Part:BBa_K3407004
Fox-1 RBD: a protein domain binding strongly and specifically to RNA sequence UGCAUGU.
Contents
Usage and Biology
In many projects involving RNA approaches, the availability of a library of proteins able to bind strongly and specifically to an RNA target sequence represents a valuable and versatile set of BioBricks. Here we describe Fox-1 RBD, a protein domain able to recognise and bind a specific RNA sequence.
Fox-1 stands for Feminizing Locus on X, a protein acting as a numerator element to count the number of X chromosomes relative to ploidy. In these worms, Fox-1 is thought to determine sex by post-transcriptional repression of Xol-1. In mammalian genes, it strongly influences the splicing of alternative exons by binding to “UGCAUG” RNA sequence [1]. Orthologs are present in a wide range of multicellular eukarya species like zebrafish [2], mice [3], rats [4], bulls [5], frogs [6], chicken [7], polar bear [8], cats [9], platypuses [10], sunfishes [11], tasmanian devils [12] and humans [13].
This protein has a domain of interaction with RNA called RNA Binding Domain (RBD), also commonly referred as RNA Recognition Motif (RRM) and Ribonucleoprotein (RNP) domain, referring to the domain formed by the residues 109 to 208 of Fox-1 (13.6 kDa when his-tagged). Its RBD has shown a high affinity (Kd = 0.49 nM at 150mM NaCl) to “UGCAUGU” RNA sequence where residues F126 and F160 play a crucial role in its binding capacity [1][14]. Interestingly, it has also shown a high specificity to the mentioned sequence where single mutations can reduce from 4,8 to more than 1.500 fold the affinity with its substrate [1], becoming a powerful BioBrick where a highly specific and affine interaction is needed between a protein and RNA. As shown in its crystal structure, C-terminal of the RBD is distant from the binding site and can accept a His-tag without showing a negative effect on the binding capacity [15], probably providing an adequate locus to fuse other domains or proteins. A mutated version of the protein domain has been expressed and tested as a control, where mutations F160A & F126A deplete its binding capacity [1] (BBa_K3407004).
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Experimental results
shRNA can be transcribed with T7 RNA polymerase
shRNA are produced in vitro using the T7 RiboMAX RNAi express kit from Promega, which makes use of the viral T7 RNA polymerase.
-
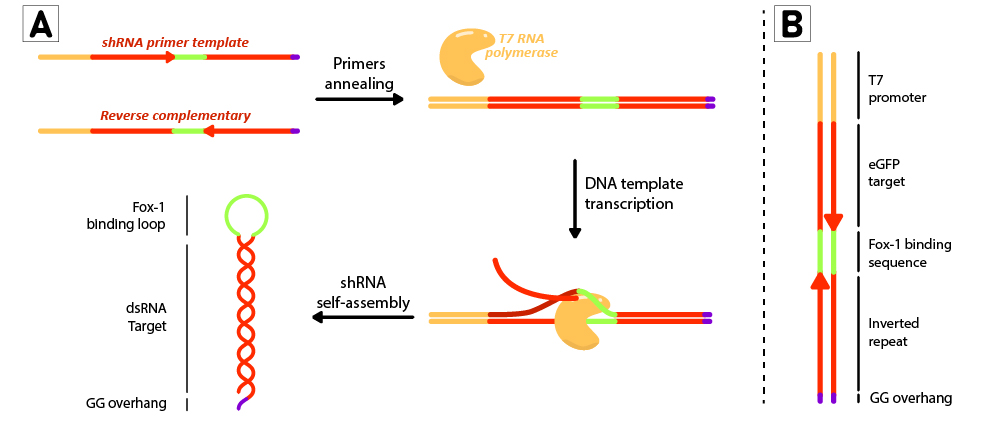 Figure 2: Schematic representation of the shRNA in vitro production using T7 RiboMAX kit from Promega. Primer pairs are annealed in the T4 ligase buffer by heating at 95ºC for 5 minutes and left cooling at room temperature for 30 minutes. Once template is annealed, T7 RNA polymerase is added to transcribe the DNA template at 42ºC for 2 hours. shRNAs self assemble as soon as they are produced. (B) DNA template design for in vitro shRNA production. T7 promoter followed by eGFP target sequences with inverted repeats are linked by the loop region, and finally ends with a GG overhang.
