Difference between revisions of "Part:pSB4K5:Experience"
Josephineum (Talk | contribs) (→Team KCL_UK 2019) |
Josephineum (Talk | contribs) (→Team KCL_UK 2019) |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
We also compared optical density (Table 3 and Figure 3) and fluorescence data (Table 4 and Figure 4) for pSB1C3 and pSB4K5 constructs and to our surprise we noticed a high fluorescence reading and that the replication origin of the pSB4K5 plasmid backbone might not confer a low copy number plasmid as originally thought. It has been observed that the difference in the fluorescent intensity between cells harbouring pSB1C3 and pSB4K5 plasmid GFP constructs is about 1.5-2 which might indicate that there are about 250 copies of pSB4K5 plasmid per cell not ~5 copies as in the wild-type pSC101 plasmid. | We also compared optical density (Table 3 and Figure 3) and fluorescence data (Table 4 and Figure 4) for pSB1C3 and pSB4K5 constructs and to our surprise we noticed a high fluorescence reading and that the replication origin of the pSB4K5 plasmid backbone might not confer a low copy number plasmid as originally thought. It has been observed that the difference in the fluorescent intensity between cells harbouring pSB1C3 and pSB4K5 plasmid GFP constructs is about 1.5-2 which might indicate that there are about 250 copies of pSB4K5 plasmid per cell not ~5 copies as in the wild-type pSC101 plasmid. | ||
| − | Similar results have been noticed by the Team Uppsala University 2012 and Team Warwick 2015 https://parts.igem.org/Part:pSB4K5:Experience.It is also known that to create part BBa_I50042 and subsequently pSB4K5 plasmids the pSC101 origin of replication had been modified to remove SpeI restriction site in the Ori region https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I50042:Design,but it is not known how this modification might have changed the plasmid copy number. It has been suggested recently in the literature https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-20016-wthat certain mutations in the RepA protein of the pSC101 origin of replication can increase plasmid copy number from 5 copies per cell to 113 copies per cell. Our analysis of the DNA sequence of the pSB4K5 plasmid construct has revealed two new mutations in the RepA protein R267H and H289Y but it is not clear how these changes might have influenced the differences in the plasmid copy numbers as these mutations have not been reported to date. Although differences in the plasmid copy numbers did not in any way negatively impacted on our project but it might be important for other teams to consider another plasmid backbone instead of the pSB4K5 if the low copy number plasmid is needed. | + | Similar results have been noticed by the Team Uppsala University 2012 and Team Warwick 2015 https://parts.igem.org/Part:pSB4K5:Experience. It is also known that to create part BBa_I50042 and subsequently pSB4K5 plasmids the pSC101 origin of replication had been modified to remove SpeI restriction site in the Ori region https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I50042:Design, but it is not known how this modification might have changed the plasmid copy number. It has been suggested recently in the literature https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-20016- wthat certain mutations in the RepA protein of the pSC101 origin of replication can increase plasmid copy number from 5 copies per cell to 113 copies per cell. Our analysis of the DNA sequence of the pSB4K5 plasmid construct has revealed two new mutations in the RepA protein R267H and H289Y but it is not clear how these changes might have influenced the differences in the plasmid copy numbers as these mutations have not been reported to date. Although differences in the plasmid copy numbers did not in any way negatively impacted on our project but it might be important for other teams to consider another plasmid backbone instead of the pSB4K5 if the low copy number plasmid is needed. |
<p> | <p> | ||
Table 3. OD600 of Xl1Blue E.coli cell culture harbouring pSB1C3_BBa_K608010, pSB1C3_BBa_K608011, pSB4K5_BBa_K608010 and pSB4K5_BBa_K608011 plasmids respectively. | Table 3. OD600 of Xl1Blue E.coli cell culture harbouring pSB1C3_BBa_K608010, pSB1C3_BBa_K608011, pSB4K5_BBa_K608010 and pSB4K5_BBa_K608011 plasmids respectively. | ||
Revision as of 08:26, 19 October 2019
This experience page is provided so that any user may enter their experience using this part.
