Part:BBa_K3196002
SLAC
Characterization
Usage and Biology
Laccase is a multicopper oxidase, capable of catalyzing one-electron oxidation of a wide range of substrates to generate radicals while concomitantly reducing molecular oxygen to water[1]. Laccases are widely distributed in nature. They have been isolated from fungi, plants, insects and bacteria[2] of which fungal laccases are well characterized [3]. Bacterial laccases, such as the small laccase from S. coelicolor (SLAC), can be useful alternatives to fungal laccases. SLAC exhibits some desirable characteristics such as activity at high temperatures and alkaline pH [4], making it a potential candidate in biotechnological applications. Extracellular expression could be a desirable alternative for expression of foreign proteins since it simplifies purification steps [5]. P. pastoris is usually the preferred host for the production of industrial enzymes.
DNA Gel Electrophoretic
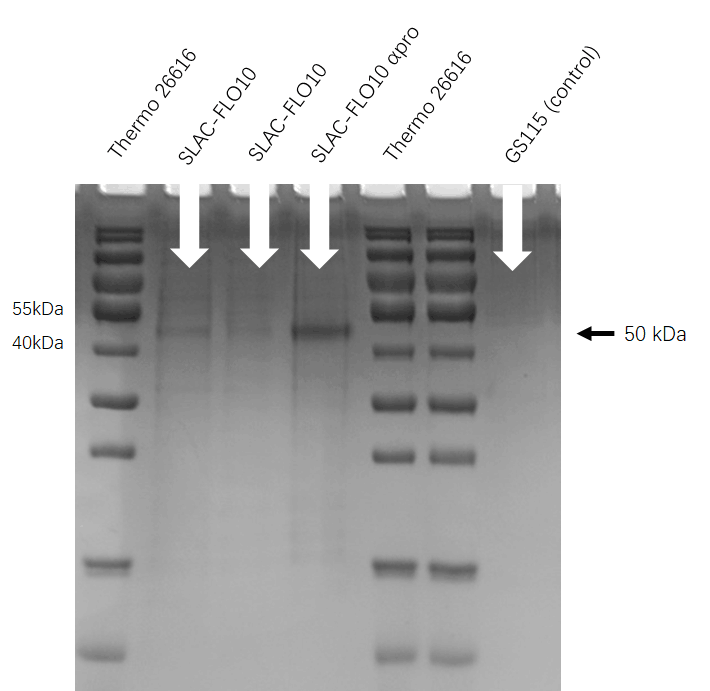
SDS-PAGE
Enzyme Activity
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 345
| None |