Part:BBa_K1326001
ChlM
Mg protoporphyrin IX S-adenosyl methionine O-methyl transferase - Magnesium-protoporphyrin O-methyltransferase (ChlM) [PMID: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12828371 12828371]; [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12489983 12489983]; [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4436384 4436384]]; ChloroP 1.1 predicts cp location
Operon Usage
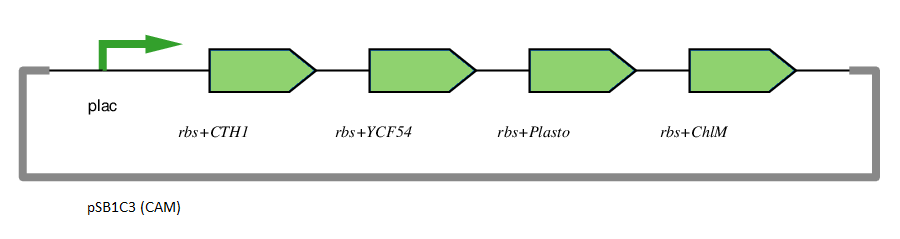
This gene has been used in an operon with other genes responsible for catalysing the biosynthesis pathway from Mg-protoporphyrin IX to Protochlorophyllide. CTH1, Plastocyanin, and YCF54 are involved in the oxidative cyclase pathway. ChlM methylates Mg-protoporphyrin IX, facilitating the highly-regulated catalysis of Mg-chelatase. CTH1 catalyses the conversion of Mg-protoporphyrin IX monomethyl into divinyl protochlorophyllide, interacting with YCF54 and Plastocyanin.
The insertion of magnesium is the key component of the chlorophyll biosynthesis pathway.
The plasmid is under the control of the lac promoter.
Structure
Figure 1: Crystal structure of ChlM from cyanobacteria Synechocystis sp. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25077963]
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 230
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 787
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Amino Acid Sequence
MASEIAQTAD VGSLTFAVGG VGAVVGLGAL LVATDHQKRR SEQMKSFDGD EKEAVKDYFN
TAGFERWRKI YGETDEVNKV QLDIRTGHAQ TVDKVLRWVD EEGSVQGITV ADCGCGTGSL
AIQLALRGAA VSASDISAAM ASEAEQRYQQ AVAAGQGKAP KVAPKFEALD LESVKGKYDT
VTCLDVMIHY PQDKVDAMIT HLAGLSDRRL IISFAPKTLS YSILKRIGEL FPGPSKATRA
YLHREEDVEA ALKRAGFKVT KREMTATSFY FSRLLEAIRE
References and documentation are available. Please note the modified algorithm for extinction coefficient.
Number of amino acids: 280
Molecular weight: 30440.6
Theoretical pI: 6.25
Amino acid composition:
Ala (A) 36 12.9%
Arg (R) 17 6.1%
Asn (N) 2 0.7%
Asp (D) 18 6.4%
Cys (C) 3 1.1%
Gln (Q) 12 4.3%
Glu (E) 20 7.1%
Gly (G) 23 8.2%
His (H) 5 1.8%
Ile (I) 13 4.6%
Leu (L) 22 7.9%
Lys (K) 19 6.8%
Met (M) 6 2.1%
Phe (F) 10 3.6%
Pro (P) 6 2.1%
Ser (S) 18 6.4%
Thr (T) 17 6.1%
Trp (W) 2 0.7%
Tyr (Y) 8 2.9%
Val (V) 23 8.2%
Pyl (O) 0 0.0%
Sec (U) 0 0.0%
(B) 0 0.0% (Z) 0 0.0% (X) 0 0.0%
Total number of negatively charged residues (Asp + Glu): 38
Total number of positively charged residues (Arg + Lys): 36
Atomic composition:
Carbon C 1340 Hydrogen H 2150 Nitrogen N 376 Oxygen O 414 Sulfur S 9
Formula: C1340H2150N376O414S9 Total number of atoms: 4289
Extinction coefficients:
Extinction coefficients are in units of M-1 cm-1, at 280 nm measured in water.
Ext. coefficient 23045 Abs 0.1% (=1 g/l) 0.757, assuming all pairs of Cys residues form cystines
Ext. coefficient 22920
Abs 0.1% (=1 g/l) 0.753, assuming all Cys residues are reduced
Estimated half-life:
The N-terminal of the sequence considered is M (Met).
The estimated half-life is:
30 hours (mammalian reticulocytes, in vitro).
>20 hours (yeast, in vivo).
>10 hours (Escherichia coli, in vivo).
Instability index:
The instability index (II) is computed to be 34.88 This classifies the protein as stable.
Aliphatic index: 85.43
Grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY): -0.198
SIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics | Disclaimer
Source
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
References
| None |