Please enter
how you used this part and how it worked out.
Applications of pSB4K5
Team KCL_UK 2019
Our team has used this pSB4K5 part to create two plasmid fluorescent reporter system. One plasmid containing part pSB1C3 and another plasmid containing pSB4K5. This part contains part BBa_I50042 which is a pSC101 replication origin and is compatible with the minimal pUC-derived high copy replication origin found in part BBa_I50022 composite part pSB1C3 and thus suitable for E.coli transformation simultaneously with two plasmids. We cloned BBa_K608010 and BBa_K608011 into this pSB4K5 plasmid backbone and created two new plasmids pSB4K5_ BBa_K608010 and pSB4K5_ BBa_K608011 respectively. Subsequently, we transformed Xl1Blue E.coli cells with these plasmids and selected positive colonies on LB agar plates containing Kanamycin (15 ug/ml). Single colony from each plate was inoculated into 10 ml LB media containing Kanamycin (15 ug/ml) and incubated overnight in a shaking incubator at 37 oC with shaking 200 rpm. After approximately 16 h of incubation E.coli cultures were diluted 1/10 with fresh 10 ml LB media containing Kanamycin (15 ug/ml) in 20 ml universal bottle. Each experiment was performed in duplicate. At this point 500 ul of the culture was collected into 1.5 ml centrifuge tube, labelled 0h incubation and stored on ice. The rest of the culture was incubated for 5 h in the shaking incubator at 37 oC with shaking 200 rpm with 500 ul samples taken every hour, labelled 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 h incubation and stored on ice. In the end 200 ul of each duplicate sample was aliquoted into black clear bottom 96 well plate. Duplicate samples of LB media containing Kanamycin (15 ug/ml) were used as a negative control. The OD600 and fluorescence (ex485, em520) were recorded using PHERAstar FS (BMG Labtech) 96well plate reader. Recorded results were normalised to LB media and average results of two duplicate samples are presented in tables 1 and 2 and figures A and B.
Table 1. OD600 of Xl1Blue E.coli cell culture harbouring pSB4K5_BBa_K608010 and pSB4K5_BBa_K608011 plasmids respectively.
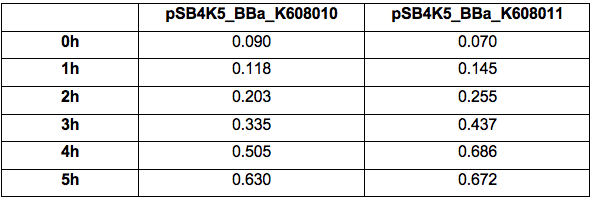
Table 2. GFP Fluorescence (ex485 nm, em520 nm) of Xl1Blue E.coli cell culture harbouring pSB4K5_BBa_K608010 and pSB4K5_BBa_K608011 plasmids respectively.
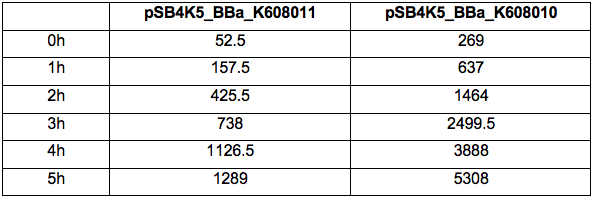
Figure 1. OD600 of Xl1Blue E.coli cell culture harbouring pSB4K5_BBa_K608010 and pSB4K5_BBa_K608011 plasmids respectively.

Figure 2. GFP Fluorescence (ex485 nm, em520 nm) of Xl1Blue E.coli cell culture harbouring pSB4K5_BBa_K608010 and pSB4K5_BBa_K608011 plasmids respectively.
