Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2916037"
Konstantinos (Talk | contribs) |
Konstantinos (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| − | This part is used for expression of Elongation Factor-G needed for the OnePot PURE cell-free system. | + | This part is used for expression of Elongation Factor-G (EF-G) needed for the OnePot PURE cell-free system. |
<!-- Add more about the biology of this part here--> | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here--> | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
===Usage and Biology=== | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
| − | + | Elongation factors are a set of proteins that function during the second step of protein biosynthesis, the elongation phase. They act upon the ribosome, to facilitate translational elongation from formation of the first to the last peptide bond of a growing polypeptide. The elongation phase is the most rapid step in translation, so the factors also regulate the procedure happening during that step to ensure high accuracy of the translation. | |
| + | |||
| + | The Elongation Factor G in particular catalyzes the translocation of the tRNA and mRNA down the ribosome at the end of each round of polypeptide elongation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In our project we used EF-G as a part of the protein solution needed for <html><a style="padding: 0px; margin: 0px;" href="https://2019.igem.org/Team:EPFL/OnePot_Pure"> OnePot PURE cell-free system </a></html> using the method of gravity flow affinity chromatography, as described in the <html><a style="padding: 0px; margin: 0px;" href="https://www.protocols.io/view/protein-purification-for-onepot-pure-cell-free-sys-8auhsew"> protocol </a></html> we designed. | ||
