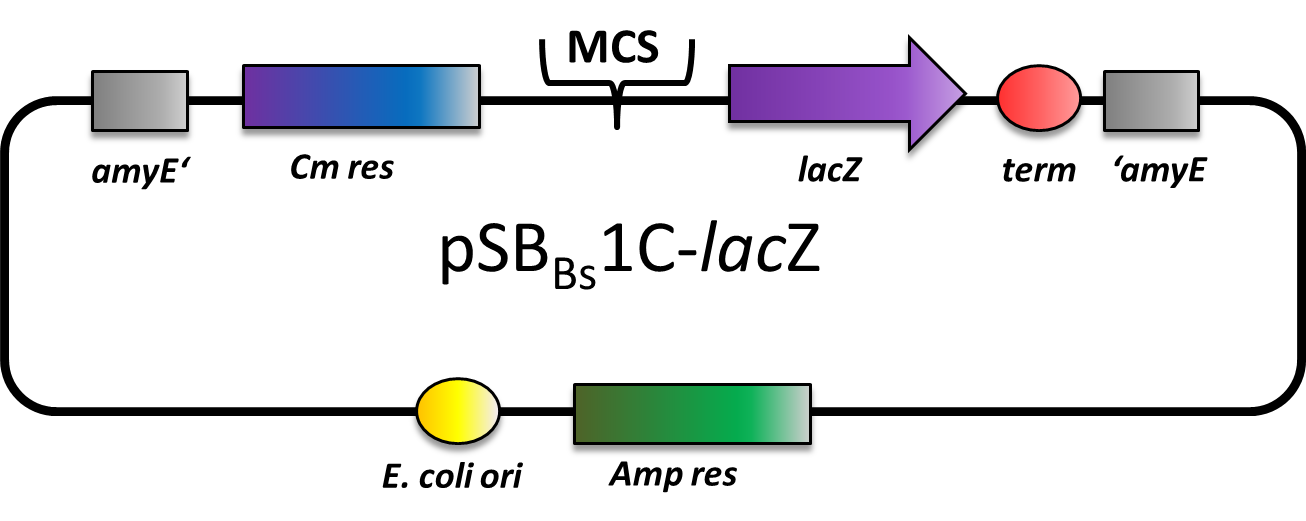Part:BBa_K823021
pSBBs1C-lacZ (lacZ reporter vector for B. subtilis)
This part is a reporter vector for Bacillus subtilis. It integrates at the amyE locus. It has a ampicillin resistance for cloning in E.coli and chloramphenicol resistance for B.subtilis. The multiple cloning site is followed by a lacZ gene for reporter assays. This backbone is a BioBricked version of the B. subtilis vector pAC6.
This BioBrick is part of the LMU 2012 igem project [http://2012.igem.org/Team:LMU-Munich/Bacillus_BioBricks BacillusBioBrickBox]
Reference: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11902727 Stülke et al.]
For handling of B. subtilis vectors, please see here.
The transformation into B. subtilis is explained here.
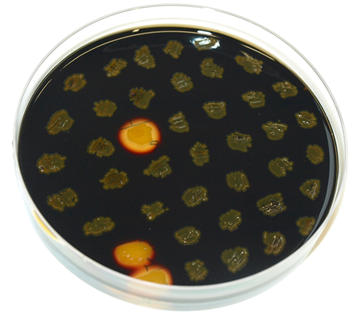
To check for integration into ths amyE locus, the starch test was performed. The colonies obtained from the transormation into B.subtilis were streaked on an LB-Agar plate with 5 mg/L chloramphenicol and onto a starch plate (also W168 as a control) and incubated at 37°C over night. The starch plate is then covered with Lugol's iodine. Colonies without a bright surrounding are correct.
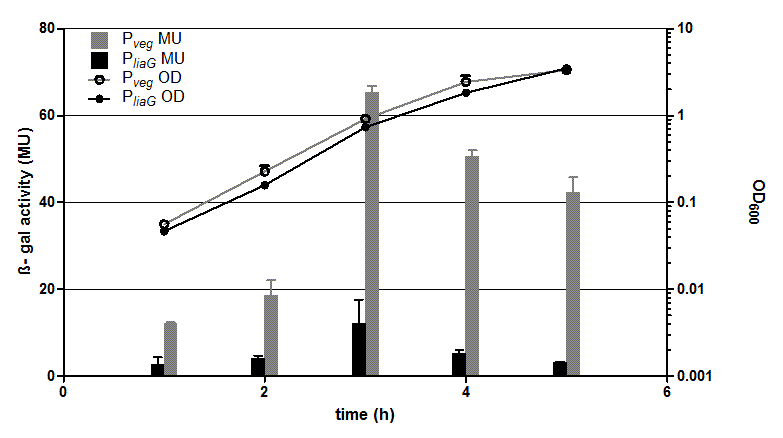
Fig. 1: β-galactosidase assay and growth curve of strains carrying the promoters PliaG (black) and Pveg (grey) fused to lacZ. β-galactosidase activity (Miller Units)and the growth curve values are the average of two independant clones with their standard deviation that were measured during the same experiment. Experiment shows representative data which was obtained in the same way from three independent experiments.
The two constitutive promoters PliaG and Pveg were evaluated with the reporter vector pSBBs1C-lacZ. Promoter activity leads to the expression of the β-galactosidase which directly correlates to the promoter activity. The β-galactosidase assay of the constitutive Bacillus promoters Pveg and PliaG was repeated three times. Data show one representative result. In the beginning of the growth curve both promoters show only low activity. But then it increases to a maximum before it decreases to the begininng level after about seven hours (Data not shown). Summing up the course of activity of both promoters Pveg and PliaG is very similar based on the growth curve. The highest β-galactosidase activity and therefore the highest activity of the promoter Pveg with a maximum of 65 Miller units can be found during the transition from the logarithmic to the stationary phase. This is about five times higher than the acitivity of the promoter PliaG with a maximum activity of about 12 Miller Units.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Plasmid lacks a prefix.
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal EcoRI site found at 9771
Illegal SpeI site found at 2
Illegal PstI site found at 16
Illegal NotI site found at 9
Illegal NotI site found at 9777 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Plasmid lacks a prefix.
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal EcoRI site found at 9771
Illegal BglII site found at 8313
Illegal BamHI site found at 22 - 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal prefix found at 9771
Illegal suffix found at 2 - 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal prefix found at 9771
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal XbaI site found at 9786
Illegal SpeI site found at 2
Illegal PstI site found at 16
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 4562
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 6888
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 8688 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Plasmid lacks a prefix.
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal BsaI site found at 4738
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 5820
//chassis/prokaryote/bsubtilis
//chassis/prokaryote/ecoli
//plasmid/chromosomalintegration
//plasmidbackbone/libraryscreening/promoter
| chassis | E.coli and B. subtilis |
| copies | integrative in B. subtilis |
| origin | pAC6 |
| resistance | A(E. coli) C(B. subtilis) |