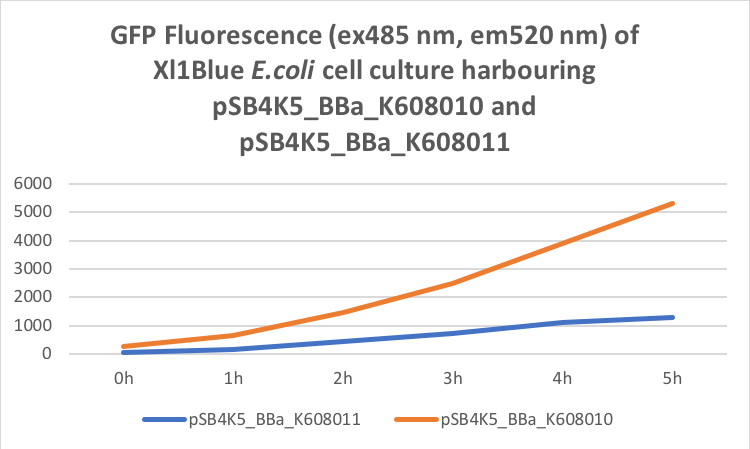
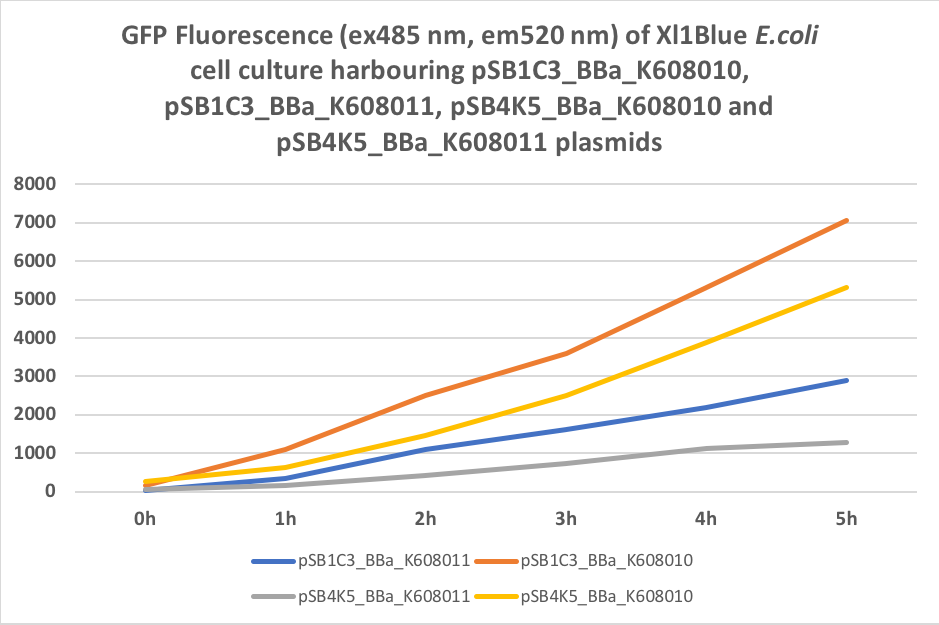
We also compared optical density (Table 3 and Figure 3) and fluorescence data (Table 4 and Figure 4) for pSB1C3 and pSB4K5 constructs and to our surprise we noticed a high fluorescence reading and that the replication origin of the pSB4K5 plasmid backbone might not confer a low copy number plasmid as originally thought. It has been observed that the difference in the fluorescent intensity between cells harbouring pSB1C3 and pSB4K5 plasmid GFP constructs is about 1.5-2 which might indicate that there are about 250 copies of pSB4K5 plasmid per cell not ~5 copies as in the wild-type pSC101 plasmid. Similar results have been noticed by the Team Uppsala University 2012 and Team Warwick 2015 https://parts.igem.org/Part:pSB4K5:Experience. It is also known that to create part BBa_I50042 and subsequently pSB4K5 plasmids the pSC101 origin of replication had been modified to remove SpeI restriction site in the Ori region https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I50042:Design, but it is not known how this modification might have changed the plasmid copy number. It has been suggested recently in the literature https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-20016- wthat certain mutations in the RepA protein of the pSC101 origin of replication can increase plasmid copy number from 5 copies per cell to 113 copies per cell. Our analysis of the DNA sequence of the pSB4K5 plasmid construct has revealed two new mutations in the RepA protein R267H and H289Y but it is not clear how these changes might have influenced the differences in the plasmid copy numbers as these mutations have not been reported to date. Although differences in the plasmid copy numbers did not in any way negatively impacted on our project but it might be important for other teams to consider another plasmid backbone instead of the pSB4K5 if the low copy number plasmid is needed.
