Part:BBa_K1041000:Experience
This experience page is provided so that any user may enter their experience using this part.
Please enter
how you used this part and how it worked out.
Team NRP-UEA_Norwich 2013
Team NRP-UEA_Norwich 2013 added an NdeI restriction site at the start of the RFP coding region of BBa_J04450 using mutagenesis. This was to allow either the promoter region or RFP gene to be excised and exchanged for a different promoter or gene and provide restriction sites for further cloning, such as we used to create part Bba_K1041002.
Characterisation
This involved comparisons with the original Bba_J04450 biobrick by performing transformations, restriction digests BLAST analysis and Fluorescent Spectroscopy. We also had our biobrick sequenced.
Transformation
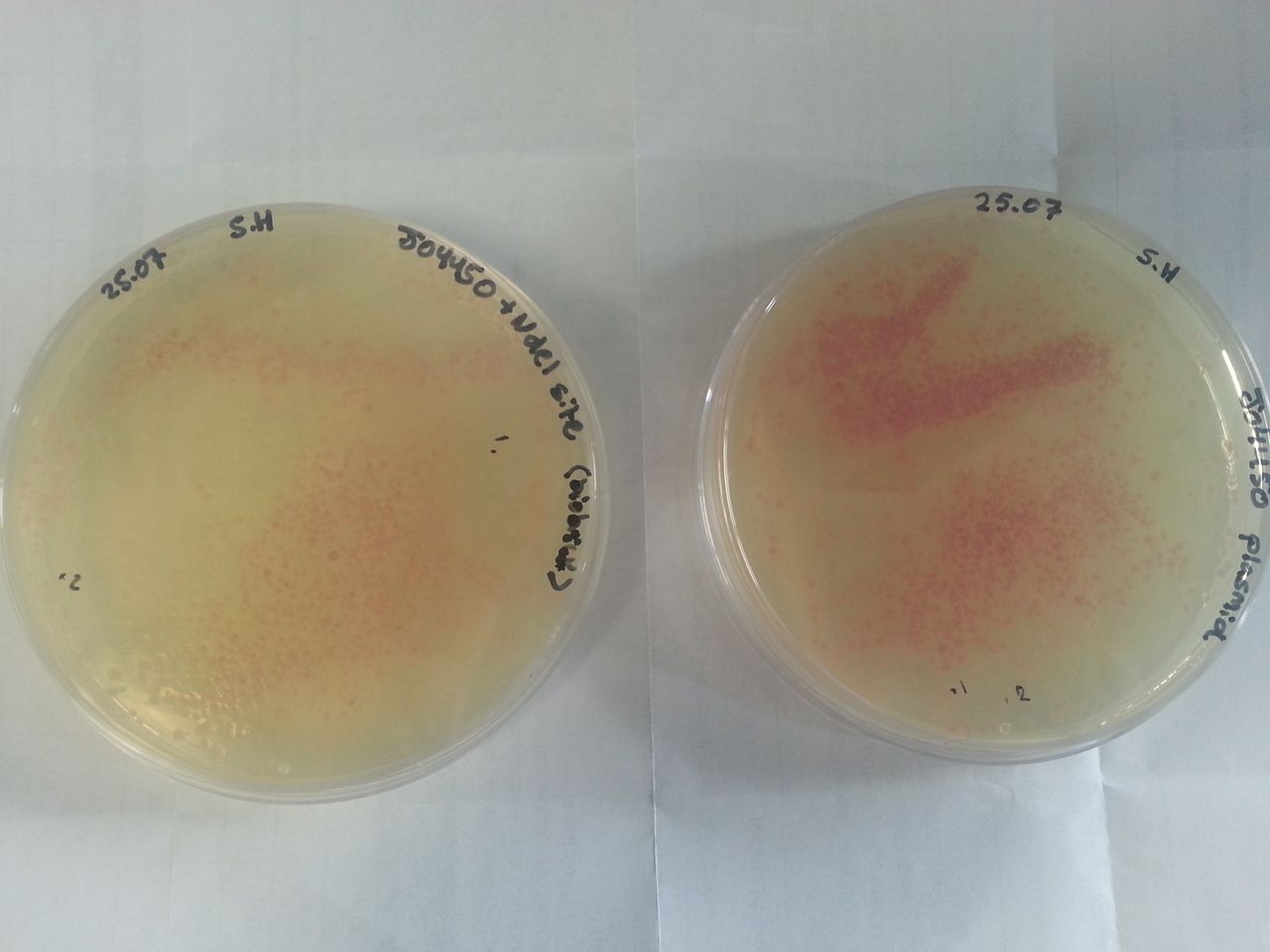
Parts BBa_K1041000 and BBa_J04450 were transformed into Alpha-Select competent E.Coli cells and plated onto LB Agar plates which contained the antibiotic ampicillin. Both plates have colonies that appear red under natural light Fig.1. Therefore the addition of a NdeI site has not effected the ability for the RFP gene to be transcribed.
