Part:BBa_K4345019
RNA Thermometer rpoH
In nature, rpoH is implemented in the mRNA structure of a Escherichia Coli heatshock gene which is important for stress tolerance. The thermometer is a structural element that is located within the 5’ UTR of protein-coding mRNA. It operates as a reversible molecular zipper that controls the availability of the RBS in its structure. When the temperature increases, the thermometer unzips and the RBS can be detected by the ribosome thus allowing translation of downstream mRNA. When the temperature is below a certain range, the RBS gets trapped.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Usage and Biology
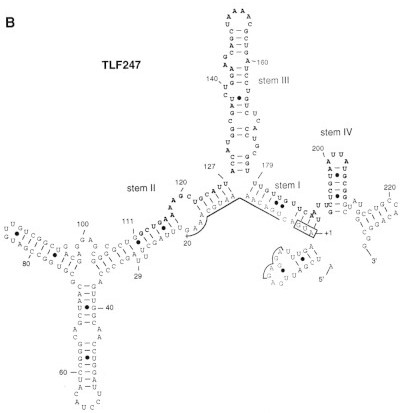
The figure below shows the secondary structure of the RNA thermometer.
Image obtained from Morita et al., 1999.
References
Morita, M. T., Tanaka, Y., Kodama, T. S., Kyogoku, Y., Yanagi, H., & Yura, T. (1999, March 15). Translational induction of heat shock transcription factor sigma 32: evidence for a built-in RNA thermosensor. Genes &Amp; Development, 13(6), 655–665. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.13.6.655
//rna/riboswitch
| biology | |
| control |