Part:BBa_I719005
T7 Promoter
Constitutive promoter derived from the T7 bacteriophage. Allows high expression of proteins only when the T7 polymerase is present. This part is identical to the part BBa_R0085 which currently hasn't been built.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Characterization in vitro
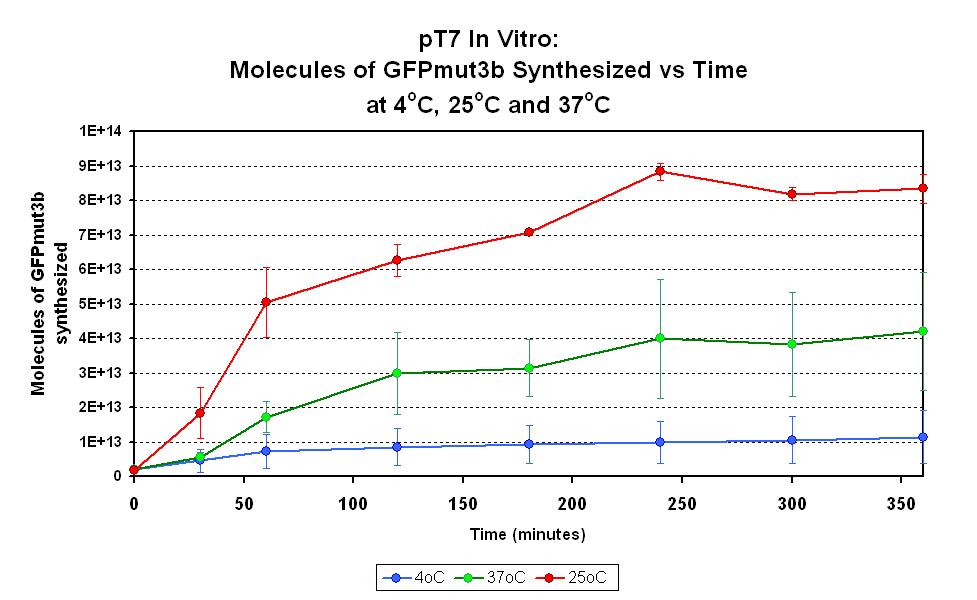
This part has been characterized for temperature sensitivity in the Cell-Free Chassis by iGEM Imperial 2007. For more detail, please check the testing [http://2007.igem.org/Imperial/Wet_Lab/Protocols/Prot1.9 protocols]and [http://2007.igem.org/Imperial/Wet_Lab/Results/Res1.9 results].
| Parameter | Value and Description |
|---|---|
| Optimum temperature | The T7 promoter has a highest output at 25°C, with a one-fold increase in GFP molecules synthesized compared to 37°C. The T7 promoter also has a minimal amount of output at 4°C. |
| Expression Life-span | The rate of GFP synthesis by the T7 promoter reaches a peak at around 30-60 minutes. |
| Peak Expression | The production of GFP decreases to minimal levels after 2 hours and tends towards nil after 4 hours. |
Team Warsaw 2010's measurement
Absolute promoter strength: 41,8pg RNA/minute/ug substrate DNA. It equals 8,92 microPoPSContribution
Group: Valencia_UPV iGEM 2018
Author: Adrián Requena Gutiérrez, Carolina Ropero
Summary: We adapted the part to be able to assemble transcriptional units with the Golden Gate assembly method
Documentation:
In order to create our complete [http://2018.igem.org/Team:Valencia_UPV/Part_Collection part collection] of parts compatible with the Golden Gate assembly method, we made the part BBa_K2656000 which is this part adapted to the Golden Gate technology.
ZJU-China 2019's improvement
I Overview
Currently, T7 promoter is one of the most widely used promoters for expression of heterogenous protein in some E.coli strains such as BL21(DE3). Though the wild-type T7 promoter has proven quite effective, in some cases, we need modified T7 promoters with even higher efficiency of protein expression to meet specific demands. Hence, we tried to transform the wild-type T7 promoter to get modified T7 promoters with increased strength . T7 RNA polymerase promoters consist of a highly conserved 23 base-pair sequence that spans the site of the initiation of transcription (+1) and extends from -17 to +6. As reported in some papers, the sequence specificty of T7 promoter is so strong that some point mutations between positions -11 and -7 may make T7 promoter fail to work. Thus, with the help of previous research, we carefully chose the site which would be mutated by PCR. These sites distribute in the range from -3 to +6. We mutated these sites by adding variable bases to primers (taatacgactcactatagggaga → taatacgactcacWNNNgSRRNN), and screened for stronger mutants.
II RESULT
To test the function of mutant promoters, we chose eGFP as our reporter, and added a lac operator behind the promotor to control transcription starts simultaneously. When the E.coli BL21(DE3) is cultured at the stage of logarithmic phase, we added 0.5 mM IPTG to induce the expression of GFP in strains BL21(DE3) for 4 hours. By assessing the absolute fluorescence and OD600, we can conclude the relative strength of all promoters. We screened out four mutants with higher intensity.
//direction/forward
//chassis/prokaryote/ecoli
//promoter
//regulation/constitutive
//chassis/bacteriophage/T7
| negative_regulators | |
| positive_regulators |

 1 Registry Star
1 Registry Star