Restriction Digests
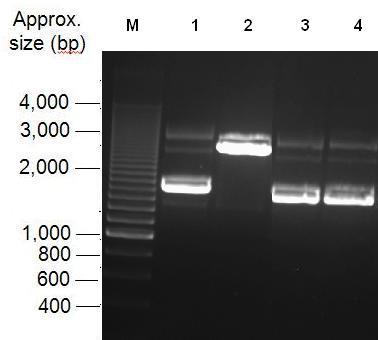
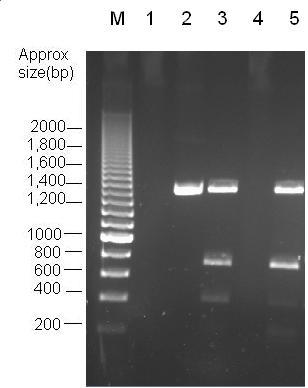
Parts Bba_K1041000 and Bba_J04450 were analysed by restriction digests and run on agarose gels. Both biobricks were cut with NdeI, Fig 2 and PvuII Fig 3. Fig 2 shows that part Bba_K1041000 has an NdeI site and part Bba_J04450 does not as when both parts are cut with NdeI only part Bba_K1041000 produces a different size band in the gel compared to uncut DNA. Fig 3 shows that the rest of the DNA sequence in Bba_K1041000 is identical to Bba_J04450 as bands of the same sized are produced when the parts are cut with the enzyme PvuII.
Fluorescent Spectroscopy
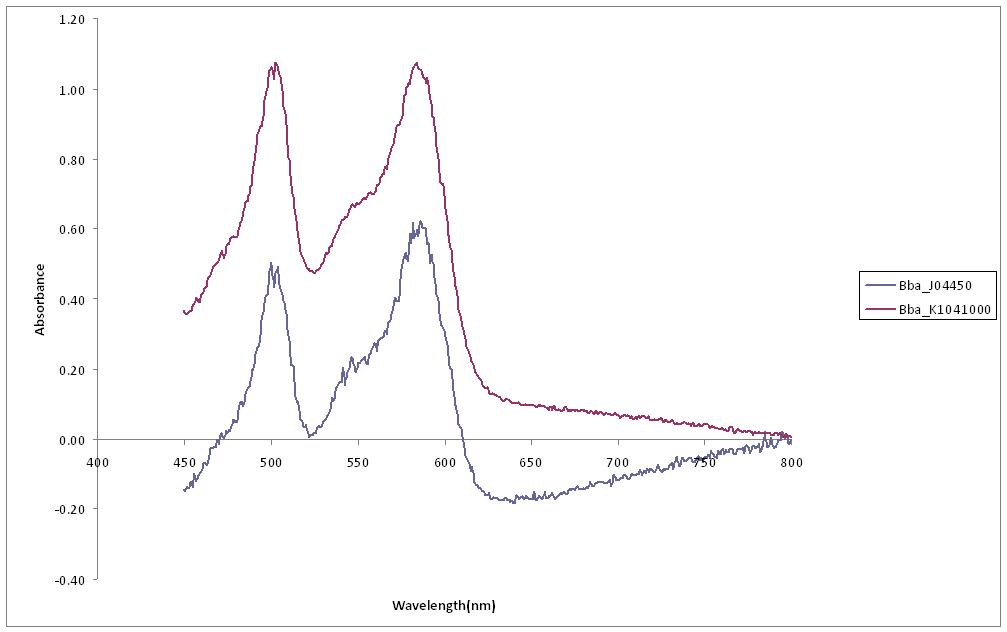
An experiment was designed to compare the intensity of red produced by RFP in part Bba_K1041000 to that produced by Bba_J04450. Both parts were transformed into E. Coli cells and spread on agar plates containing Chlorophenicol. A culture from each plate was used to inoculate a 10ml LB solution each and left to incubate overnight at 37C. After 24 hours of growth both cultures contained a red colour. The cultures were then analysed using Fluorescent Spectroscopy, Fig 4 to measure the absorbance of the cultures at a range of wavelengths from 450-800nm.
