Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2660006"
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
identification and sequencing of the PCR products. | identification and sequencing of the PCR products. | ||
| − | + | (<html><img class="card-img-top" src="https://2019.igem.org/wiki/images/f/f8/T--USTC--Cas9.png" alt="Card image"></html>) | |
| − | + | ||
Figure1. Electrophoresis result PCR of C-Cas9+pMag and | Figure1. Electrophoresis result PCR of C-Cas9+pMag and | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
pictures are blurred because of the poor photographic equipment) | pictures are blurred because of the poor photographic equipment) | ||
| − | + | (<html><img class="card-img-top" src="https://2019.igem.org/wiki/images/1/14/T--USTC--SDS_PAGE.png" alt="Card image"></html>) | |
| + | |||
Figure2. SDS-PAGE for strain expressing aNAT, C-Cas9+pMag | Figure2. SDS-PAGE for strain expressing aNAT, C-Cas9+pMag | ||
Revision as of 22:55, 21 October 2019
N-Cas9
Coding sequence for the N-terminal section of split Cas9 nuclease.
This BioBrick was engineered to be the N-terminal domain of cas9 (BBa_K2457001) coding sequence from Streptococcus pyogenes. It was designed to be an inactive domain linked with proteins like pMag (BBa_K2660009) to control to control the kinetics of activation by blue light and induce targeted genome sequence modifications (to kill or remove the recombinant DNA). This activity can be switched off simply by extinguishing the light.
The nuclease activity requires the use together with nMag(BBa_K2660008) linked with the c-cas9 domain (BBa_K2660007)
N-Cas9 This part is inserted into plasmid, and the correct construction of this recombinant plasmid was confirmed by PCR
identification and sequencing of the PCR products.
(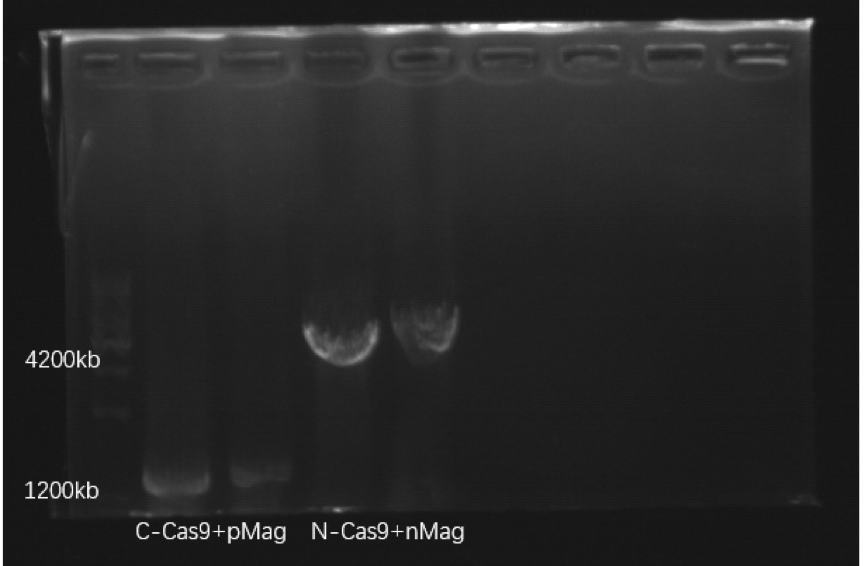 )
)
Figure1. Electrophoresis result PCR of C-Cas9+pMag and
N-Cas9+nMag.
Besides, the E.coli was grown in LB liquid medium, and obtain protein by heating them. The sample was
electrophoresed on a sodium dodecyl sulfate(SDS)-polyacrylamide gel, followed by Coomassie blue staining.( The
pictures are blurred because of the poor photographic equipment)
(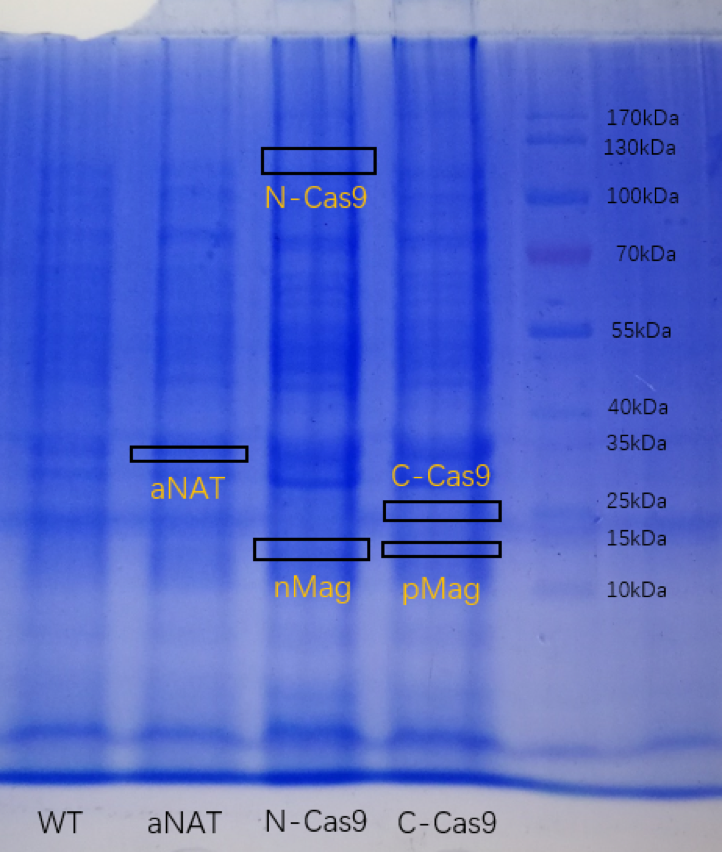 )
)
Figure2. SDS-PAGE for strain expressing aNAT, C-Cas9+pMag
and N-Cas9+nMag.
references
Nihongaki, Y et al. Photoactivatable CRISPR-Cas9 for optogenetic genome editing. Nature Biotechnology volume 33, pages 755–760 doi: 10.1038/nbt.3245 (2015)
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