| + | |||
Latest revision as of 02:37, 22 October 2019
Expression of EF-G in E.coli
This part is used for expression of Elongation Factor-G (EF-G) needed for the OnePot PURE cell-free system.
Usage and Biology
Elongation factors are a set of proteins that function during the second step of protein biosynthesis, the elongation phase. They act upon the ribosome, to facilitate translational elongation from formation of the first to the last peptide bond of a growing polypeptide. The elongation phase is the most rapid step in translation, so the factors also regulate the procedure happening during that step to ensure high accuracy of the translation.
The Elongation Factor G in particular catalyzes the translocation of the tRNA and mRNA down the ribosome at the end of each round of polypeptide elongation.
In our project we used EF-G as a part of the protein solution needed for OnePot PURE cell-free system using the method of gravity flow affinity chromatography, as described in the protocol we designed.
Characterization
Expression and purification of EF-G
EF-G is one of the proteins we used for the OnePot PURE cell-free system. We expressed it in M15 E.coli strain using a pQE60 vector. The expression system has a T5 lac operator, RBS and a lambda t0 Terminator, enabling us to regulate the expression with IPTG.
Methods
EF-G was purified using our protocol . To test if the protein was actually expressed, we performed a SDS-PAGE that is presented below. On the left side we can see the results included in the initial OnePot PURE paper (Lavickova et al, 2019) while on the right (batch1_a,b and batch2_a,b) are the solutions we produced ourselves. (The procedure we followed and the conditions of the experiment can be found here).