Table 3. OD600 of Xl1Blue E.coli cell culture harbouring pSB1C3_BBa_K608010, pSB1C3_BBa_K608011, pSB4K5_BBa_K608010 and pSB4K5_BBa_K608011 plasmids respectively.
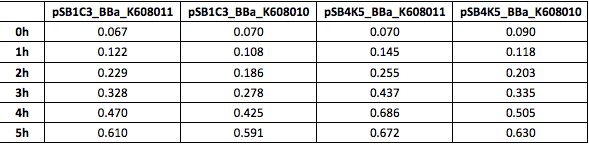
Figure 3. OD600 of Xl1Blue E.coli cell culture harbouring pSB1C3_BBa_K608010, pSB1C3_BBa_K608011, pSB4K5_BBa_K608010 and pSB4K5_BBa_K608011
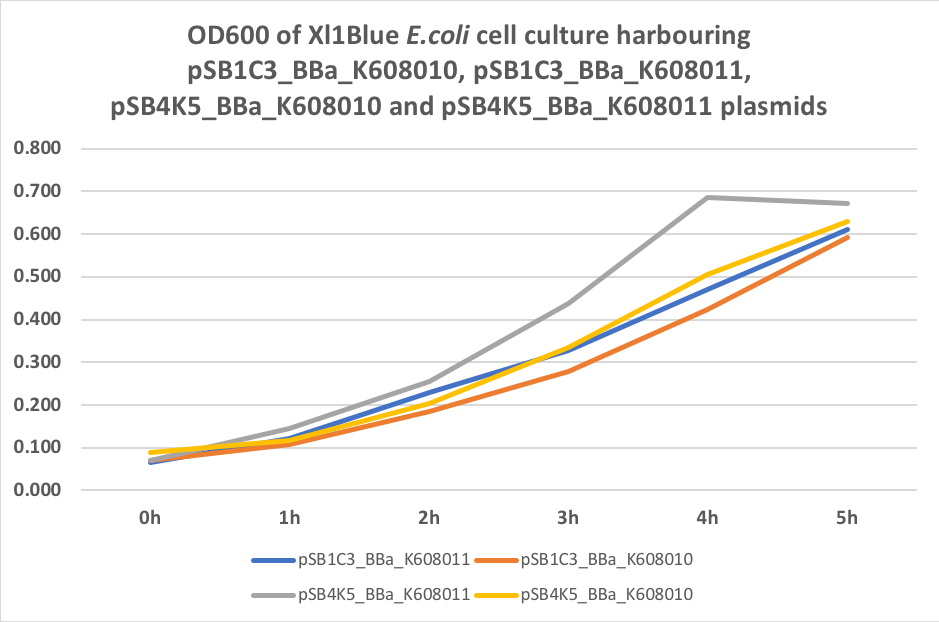
Table 4. GFP Fluorescence (ex485 nm, em520 nm) of Xl1Blue E.coli cell culture harbouring pSB1C3_BBa_K608010, pSB1C3_BBa_K608011, pSB4K5_BBa_K608010 and pSB4K5_BBa_K608011 plasmids respectively.
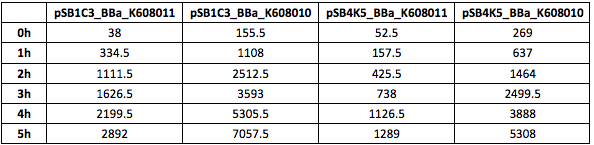
Figure 4. GFP Fluorescence (ex485 nm, em520 nm) of Xl1Blue E.coli cell culture harbouring pSB1C3_BBa_K608010, pSB1C3_BBa_K608011, pSB4K5_BBa_K608010 and pSB4K5_BBa_K608011 plasmids
Team Warwick 2015
Our team considered using this part as part of a system of binding different coloured cells together in order to demonstrate specific cell placement. We characterised this part is order to determine the optimal amount of IPTG required for inducing the gene, and the copy number necessary to express the fluorescence brightly. The results for this can be seen below.
