Part:BBa_K1379000
PcelA
Usage and Biology
PcelA (or celAp) is a σX regulated promoter from Streptococcus pneumoniae. It is a member of the Cin-Box or Com-Box promoter family that share the 8 base pair consensus sequence of TACGAATA, where the sigma factor σX BBa_K1379004 (or ComX) binds to and promotes transcription initiation. During the exponential growth of S. pneumoniae, Competence Signal Peptide (CSP) mediated quorum sensing induces expression of σX. σX as a global regulator then directs S. pneumoniae to enter a transient competent cell state. PcelA, alongside with other Com-Box promoters, is turned on by σX and drives expression of the competence protein CelA.
Voigt and his colleagues have demonstrated that orthogonal gene expression could be achieved through the use of σs, anti-σs and synthetic promoters. (Rhodius et al., 2013). This principle has been demonstrated to work in E. coli (see characterization below), in which PcelA can only be turned on in the presence of σX.
iGEM 2014 Hong_Kong_HKUST Team has cloned PcelA from S. pneumoniae strain NCTC7465 and characterized its Relative Promoter Units (RPU) in presence and absence of a σX generator BBa_K1379006. Promoter PcomFA (BBa_K1379001), which is another Com-Box promoter recognized by σX, has also been characterized.
Characterization
Characterization has been performed following protocol described in “Measuring the activity of BioBrick promoters using an in vivo reference standard” (Kelly et al., 2009). Briefly, PcelA promoter was assembled with the promoter measurement kit BBa_E0240 in plasmid pSB3K3 with or without a σX generator BBa_K1379006. E. coli DH10B strains holding the two constructs respectively then grown to mid-log phase. GFP intensities and cell densities were then sampled every 30 minutes for 5 consecutive time points to obtain growth rates and GFP synthesis rates. The GFP synthesis rate was then compared to that of standard reference promoter BBa_J23101 measurement device BBa_I20260 to obtain the Relative Promoter Units (RPUs). For subtraction of background fluorescence, pSB3K3 holding BBa_E0240 was measured alongside.
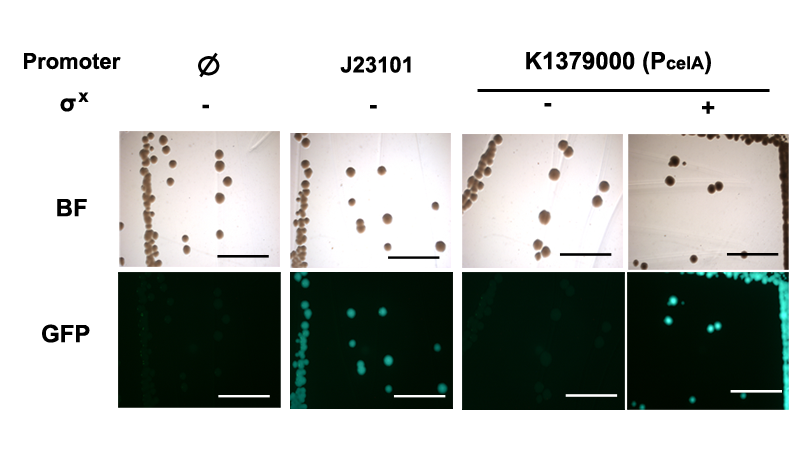
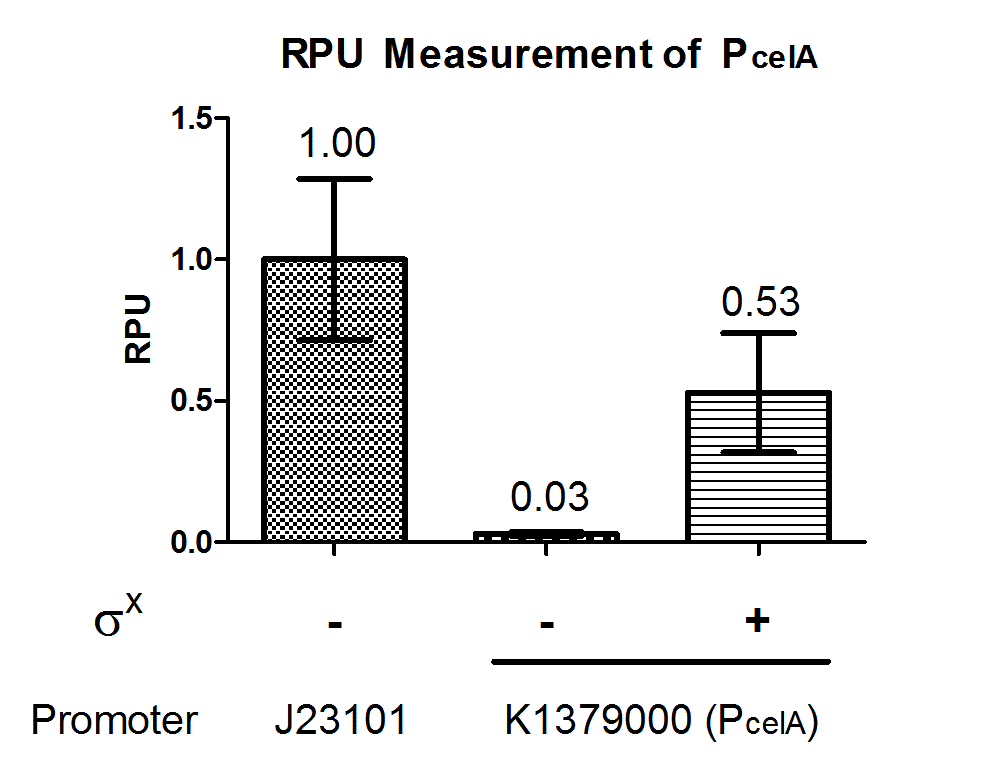
Extensive documentation of this characterization, including the wet lab protocols and data processing, can be found in [http://2014.igem.org/Team:Hong_Kong_HKUST/pneumosensor/characterization iGEM HKUST 2014 Wiki Page].
PcelA promoter is working in E. coli DH10B strain, and express GFP when induced with SigmaX protein. In comparison to the reference promoter BBa_J23101, the R.P.U (Relative Promoter Unit) of PcelA promoter is around 0.5. From Figure 2, we could tell that this promoter is specific as there is almost no GFP expression in the absence of SigmaX protein inducer. This might indicate that the 8 basepairs combox region in PcelA promoter is specific to SigmaX. However, further characterization needs to be done to evaluate crosstalks between this inducer-promoter system.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Reference
J. R. Kelly, A. J. Rubin, J. H. Davis, J. Cumbers, M. J. Czar, ..., D. Endy. (2009). Measuring the activity of BioBrick promoters using an in vivo reference standard. Journal of Biological Engineering, 3, 4. doi: 10.1186/1754-1611-3-4
//classic/regulatory/uncategorized
| None |
