Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K404201"
VolkerMorath (Talk | contribs) |
VolkerMorath (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
| − | |||
<br><br><br><br> | <br><br><br><br> | ||
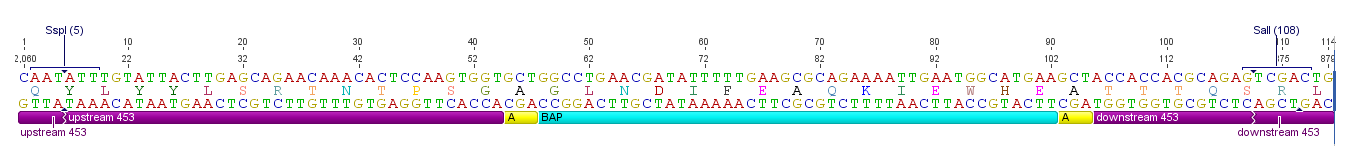
[[image:Freiburg10_ViralBrick-453-BAP.png|thumb|920px|Schematic representation of the BioBrick with all relevant annotations]] | [[image:Freiburg10_ViralBrick-453-BAP.png|thumb|920px|Schematic representation of the BioBrick with all relevant annotations]] | ||
Revision as of 22:19, 1 September 2010
ViralBrick-453-BAP
| ViralBrick-453-BAP | |
|---|---|
| BioBrick Nr. | BBa_K404201 |
| RFC standard | RFC 25RFC 10 |
| Backbone | pSB1C3_VCK |
| Source | synthetic |
| Submitted by | [http://2010.igem.org/Team:Freiburg_Bioware FreiGEM 2010] |
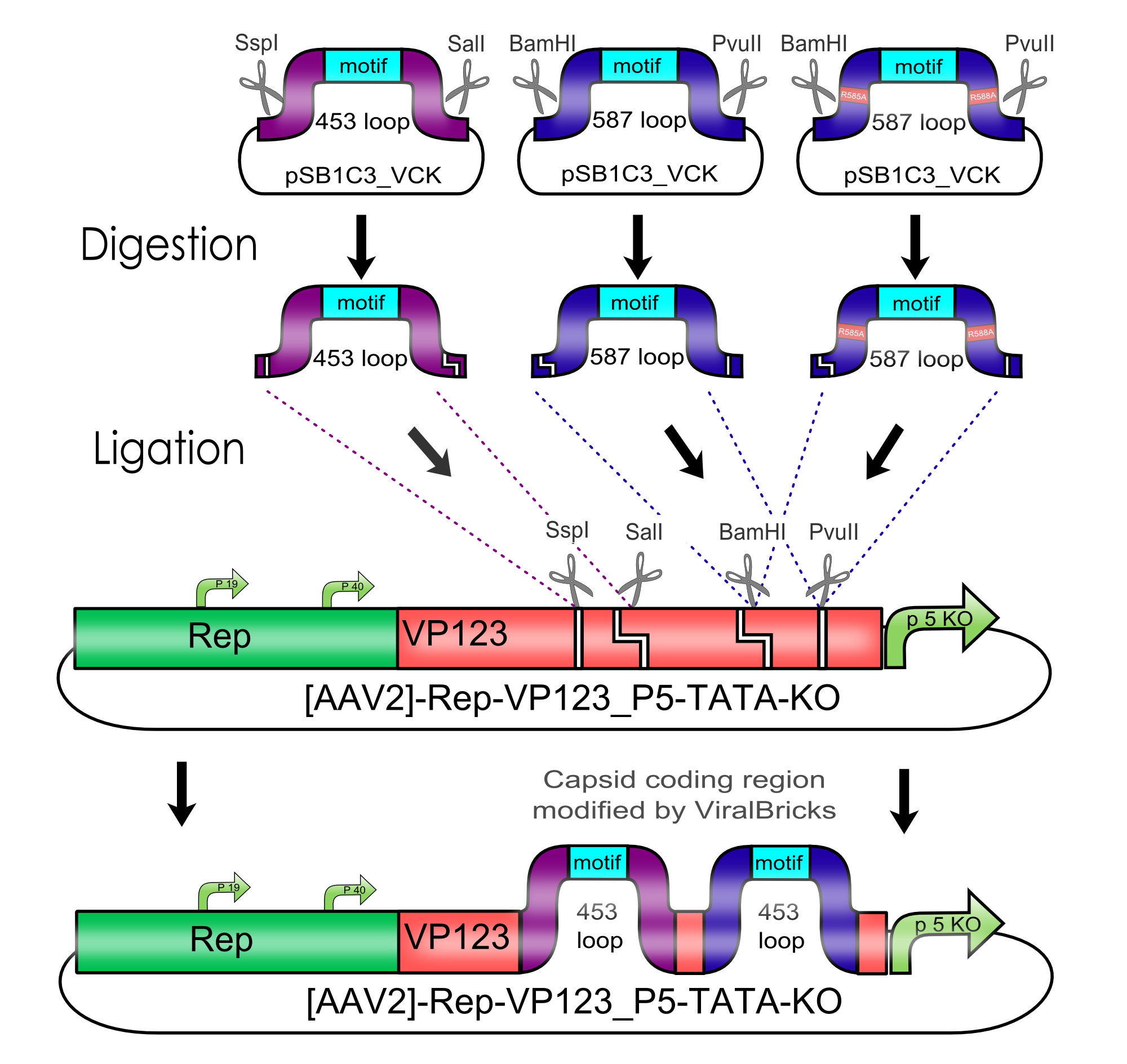
All capsid coding parts (e.g. (AAV2)-RepVP123) of the Virus Construction Kit designed by the iGEM Team Freiburg contain single cutting restriction sites on the side of the sequences coding for the two major surface exposed loops.
Using these restriction sites it is possible to insert functional motifs into the coding sequence for the viral capsid.
This BioBrick contains one of these functional motifs fanked by bilateral linkers and the viral sequences that code for the loop.
This category of BioBricks was termed ViralBrick to clarify that cloning does not function with the usual iGEM RFC restriction sites but with the mentioned ViralBrick restriction sites.
The four restriction sites for the ViralBrick insertion were designed in a way that the amino acid sequence of the viral capsid could be absolutely conserved. This was advisable because even slight changes in the viral capsid lead to drastically changed interactions with cellular surface receptors. For this reason we decided to insert these restriction sites in stead of using BioBrick assembly that would define at least two amino acids in the viral loop.
