Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3861017"
Martje1998 (Talk | contribs) |
Martje1998 (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
| − | <img src="https://2021.igem.org/wiki/images/ | + | <img src="https://2021.igem.org/wiki/images/7/71/T--Humboldt_Berlin--dose_dependent.png" alt="PlldR-GFP" width="500"> |
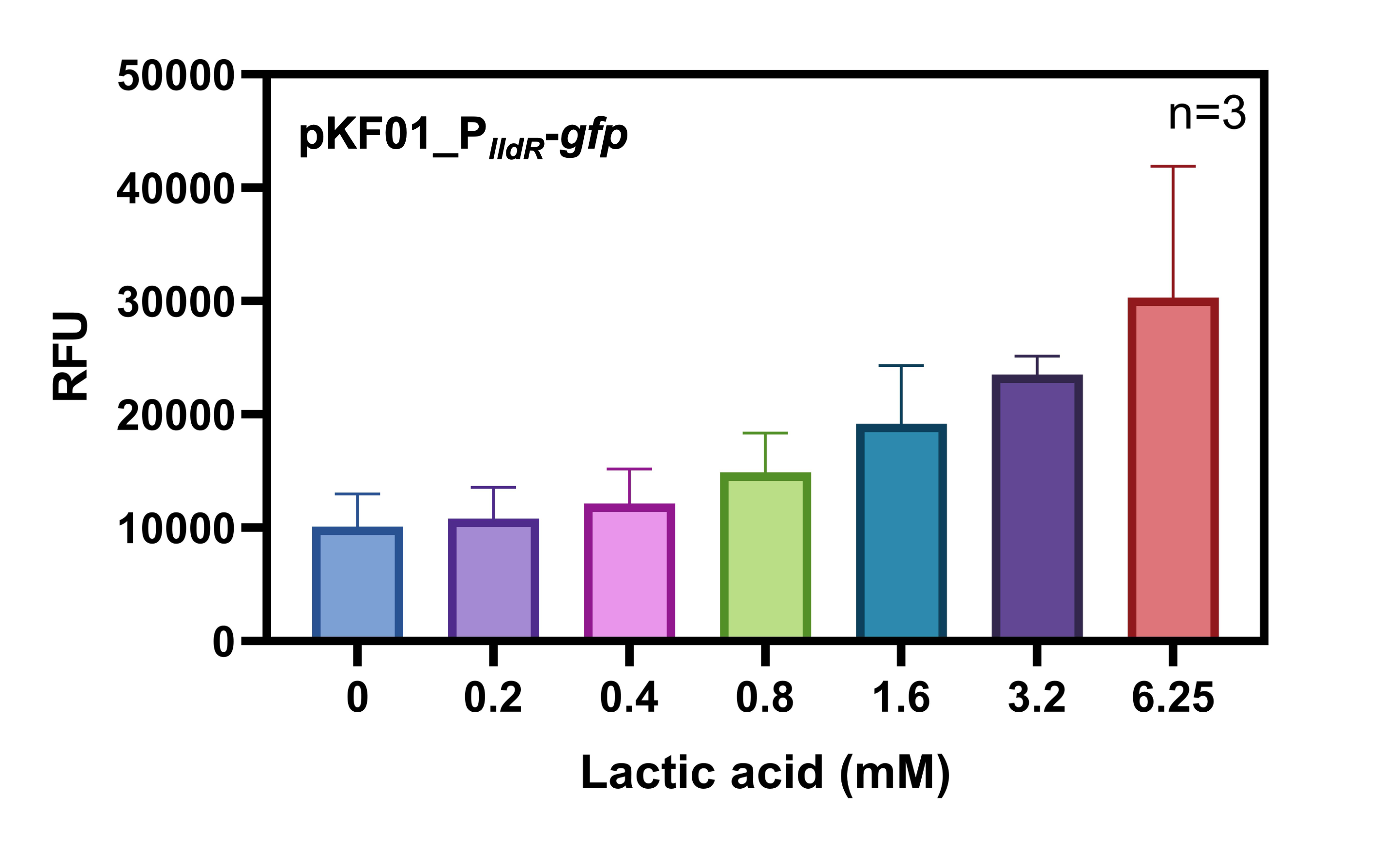
<figcaption>Fig. 1 - Characterization of the lldR promoter using GFP as reporter. RFU = relative fluorescene unit; n = number of replications.</figcaption> | <figcaption>Fig. 1 - Characterization of the lldR promoter using GFP as reporter. RFU = relative fluorescene unit; n = number of replications.</figcaption> | ||
</figure> | </figure> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
Revision as of 21:50, 21 October 2021
PlldR-GFP
Introduction
Composite part containing the PlldR promoter (BBa_K1847008) fused to GFP (BBa_E0840) as a reporter gene. Both parts were already characterized in depth by other teams. We used this part in Salmonella Typhimurium.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 78
Illegal NheI site found at 101 - 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 816
Characterization
We wanted to know if the lactate-inducible lldR promoter is still functional in Salmonella minicells, as minicells only exhibit a limited lifespan and transcriptional and translational activity. To check this, we conducted a lactate assay with 2 replications using newly purified minicells following our optimized minicell purification protocol. The GFP expression is increasing with rising lactate-concentration, thus we concluded that minicells have enough expression capacity available for GFP expression and that the lldR promoter is functional (Fig. 1).