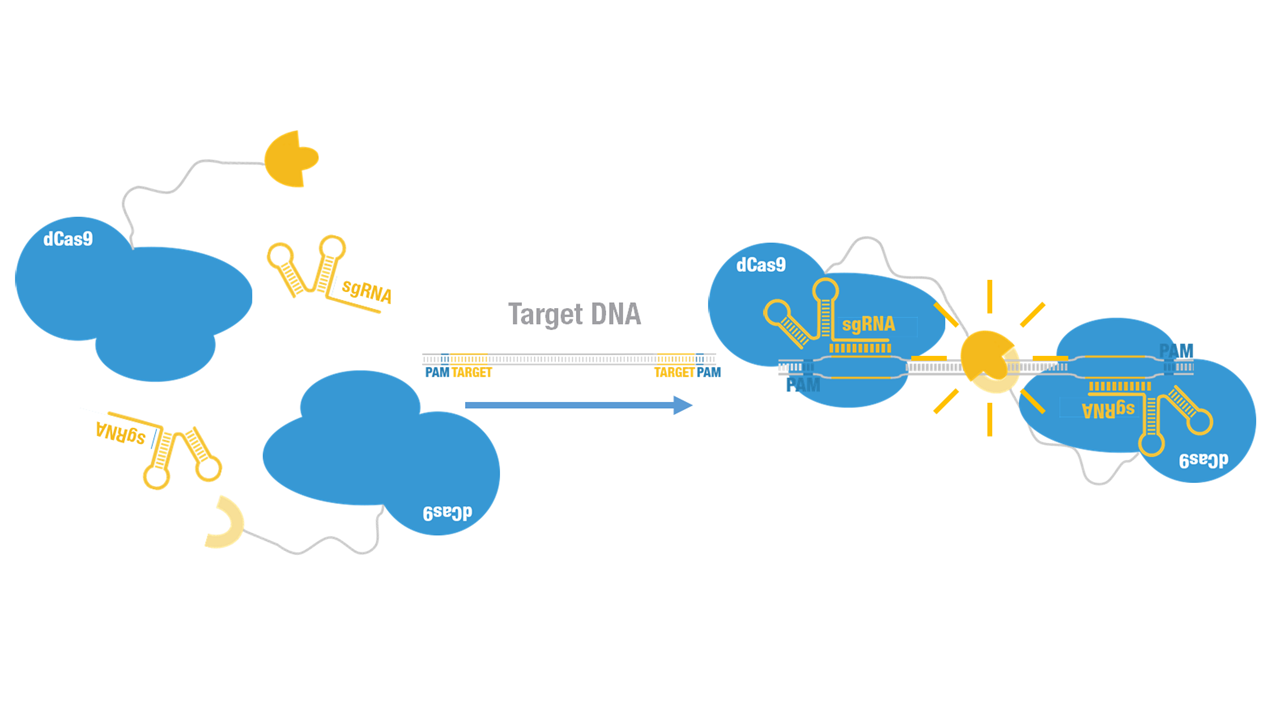
Peking iGEM 2015 fused Cluc to C terminus of dCas9 (Figure 1). Guided by sgRNA, it binds to target DNA sequence. Together with another part,dCas9-Nluc (BBa_K1689008):sgRNA complex,our paired dCas9 (PC) reporter system would work to (Figure 2) to convert the sequence-specific information of pathogenic bacteria's genome (in our case, M. tuberculosis) into easily readable bioluminescence signal.
Figure 1. Schematic cartoon of dCas9-Cluc fusion protein.
Figure 2. Working mechanism of the paired dCas9 (PC) reporter system.