Sequencing
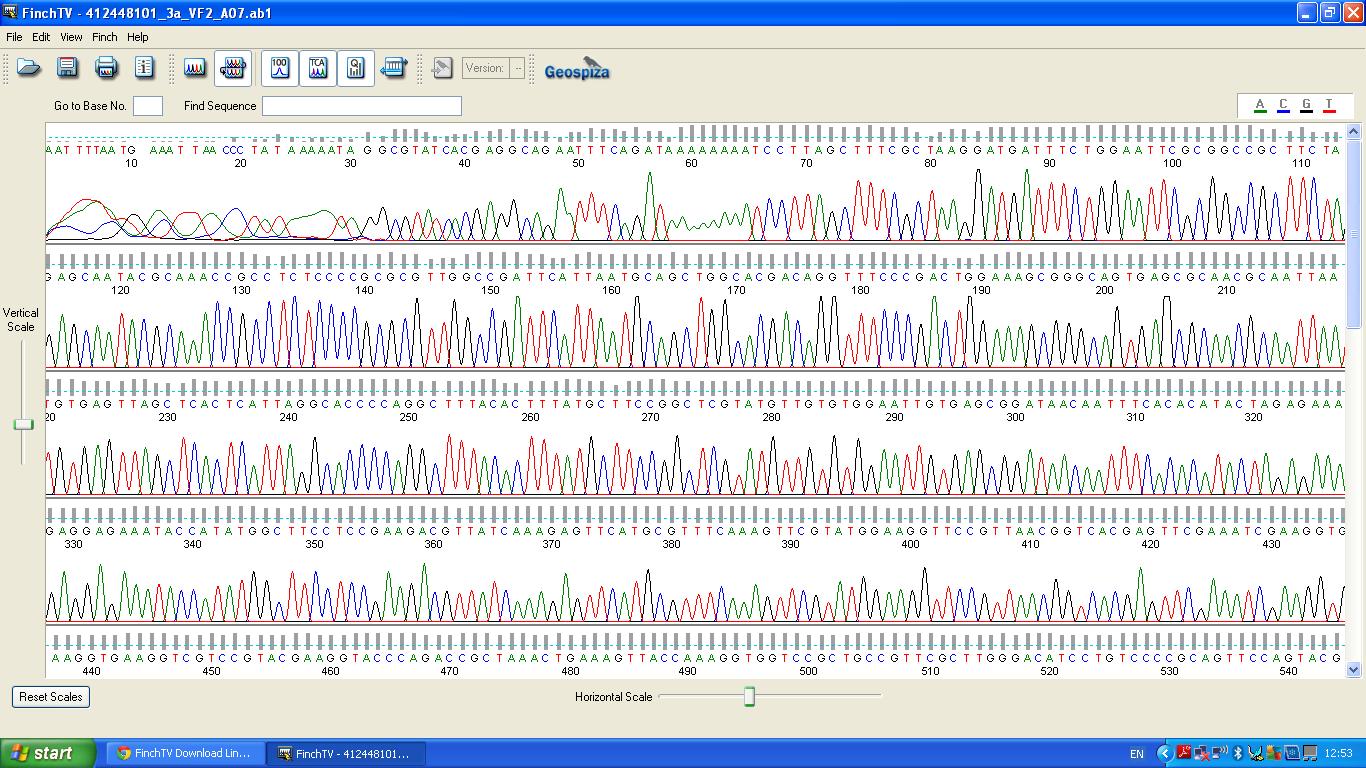
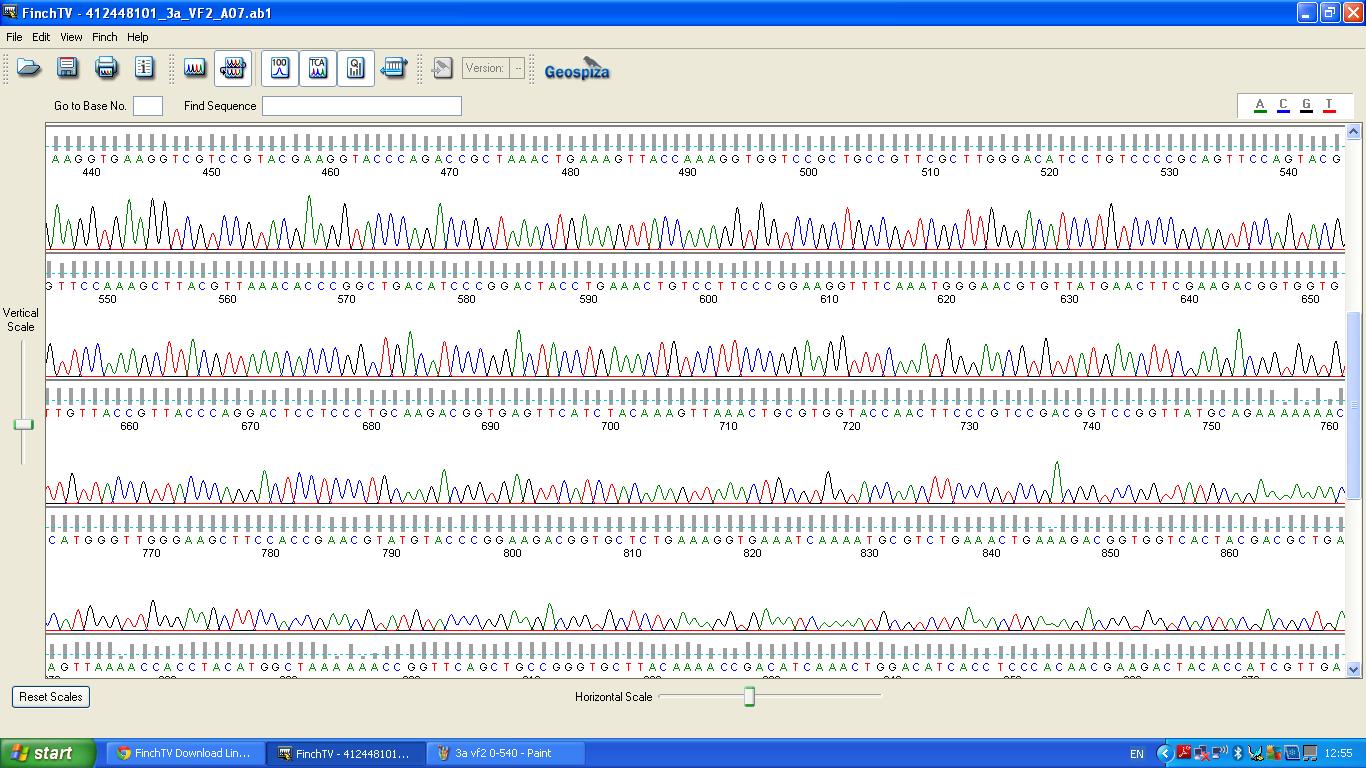