Modification of the Viral Capsid of the AAV2 using Viral Bricks
For therapeutical applications in human gene transfer the broad tropism for heparan sulfate proteoglycan (HSPG) has to be knocked-out and a novel tropism has to be inserted.
This retargeting can be realized either by insertion of functional motifs into the two major surface exposed loops or by fusion of these motifs to the N-terminus of the viral coat proteins.
The graphic on the right shows parts of the three-dimensional structure of a viral coat protein. The parts of the loop regions that are coded in the ViralBricks are shown in purple for the 453 loop and in blue for the 587 loop.
Cloning of Viral Bricks into capsid coding parts
In order to make loop insertions more convenient the following restriction sites were inserted into all capsid coding parts and already existing restriction sites were removed from the constructs.
The choice of these restriction sites was reasoned by enzyme performance, buffer compabilities and the number of existing restriction sites that had to be removed at other positions.
All restriction endonucleases were purchased from [http://www.neb-online.de NEB].
Risk assessment and terms of use
Viral Systems based on the Adeno-associated Virus of the serotype 2 are to handle under Biosafety level 1 according to the german [http://bundesrecht.juris.de/gentg/index.html Act on Genetic Engineering] and the specification of the ZKBS on working with the AAV. This general classification is restricted to experiments that use the ITRs (Inverted Terminal Repeats) of the AAV2 and do not contain hazzardous gene sequences on the vector plasmid.
Please consider special provisions of law in your contry before using parts that contribute the production of genetically modified viral vectors.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]