Part:BBa_K3036004
Cold triggered kill switch
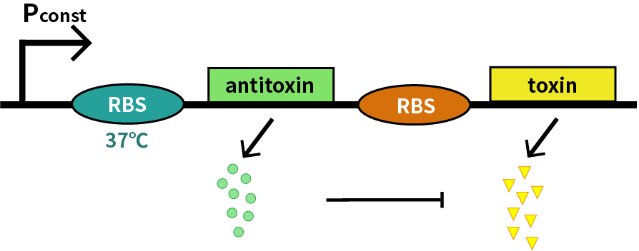
Kill switch consists of RNA thermometer (BBa_K115002), relE (BBa_K185000), and relB (BBa_K185048), aiming to prevent environmental contamination from the engineered bacteria through a cold-triggered toxin system. The toxin RelE shuts down protein synthesis and causes the death of microbe by cleaving mRNA within the ribosomal A site [1]. The antitoxin RelB counteracts RelE and thereby the inhibits cleavage of mRNA by RelE [2]. In addition, the RNA thermometer mediates expression at a temperature near 37℃ (body temperature), but not at 27℃ (room temperature).Only when the temperature reaches human body temperature can RelB be expressed. When the engineered bacteria get out of human body, temperature drops, inhibiting expression of the antitoxin RelB, and the bacteria die of the excessive toxin RelE, preventing contamination.
| Cold-triggered kill switch | |
| Function | Cold-triggered kill switch |
| Use in | Prokaryotes |
| RFC standard | RFC10 compatible |
| Backbone | pSB1C3 |
| Derived from | Escherichia. coli DH5alpha |
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal XhoI site found at 161
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Design and Properties
Cold-triggered kill switch is characterized in a system where the downstream relE (BBa_K185000) gene encodes for a constantly expressed stable toxin and the upstream relB (BBa_K185048) gene encodes for a labile antitoxin under the control of the RNA thermometer (BBa_K115002). In order to measure the function of this kill switch at 27℃ and 37℃, we take E. coli introduced with a vector with the same backbone as control group.
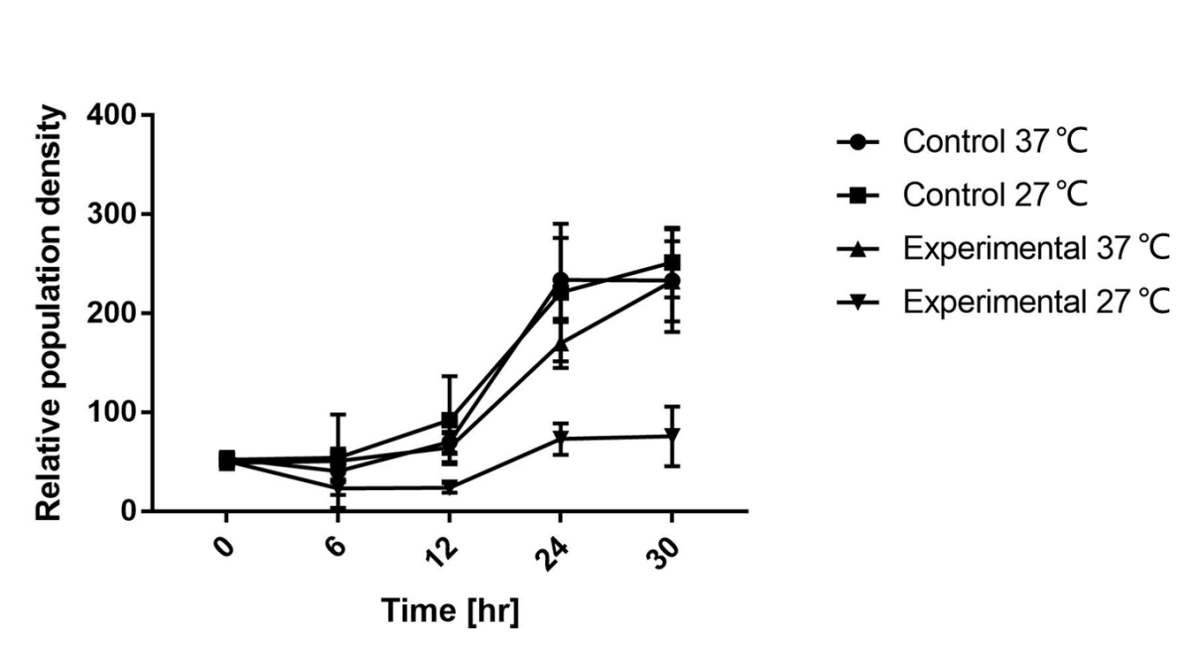
As is shown in Fig.1, there is nearly no difference of the relative population density between control and experimental groups at 37℃, which indicates the kill switch is not triggered. However, the population density of experimental group shows a significant decrease compared to control group at 27℃, caused by lack of antitoxin, which indicates the kill switch is activated at 27℃.
Experimental approach
1.Transform the plasmids into E. coli DH5α competent cells.
2.A strain containing a vector with same backbone is used as control. Experimental groups and control groups are both cultured in 60mL LB-ampicillin (50 ng/µl) medium overnight at 37℃, 200rpm.
3.Equally divide each group into two flasks, which is 30mL respectively. One of each group is cultured at 27℃, 200rpm and the other at 37℃, 200rpm.
4.Extract 5μl samples of each culture system every 6 hours. Diluted all of the samples to 10^7 times and then spread them on solid LB-ampicillin (50 ng/µl) medium separately.
5.Count the number of colonies in 5 cm^2 per plate after cultured for 24 hours at 37℃.
6.Three repicas are tested in each group.
Reference
[1] Overgaard M , Borch J , Gerdes K . RelB and RelE of Escherichia coli Form a Tight Complex That Represses Transcription via the Ribbon–Helix–Helix Motif in RelB[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2009, 394(2):0-196.
[2] Andreas Bøggild, Sofos N, Andersen K R, et al. The Crystal Structure of the Intact E. coli ReIBE Toxin-Antitoxin Complex Provides the Structural Basis for Conditional Cooperativity[J]. Structure, 2012, 20(10):1641-1648.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal XhoI site found at 161
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
| None |