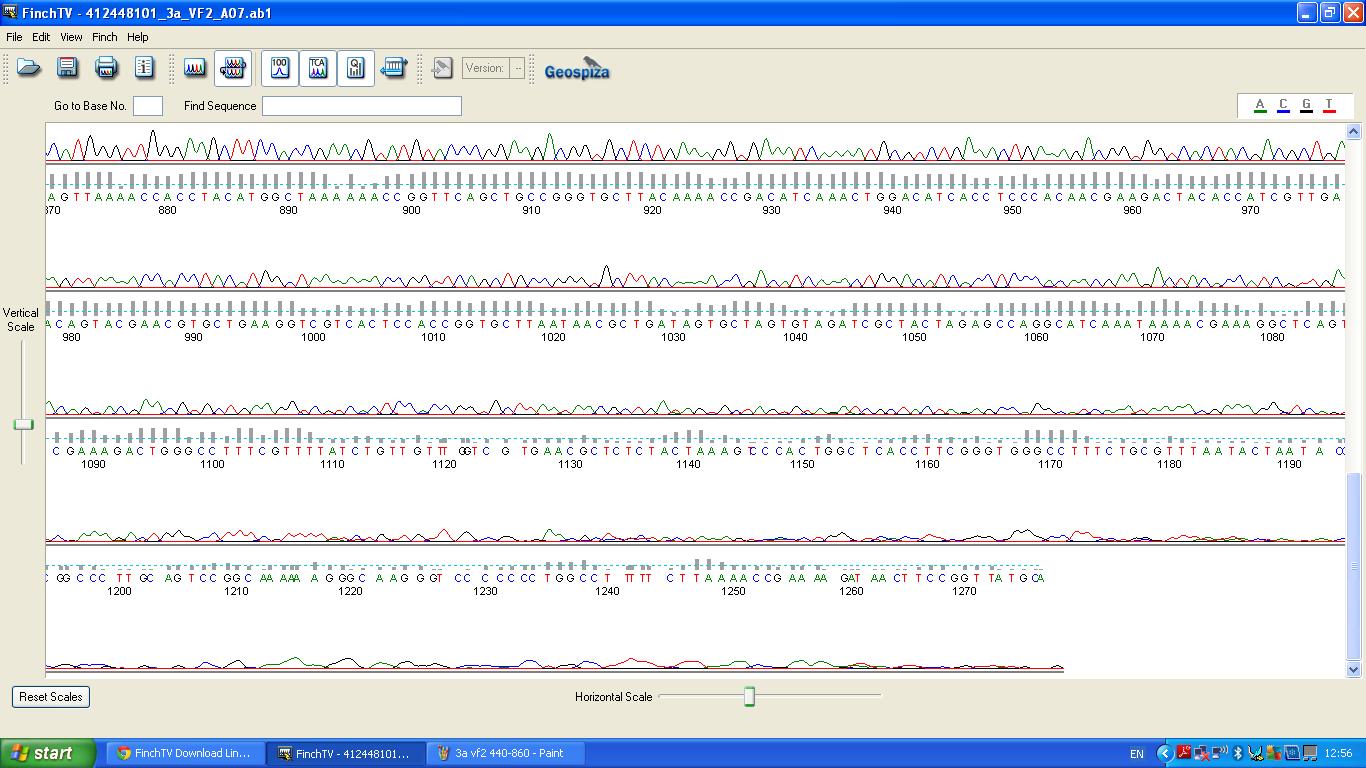
The biobrick was sent off to a company for sequencing, Fig 4,5,6.The data we recieved back showed the DNA is of good quality as strong peaks were produced throughout analysis of the sample.
