Part:BBa_E0240
GFP generator
B0032.E0040.B0015
2022 team HUS_United's contribution
We frequently used this part this year, therefore we want to perform a comprehensive characterization to provide information for other teams to use. Since this part could stand as one of the building materials for higher-order devices and circuits and is frequently used in iGEM kit plates, a well-documented characterization would help to provide more information about these parts for future use by other teams.
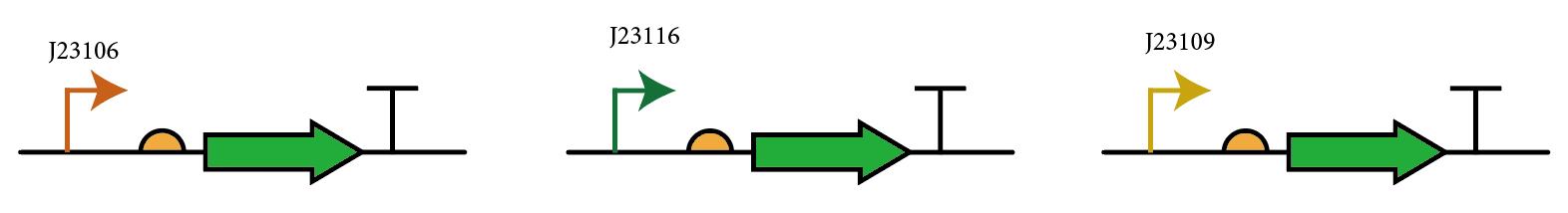
The most probable way for usage of this composite part is to integrate various promoters upstream of the RBS and use GFP as reporters to measure expression, so we add three constitutive promoters with different strengths (J23106, J23109, J23116) upstream of the RBS and compare the bacterial fluorescence to test the performance and universality of this device.
The samples for measurement are prepared as follows:
1. Use inverse PCR to obtain the vector fragment, and the position of the joint is right upstream of the RBS B0032.
2. Commercially purchased single-stranded DNA integration fragments(promoter sequences) with two homologous arms are inserted into the linearized vector through HiFi assembly. (Approximately 50:1 in molar ratio)
3. E.coli DH5α competent cells are transformed with finished HiFi assembly reactions, and colonies are picked and sequenced on the next day.
4. Colonies with correct sequences are cultured for 8h and then transferred to a microplate with 100-fold dilution, GFP fluorescence (excitation=488 nm, emission=515 nm) and OD600 are measured every 15 minutes for 16 h duration.
