Part:BBa_K4345000
NarX fused to mNeonGreen with a rigid linker
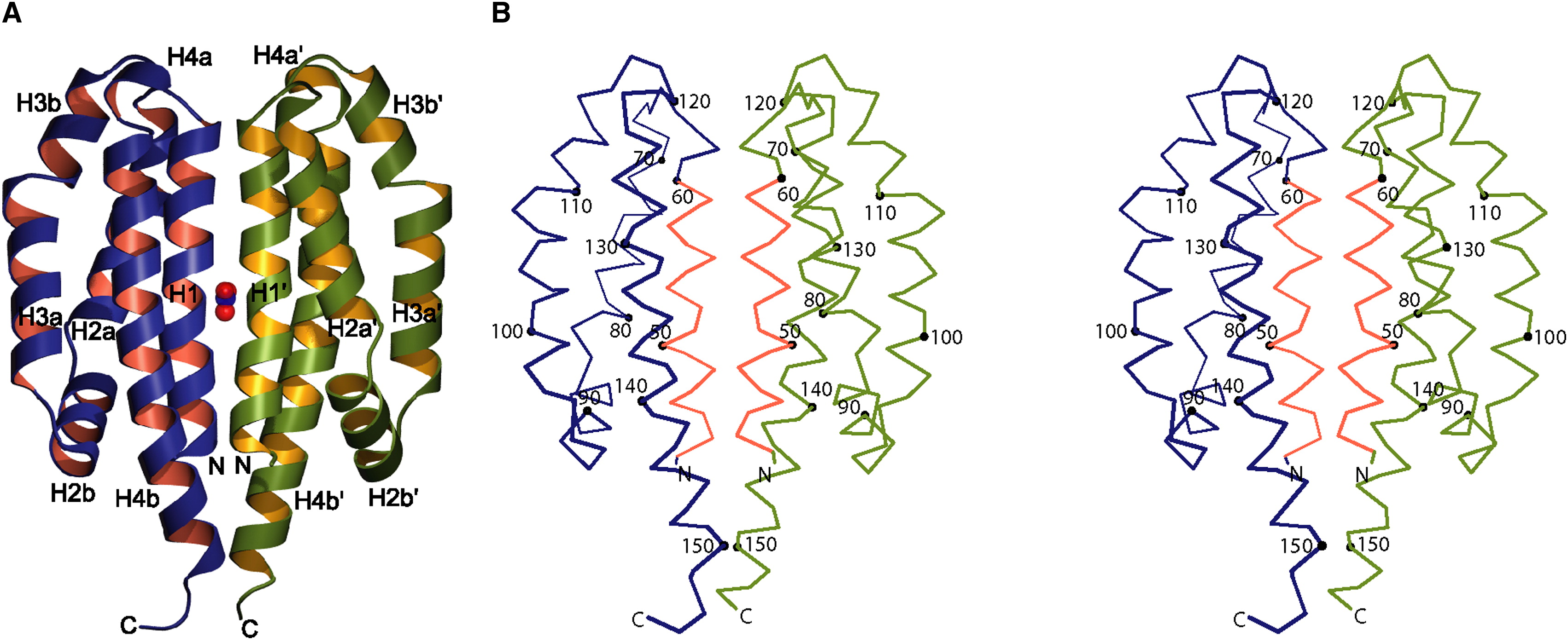
Three proteins constitute a two-component nitrate sensing system in Escherichia coli: NarX, NarL and NarQ. Together they are responsible for the expression of anaerobic respiratory genes. NarX and NarQ are histidine kinases that independently detect the presence of nitrate an transmit the signal to NarL. After autophosphorylation and thus dimerization of NarX or NarQ, NarL is phosphorylated. This enables the activated NarL to bind DNA and induce expression of specific genes. Both NarX and narQ contain two conserved histidine residues that correspond to the autophosphorylation sites of other, homologous, sensor-transmitter proteins (Cavicchioli et al., 1995). Cheung & Hendrickson (2009) elucidated the structure of the histidine kinase in the apo- and holo-state to be a four-helix bundle. To follow the expression of NarX, it is fused to mNeonGreen with a rigid linker.
This part is composed of BBa_K4345007 (NarX), BBa_K4345002 (rigid linker) and BBa_K4345009 (mNeonGreen).
Usage and Biology
This particular narX protein was derived from E. coli.
Image obtained from Cheung & Hendrickson, 2009
References
//cds/membrane/receptor
| activation_coeficient | |
| protein | |
| signalling_molecule |