Part:BBa_K3078012
SfGFP under the mutated T7 promoter (BBa_K3078012).
A mutated T7 promoter(BBa_K3078012), RBS (BBa_J64022), coding region of sfGFP (BBa_K2541400), and a double terminator (BBa_B0014) were used. This part is used to test the intensity of T7 promoter after mutation.
1. Design
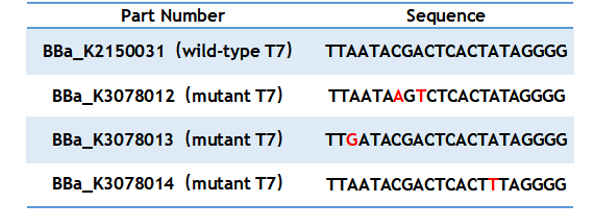
T7 promoter is one of the most common promoters. But the intensity of the wild type T7 promoter often can’t meet our demand, so we mutated it and obtained an improved T7 promoter. According to previous studies, we selected the mutation site and constructed three mutated promoters (BBa_K2150012, BBa_K2150013, BBa_K2150014)based on the wild-type T7 promoter (BBa_K2150031) into the measurement vector (BBa_K3078100).
Table 1. Sequence of wild type and mutant T7 promoter.
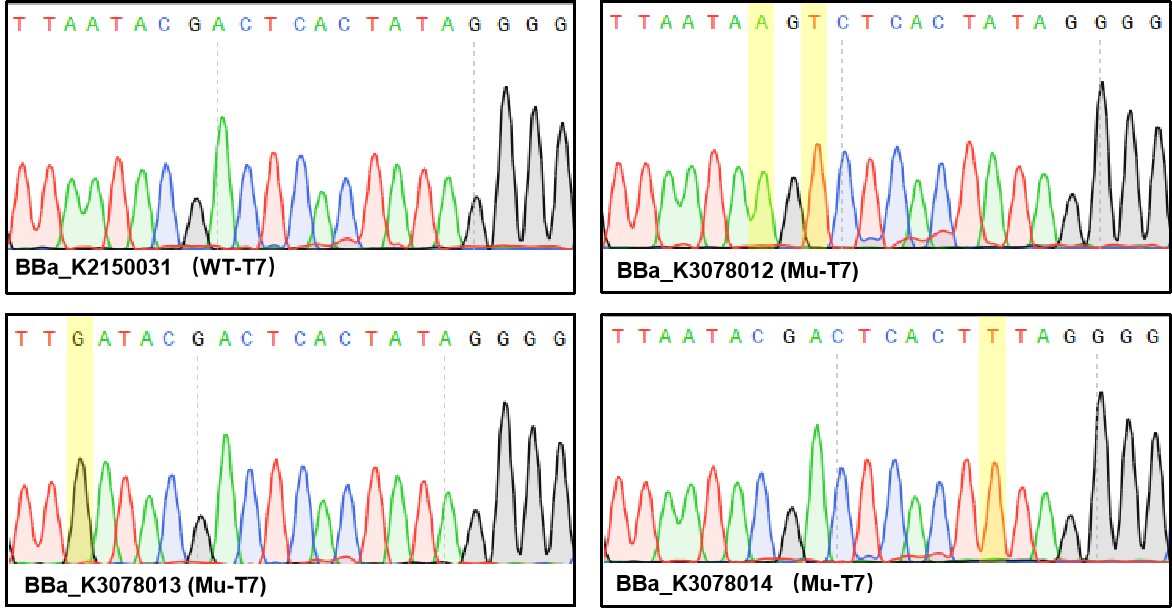
Figure 1. Sequencing the plasmids.
2. Measurement
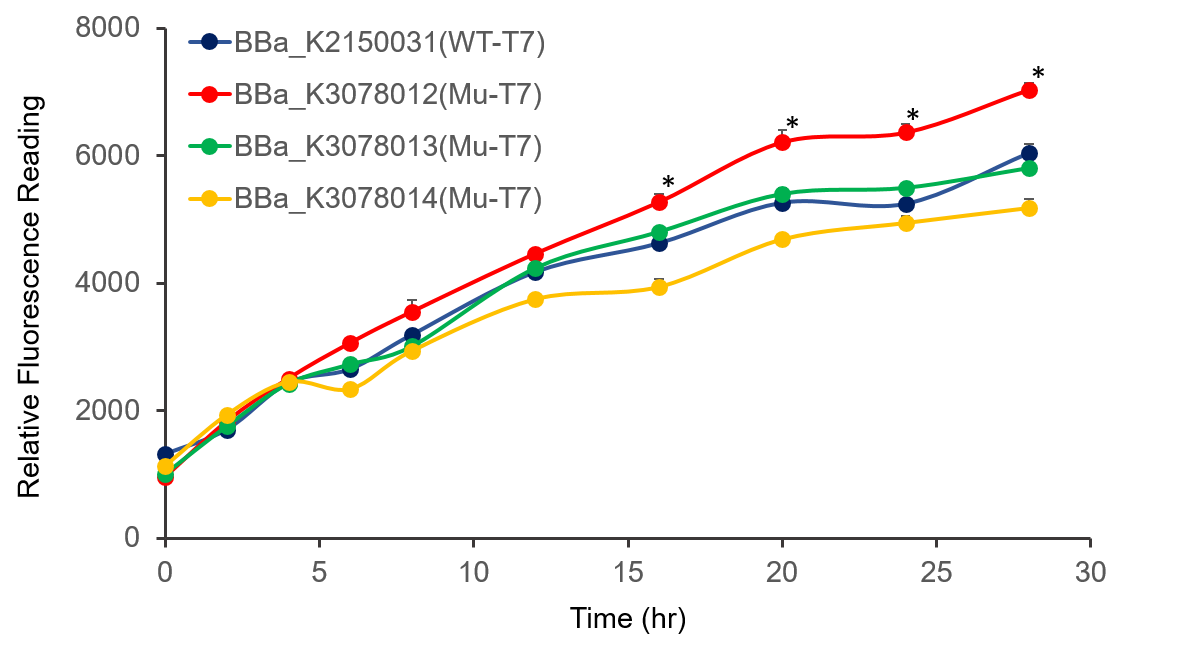
The promoter activity of wild-type and mutant T7 were measured through fluorescence intensity and normalized by OD600. BBa_K2150031 and the mutated T7 promoter lack of T7 RNA polymerase, so we added IPTG to induce the expression of T7 RNA polymerase downstream of promoter lacUV5 of on the BL21(DE3) genome, as shown in Figure 2.
It can be seen from the figure that the promoter strength of mutant is higher than wild type.
Figure 2. The plasmid was transferred to E.coli BL21, cultured overnight, and diluted OD600 0.02. IPTG was added at OD600 0.3 to make the final concentration of IPTG reach 1mM to measure at the indicated time. .
3. Conclusion
In conclusion, we constructed wild-type and mutanted T7 promoters into the measurement vector (BBa_K3078100) by Golden Gate method, and confirmed by the fluorescence measurement of the expression intensity of BBa_K3078012 was 30% higher than that of wild-type T7 promoters.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 274
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 483
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 622 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
| None |