We cloned J04450 into three plasmid with varying copy numbers, in order from highest to lowest copy number they are: pSB1K3, pSB3K3, and pSB4K5. These plasmids were then transformed into electrocompetent MG1655 Z1 cells and grown overnight. THe next morning the cells were refreshed, and different concentrations of IPTG (0uM, 250uM, and 500uM) were added to induce them. For each of the three plasmids in each IPTG concentrations, three biological replicates were made, and when OD600 and RFP absorbance were measured, three technical replicates were made, for a total of 81 copies of the gene grown. The RFP absorbance and OD600 of these cells were measured over 20 hours. The OD600 over time was used to determine at what OD the cells were in steady state. This was then compared to the RFP measured at that time and graphed to show RFP expression per cell.

The graph shows that RFP expression was highest in the pSB1K3 and pSB4K5 plasmids, and that there was little difference in expression between the 250uM and 500uM concentration of IPTG. 0uM IPTG universally showed almost no expression. pSB1K3 should have the highest copy number and pSB4K5 should have the lowest copy number, so it's curious that they both expressed RFP very well. This could be due to a mutation in the pSB4K5 causing it to have a much higher copy number than usual. It is documented here (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1283002) that a single point mutation can increase the copy number of a plasmid. The pSB4K5 plasmid we tested has been sent for sequencing in order to determine whether this is the case.
The raw data for this characterisation can be found here:
https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/7/70/Warwick_J04450_raw_data.txt
https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/b/bc/Warwick_J04450_in_pSB1K3_analysed_results.txt
https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/8/8f/Warwick_J04450_in_pSB3K3_analysed_results.txt
https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/5/54/Warwick_J04450_in_pSB4K5_analysed_results.txt
https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2015/6/64/Warwick_J04450_RFP_OD_analysed_results.txt
User Reviews
UNIQ557e73436e243048-partinfo-00000000-QINU
|
•
|
iGEM Team Uppsala University 2012 Warning: This is not a low copy backbone. The copy number of a sibling, pSB4C5 plasmid, with the same I50042 ori, has been estimated by three methods and compared to the pSB3C5 (with p15A ori) and the pSB4C15. The results shows strong evidence of BBa_I50042 ori having a significantly higher copy number than specified, comparable to or higher than the p15A ori.
Flow cytometry E coli MG1655 was transformed with plasmids of different backbones with the J04450 standard RFP cassette. Liquid cultures were analysed by fluorescence with a Fluorescence activated cell sorter (FACS), quantitivly measuring the fluorescence of individual cells. Due to the active native lacI repression system in the bacteria, the experiment was performed with and without IPTG for promoter induction. Read about I50042 for details and other measurments. Conclusions The results demonstrate that pSB4C5 has a significantly higher copy number than specified, of the same magnitude as pSB3C5. We are confident to conclude that the copy number regulation of pSB4C5 is broken. This conclusion can be expanded to the other pSB4x5 backbones, since they all share the I50042 origin of replication. Casual observations also support this result. The classic pSB4C5, and most likely the whole pSB4x5 series, are not low copy backbones as specified in the registry. They should not be used as low copy backbones. A possible future use of the pSB4x5 series is as a middle copy backbone that is compatible with the existing pSB3x5 (with p15A ori), something that is certainly useful from a syntetic biology standpoint. |
|
••••• |
When miniprepped, pSB4K5-I52002 gives high miniprep yield similar to a high copy plasmid. I also successfully used this plasmid to clone 3 constructs that I could not assemble using either pSB1AC3 or pSB3K5. (I think the lower copy number of the plasmid was key to this construction working.) |
UNIQ557e73436e243048-partinfo-00000006-QINU

