Part:BBa_K2201009
Flanking sequences for deletion of codA
Flanking sequences for the homologous recombination based deletion of codA, coding for cytosine deaminase.
Usage and Biology
To retain the unnatural base pair formed between isoCm and isoG, the degradation of the unnatural nucleotides must be minimized. In E. coli, the gene codA codes for the cytosine deaminase, an enzyme of the pyrimidine metabolism. The cytosine deaminase catalyzes the reaction of cytosine to uracil. Furthermore, it can catalyze the deamination of isoguanosione and isocytosine. Isoguanosine is formed during oxidative stress by reaction of the radical oxygen species (ROS) •OH with adenine. Other products from reactions of adenine with ROS include 8-oxoadenine and 6-N-hydroxyaminopurine. This part provides the flanking sequences needed for a chromosomal deletion of codA in E. coli BL21(DE3) using CRISPR/Cas9 as described in our wiki. Sequence and Features
- 10INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]Illegal PstI site found at 580
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal PstI site found at 580
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal PstI site found at 580
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal PstI site found at 580
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
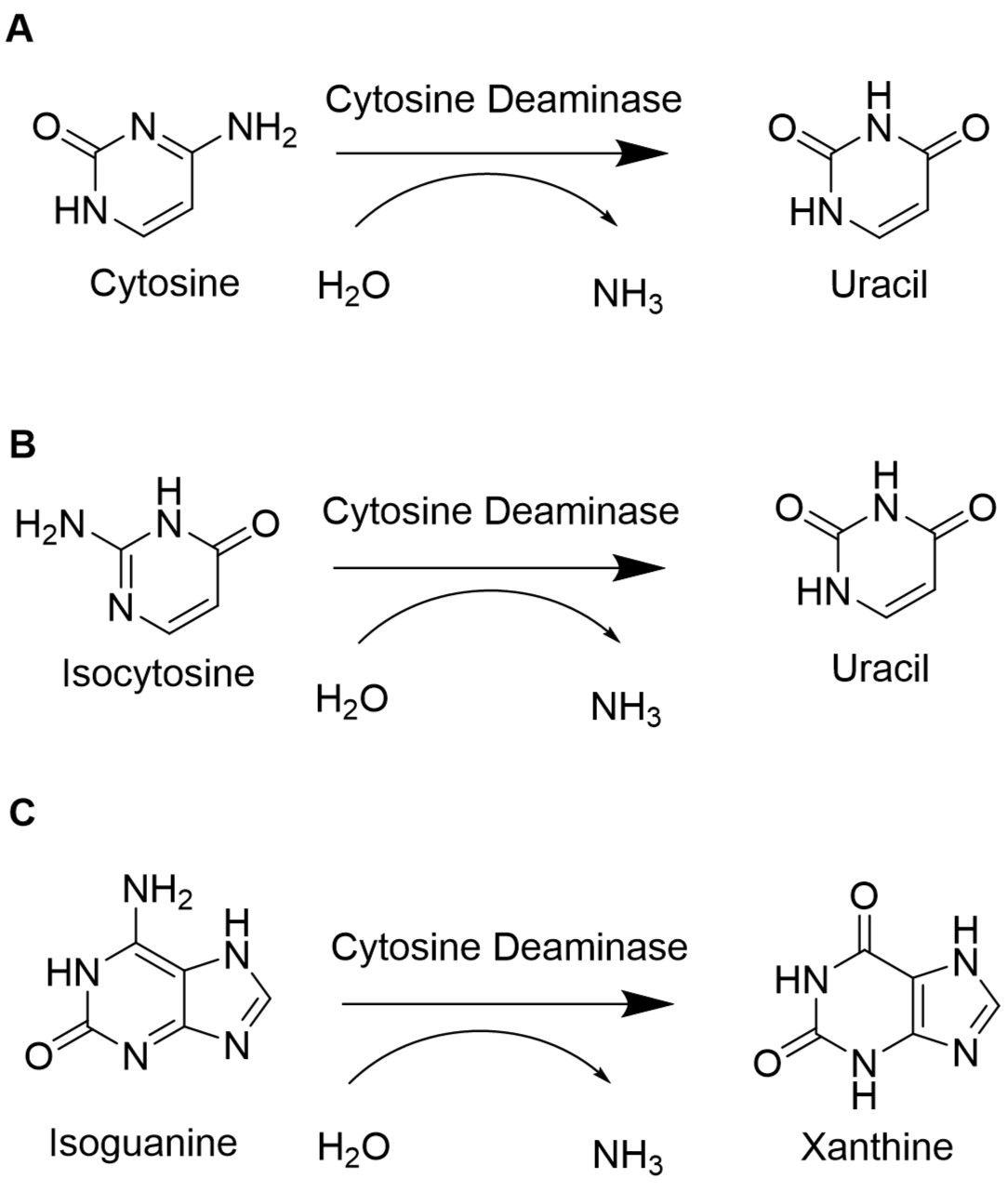
In E. coli, the codA gene is part of the codBA operon. Cytosine permease is encoded by codB, while codA encodes cytosine deaminase. The only way how cytosine can be metabolized is via hydrolytic deamination, a reaction that yields ammonia and uracil and is catalyzed by cytosine deaminase (Danielsen et al., 1992). When isoguanosine and isocytosine are provided to the cell, they are converted to uracil in the wildtype. Therefore, it is necessary to knock out or delete the codA gene to enable the stable availability of isoguanosine and isocytosine.
codA is 1281 bp in size, resulting in a protein composed of 427 amino acids after translation. The protein CodA is located in the cytosol and has an atomic mass of 47,5 kD.
References
| None |