Figure 2: Schematic representation of the shRNA in vitro production using T7 RiboMAX kit from Promega. Primer pairs are annealed in the T4 ligase buffer by heating at 95ºC for 5 minutes and left cooling at room temperature for 30 minutes. Once template is annealed, T7 RNA polymerase is added to transcribe the DNA template at 42ºC for 2 hours. shRNAs self assemble as soon as they are produced. (B) DNA template design for in vitro shRNA production. T7 promoter followed by eGFP target sequences with inverted repeats are linked by the loop region, and finally ends with a GG overhang.
For each short hairpin, a pair of complementary primers were annealed to form a DNA template for transcription (Figure 2B). The DNA template was designed to possess a T7 promoter followed by a 27nt inverted repeat sequence taken from the eGFP gene (nt 78 to 105), and linked together by the 9nt sequence containing the target of Fox-1 RBD. On the 3’ termini, two GG were added to produce the desired overhang (BBa_K3407022). This leads to a successful transcription without the need to use a terminator (Figure 2A).
-
 Figure 2: Schematic representation of the shRNA in vitro production using T7 RiboMAX kit from Promega. Primer pairs are annealed in the T4 ligase buffer by heating at 95ºC for 5 minutes and left cooling at room temperature for 30 minutes. Once template is annealed, T7 RNA polymerase is added to transcribe the DNA template at 42ºC for 2 hours. shRNAs self assemble as soon as they are produced. (B) DNA template design for in vitro shRNA production. T7 promoter followed by eGFP target sequences with inverted repeats are linked by the loop region, and finally ends with a GG overhang.
Figure 2: Schematic representation of the shRNA in vitro production using T7 RiboMAX kit from Promega. Primer pairs are annealed in the T4 ligase buffer by heating at 95ºC for 5 minutes and left cooling at room temperature for 30 minutes. Once template is annealed, T7 RNA polymerase is added to transcribe the DNA template at 42ºC for 2 hours. shRNAs self assemble as soon as they are produced. (B) DNA template design for in vitro shRNA production. T7 promoter followed by eGFP target sequences with inverted repeats are linked by the loop region, and finally ends with a GG overhang.
References
- Auweter, S., Fasan, R., Reymond, L., Underwood, J., Black, D., Pitsch, S. and Allain, F., 2020. Molecular Basis Of RNA Recognition By The Human Alternative Splicing Factor Fox-1.
- UniProtKB - Q642J5 (RFOX1_DANRE)
- UniProtKB - Q9JJ43 (RFOX1_MOUSE)
- UniProtKB - A1A5R1 (RFOX2_RAT)
- UniProtKB - A6QPR6 (RFOX2_BOVIN)
- UniProtKB - Q66JB7 (RFOX2_XENTR)
- UniProtKB - F1NCA4 (F1NCA4_CHICK)
- UniProtKB - A0A384DA29 (A0A384DA29_URSMA)
- UniProtKB - A0A337SR52 (A0A337SR52_FELCA)
- UniProtKB - F6SR19 (F6SR19_ORNAN)
- UniProtKB - A0A3Q4B4Y5 (A0A3Q4B4Y5_MOLML)
- UniProtKB - G3VXH1 (G3VXH1_SARHA)
- UniProtKB - Q9NWB1 (RFOX1_HUMAN)
- Jin, Y., 2020. A Vertebrate RNA-Binding Protein Fox-1 Regulates Tissue-Specific Splicing Via The Pentanucleotide GCAUG.
- NMR Structure of the RNA Binding Domain of Human Fox-1 in Complex with UGCAUGU
| None |