BLAST Analysis
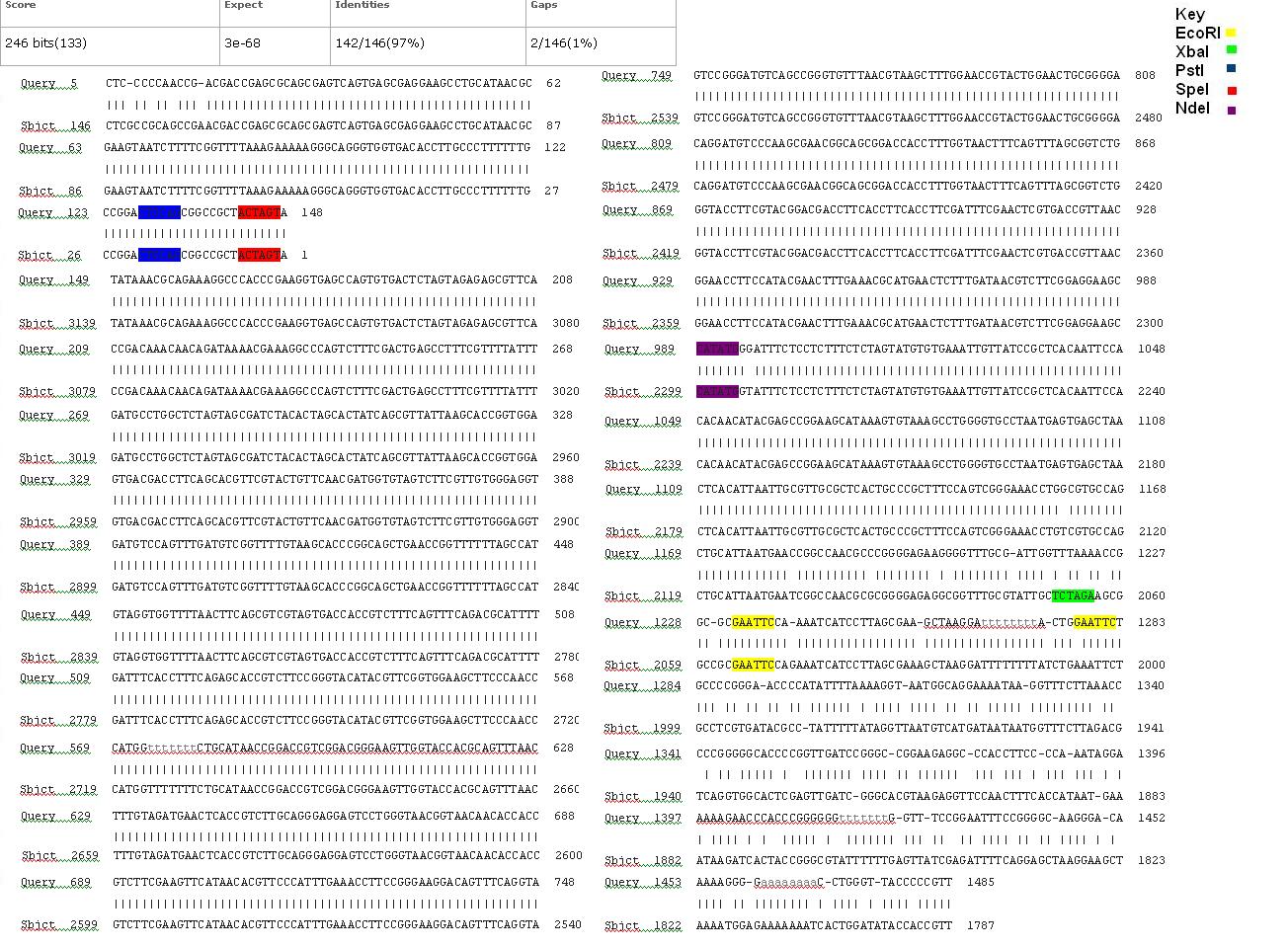
The data we recieved back from the sequencing company was aligned using BLAST with the expected DNA sequence. The sequencing with both the forward and reverse primers had over 97% matches with the expected DNA sequence. Fig 7,8
User Reviews
UNIQb5c7b9a5811a0fa8-partinfo-00000000-QINU UNIQb5c7b9a5811a0fa8-partinfo-00000001-QINU