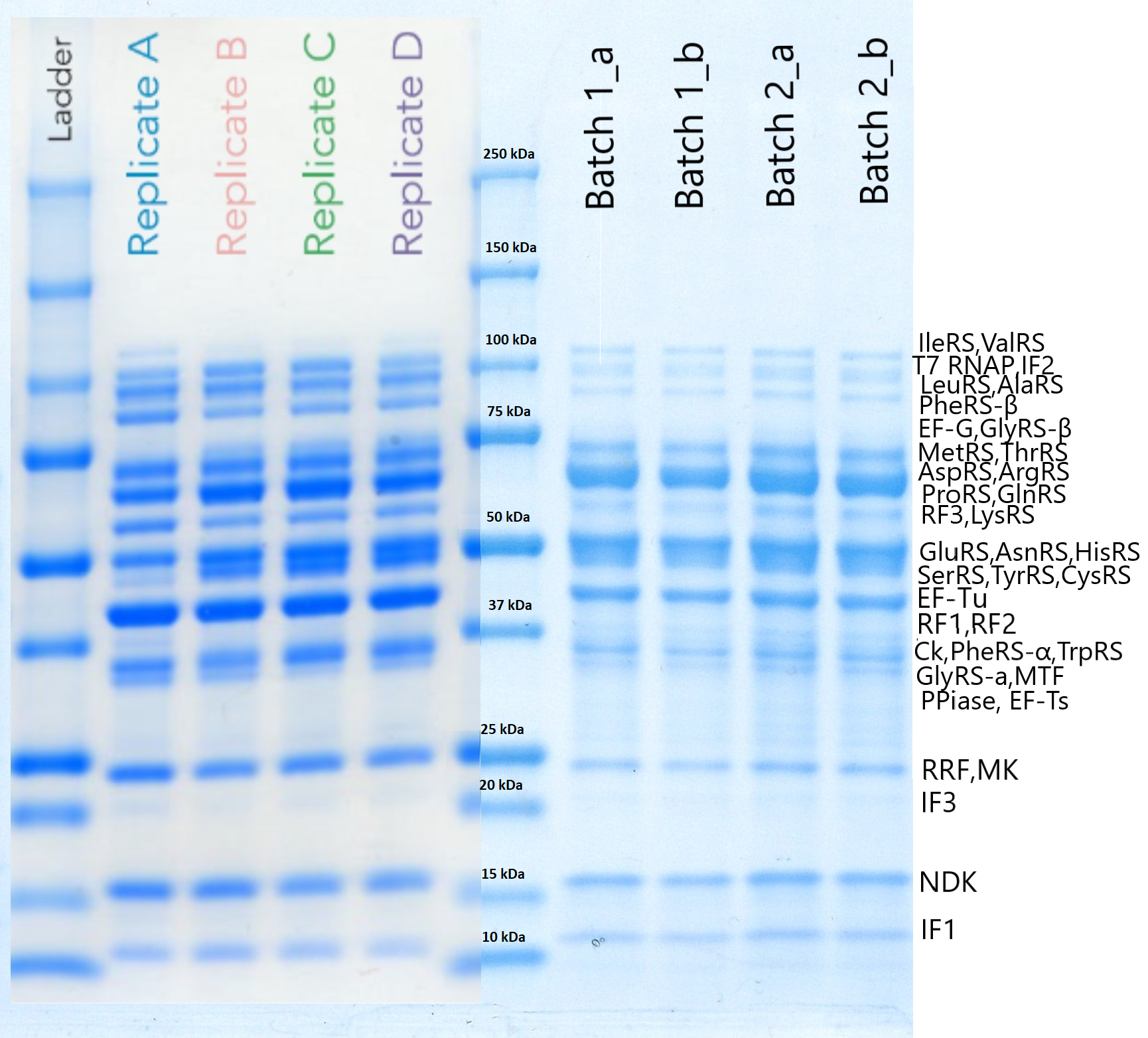
Conclusion
EF-G has a molecular weight of around 76kDa, but even though we cannot be absolutely sure if the band shown is only due to it, we may assume that it is expressed. To verify the existence and functionality of this protein we need to proceed with more experiments that would be mainly focused on the efficiency of the system.
OnePot PURE functionality test
To make sure that we have all the proteins in our OnePot PURE protein solution, and that they all function properly we need check if proteins can be expressed in our OnePot PURE cell-free system.
Methods
We expressed superfolding GFP following the protocol we designed in 10μl reactions, and measured the fluorescence on a plate reader at excitation wavelength of 535nm. We tested the expression using different concentrations of the sf GFP DNA template and also compared it with the fluorescence produced in PURExpress from NEB.
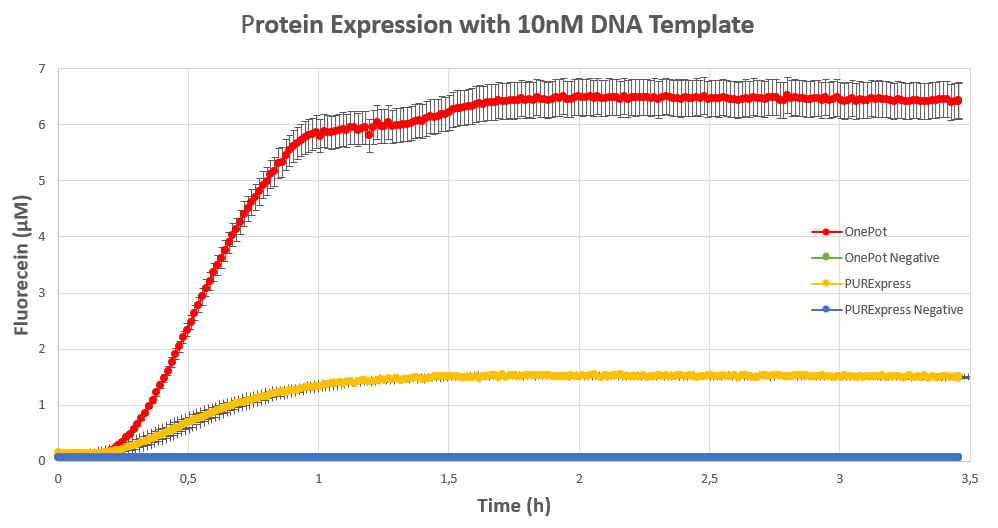
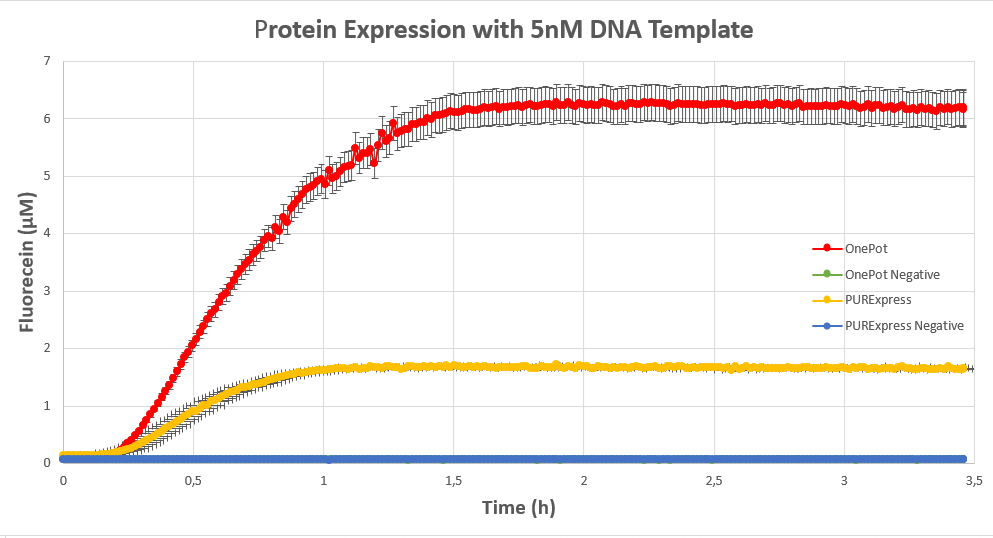
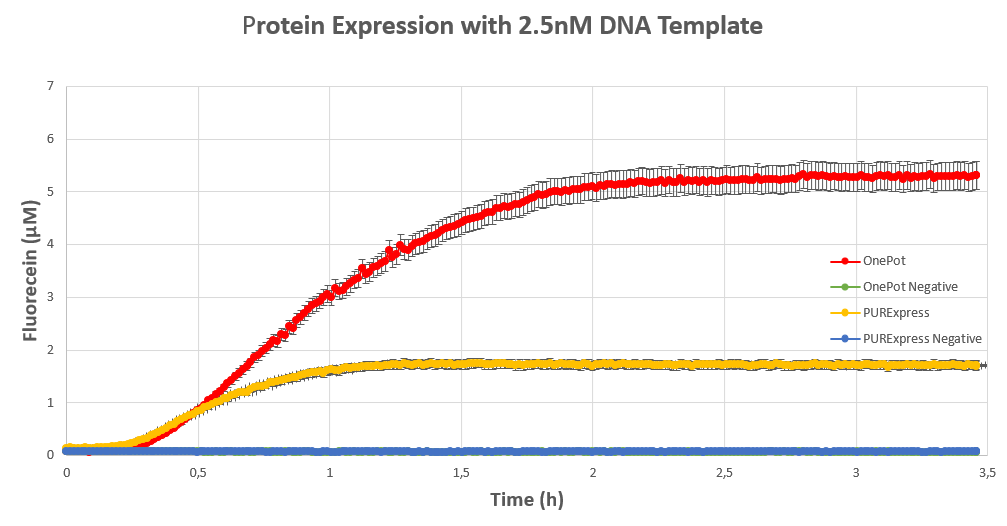
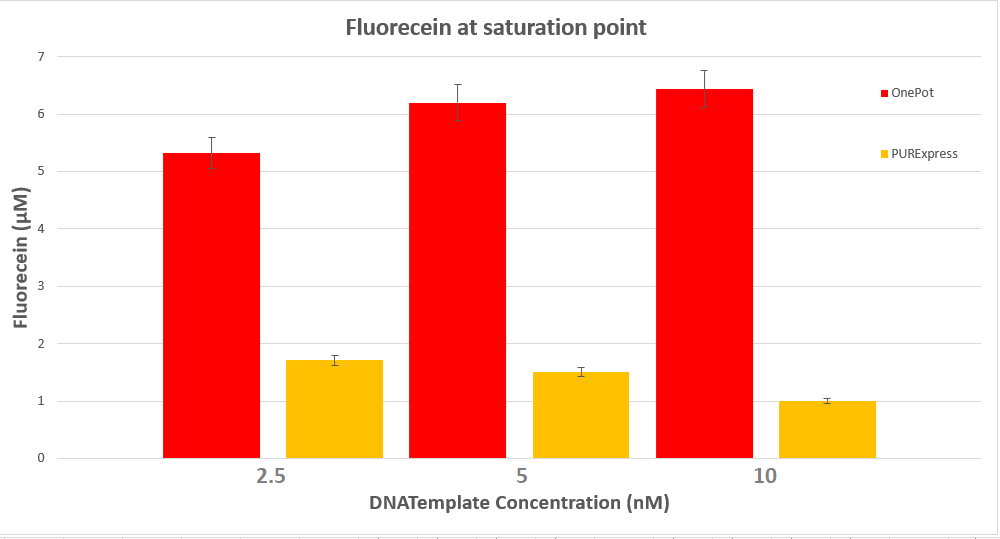
Conclusion
The expression was successful so we can confirm that EF-G exists in our protein solution and is also functioning properly.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 2222
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 209
Illegal AgeI site found at 647
Illegal AgeI site found at 1991 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal SapI.rc site found at 800