The results are as follows:
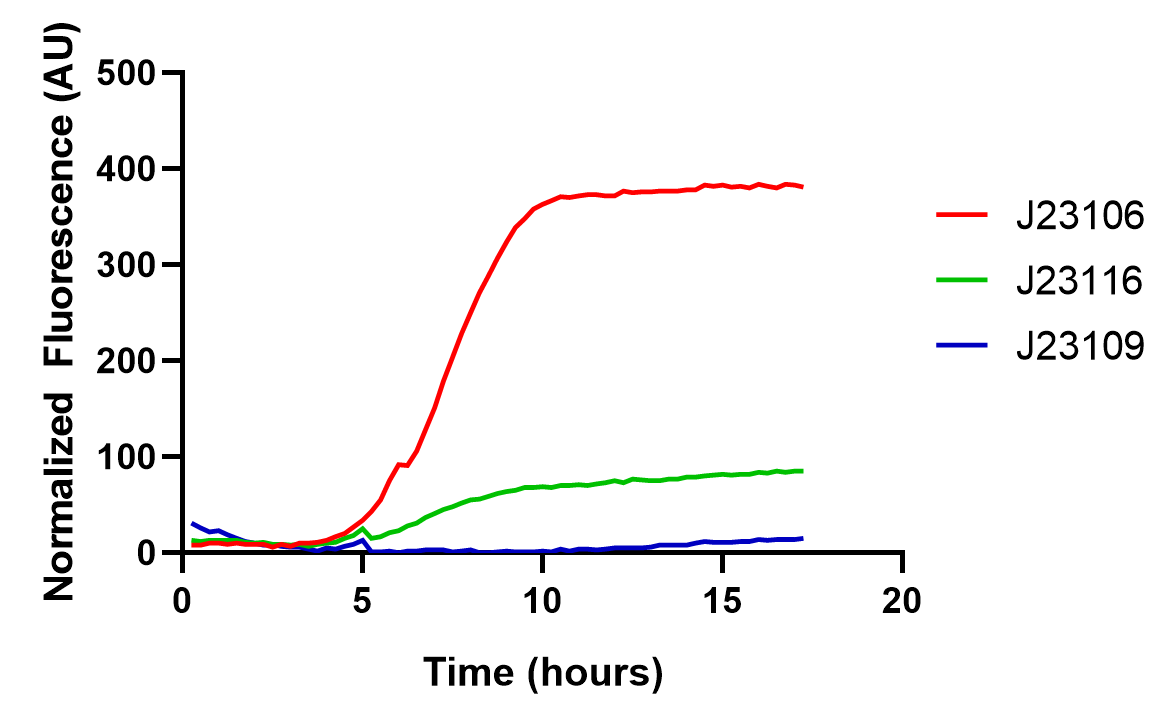
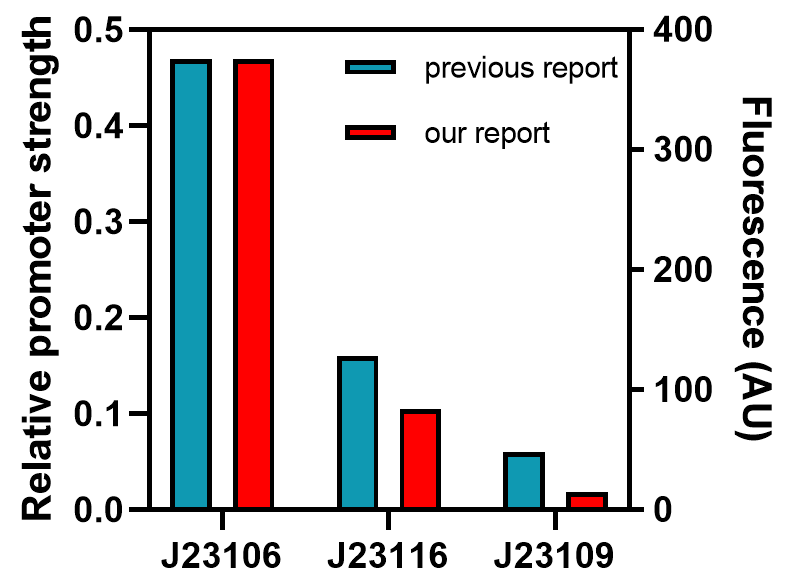
From this graph, we clearly see that the promoter strength order is J23106, J23116, and J23109, from high to low. The qualitative analysis accord with previous reports, but the comparison of quantitative promoter strength should be compared to ensure the validity of this part, and we take the fluorescence peak value as a measuring standard for promoter strength.
As the graph shows, we found good correlations between previously reported promoter strengths and our data, some still observed deviations could be attributed to the difference in measurement procedures or data processing. Anyhow, the result indicates this part might be a good material for constructing genetic circuits.
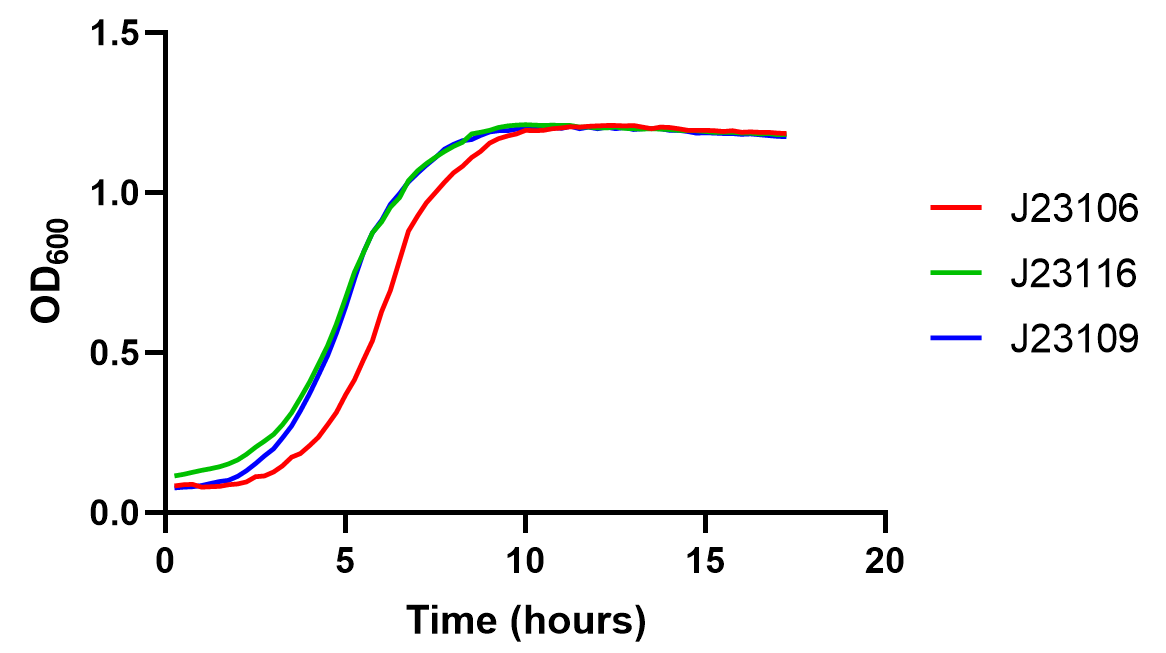
Since the vector of this part is a high-copy plasmid(pSB1A2), we also collected the growth curve of these transformants to test the metabolic burden of this part under the control of different promoters. The result shows that the bacteria growth is barely affected, and all three transformants' density reaches their plateau within 10 hours with a slight yet observable difference between medium strength J23106 and the rest two. This should raise caution for using high-strength promoters such as J23100 as it might introduce high metabolic pressure.
Usage and Biology
gfp tri-part; medium rbs
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 663
//plasmid/measurement
| emission | Green |
| excitation | |
| tag | None |

 1 Registry Star
1 Registry Star