Part:BBa_K1033001
4-coumarate ligase (4CL) with RBS
4-coumarate ligase (4CL) is an enzyme that catalyses the reaction from p-coumaric acid to 4-coumaroyl-coenzyme A (4-coumaryl-CoA). This enzyme is derived from the plant arabidhopsis thaliana, but exists in many other plants. [1]
In our project, we have been using it together with stilbene synthase, that produces resveratrol with the help of this enzyme.
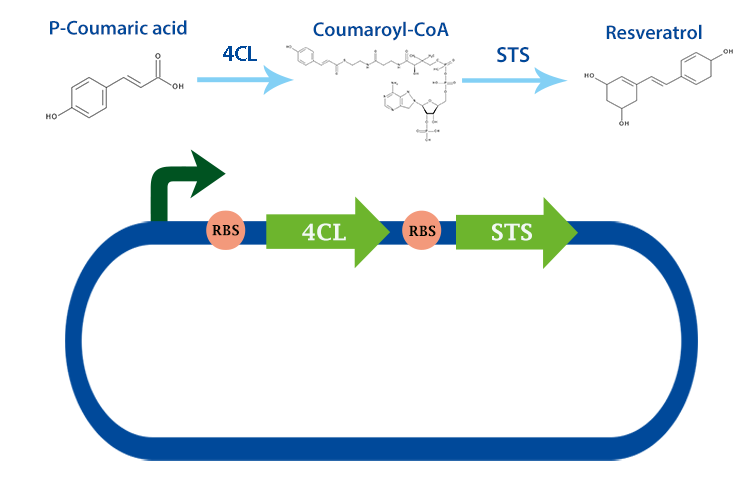
Applications With the help of this enzyme one can produce 4-coumaryl-CoA which is an important precursor in many metabolic pathways. For example, it can be used to produce resveratrol with stilbense synthase. [2]
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 1108
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 1675
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 1307
iGEM 2022 SHSBNU-China, new documentation (For Bronze)
Group: SHSBNU-China iGEM 2022
In this year’s iGEM competition, SHSBNU_China team focused on anthocyanins production, especially delphinidin. 4CL gene is one of the key genes in the synthetic pathway of delphinidin, which catalyzed phenylalanine into 4-coumaryl coenzyme A.
We synthesized the sequence and constructed into plasmid pETDuet.
After transforming to E.coli BL21 and induced by IPTG overnight at 16 degree Celsius at various concentrations (0.25 to 2 uM), we lysed the bacteria and performed SDS-PAGE and we confirmed 4CL enzyme to be expressed successfully. Judged by the thickness of the SDS-PAGE bandwidth and darkness, concentrations of iPTG don’t play a critical role in the expression of 4CL enzyme.
//collections/probiotics/production
| None |