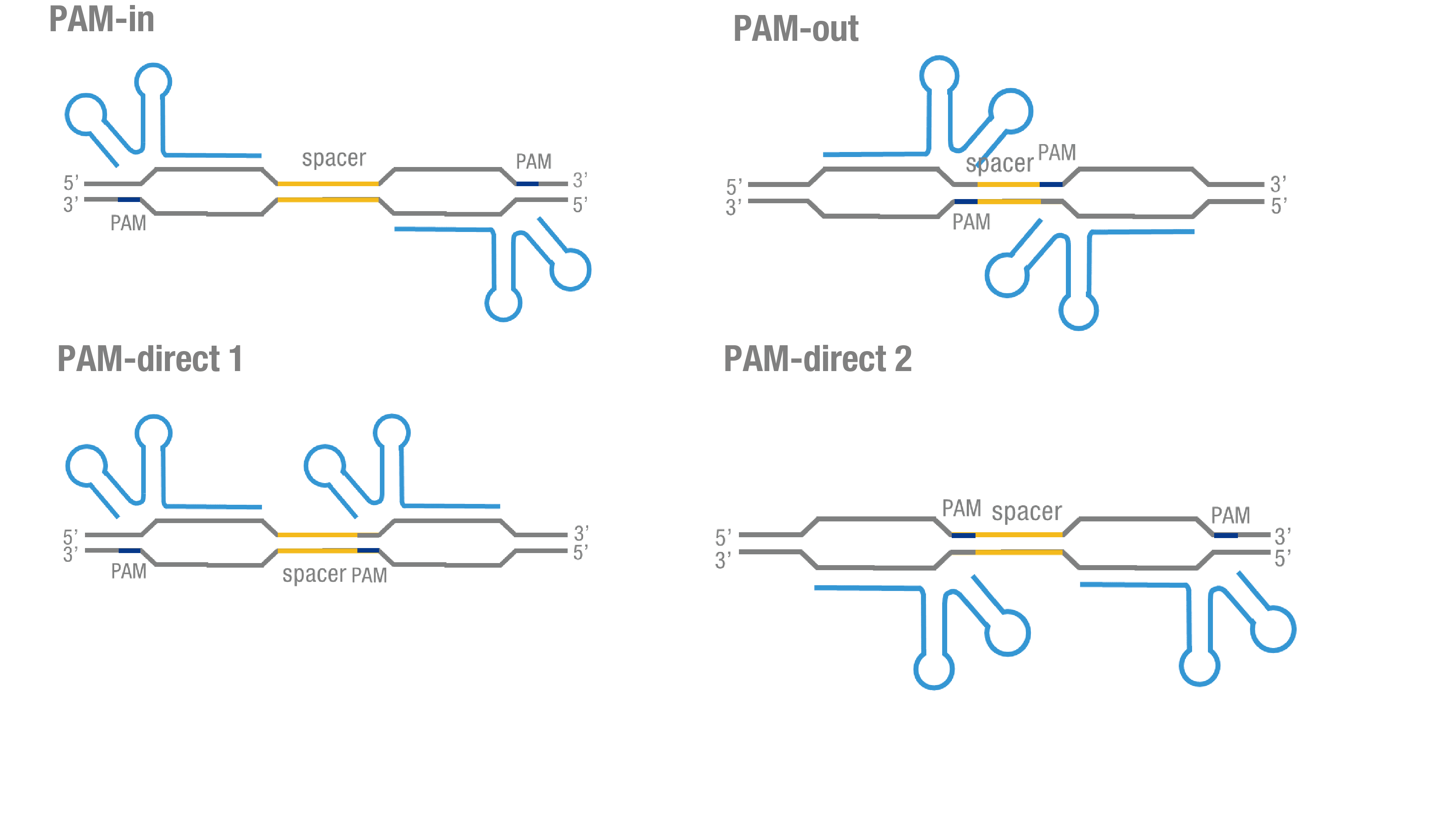
We thoroughly optimized the configuration of our PC reporter system (see [http://2015.igem.org/Team:Peking/Design/PC_Reporter Methods]). Provided that the initial binding of dCas9 to DNA depends on the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM, a short 3’ motif adjacent to target sequence), four sets of sgRNA orientation settings were tested (Figure 3a). To find out how split luciferase-dCas9 fusion strategy influences our PC reporter system, we constructed and tested Nluc-dCas9(BBa_K1689010), dCas9-Nluc (BBa_K1689008) fusion strategy to pair with dCas9-Cluc (Figure 3b) respectively.
a
b
Figure 3. Thorough optimization on the configuration of our PC reporter system. (a) 4 different sgRNA orientation settings. In orientation PAM-out, the pair of PAM sequences are distal from the spacer sequence, with the 5' end of the sgRNA adjacent to the spacer; in orientation PAM-in, the pair of PAM sequences are adjacent to the spacer sequence, with the 3' end of the sgRNA in proximity to the spacer; in orientation PAM-direct 1 and PAM-direct 2, one PAM sequence is adjacent to and another distal from the spacer. (b)4 different protein fusion strategies for the integration of split luciferase fragments into dCa9.
References
1. Lei S. Qi, Matthew H. Larson, Luke A. Gilbert et al. Repurposing CRISPR as an RNA-guided platform for sequence-specific control of gene expression. Cell, 2013, 152: 1173-1183.
2. Kathryn E. Luker, Matthew C. P. Smith, et al. Kinetics of regulated protein–protein interactions revealed with firefly luciferase complementation imaging in cells and living animals. PNAS, 2004, 101: 12288-12293. Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 1176
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 3
Illegal BamHI site found at 3455 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 4457
Illegal AgeI site found at 4596 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal SapI site found at 4207
| None |