Part:BBa_I13453
Pbad promoter
PBad promoter from I0500 without AraC.
Usage and Biology
Has been used as a second promoter in a system containing BBa_I0500 (PBad+AraC). In this system, it showed behavior qualitatively indistinguishable from the BBa_I0500 copy of PBad. Has not been tested independent of AraC. A second part, BBa_I13458, should allow decoupling of PBad and AraC.
See this OpenWetWare article on [http://openwetware.org/wiki/Titratable_control_of_pBAD_and_lac_promoters_in_individual_E._coli_cells#pBAD_promotersOpenWetWare pBAD and lac promoters] for additional usage and biology information
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 125
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 65
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Characterization
For the 2009 iGEM competition, British_Columbia characterized BBa_I13453 in the context of a pBAD promoter family. For the results of this characterization, see here.
For the 2010 iGEM competition, Tec-Monterrey characterized BBa_I13453 again, using a construct of GFP reporter after the pBad promoter. The transfer function was modeled with a Hill equation.
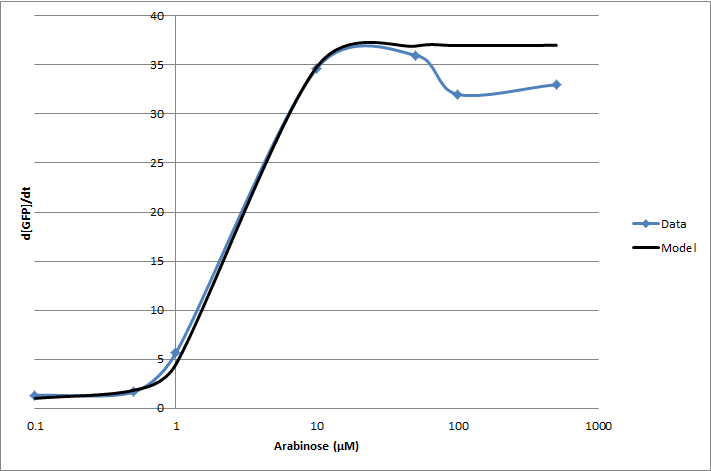
(d[GFP]/dt)/OD600 = C+A*Xn/(Xn+Kn)
| Experiment | Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Transfer Function | Basal rate (C) | 1 d[GFP]/dt |
| Gain (A) | 36 d[GFP]/dt | |
| Hill coefficient (n) | 2.16 | |
| Switch Point (K) | 2.8 [ara] (µM) |
MetA Knockout Complementation by inducing arabinose promoter by British Columbia iGEM 2012
This part consists of an arabinose promoter, a strong RBS, and the MetA coding gene. It is able to complement a metA knockout, and the growth rate appears to be proportional to the amount of arabinose that is added.

To generate this graph we cultured an E. coli MetA knockout transformed with this part in M9 minimal media with the indicated concentrations of arabinose, and measured the OD600 every 15 minutes.
TrpA Knockout Complementation by inducing arabinose promoter by British Columbia iGEM 2012
This part consists of an arabinose promoter, a strong RBS, and the TrpA coding gene. It is able to complement a metA knockout, and the growth rate appears to be proportional to the amount of arabinose that is added.

To generate this graph we cultured an E. coli TrpA knockout transformed with this part in M9 minimal media with the indicated concentrations of arabinose, and measured the OD600 every 15 minutes. See BBa_K804009 for negative controls for this part as well as linked fluorescent data.
===MetA Knockout Complementation by inducing arabinose promoter by British Columbia iGEM 2012===
This part consists of an arabinose promoter, a strong RBS, and the MetA coding gene. It is able to complement a metA knockout, and the growth rate appears to be proportional to the amount of arabinose that is added.
https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/parts/thumb/d/d3/MetA_complementation_no_fluor.png/800px-MetA_complementation_no_fluor.png
To generate this graph we cultured an E. coli MetA knockout transformed with this part in M9 minimal media with the indicated concentrations of arabinose, and measured the OD600 every 15 minutes. Not understood
//direction/forward
//chassis/prokaryote/ecoli
//promoter
//regulation/positive
//classic/regulatory/uncategorized
| negative_regulators | |
| positive_regulators | 1 |

 1 Registry Star
1 Registry Star