Difference between revisions of "Plasmid backbones"
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
|'''[[Help:Plasmids|Help]]''': Have questions about plasmid backbones? Want to know how to enter new plasmid backbones into the Registry, how to build new BioBrick® plasmid backbones, or how to name new BioBrick® plasmid backbones? See the help pages for more information. | |'''[[Help:Plasmids|Help]]''': Have questions about plasmid backbones? Want to know how to enter new plasmid backbones into the Registry, how to build new BioBrick® plasmid backbones, or how to name new BioBrick® plasmid backbones? See the help pages for more information. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 04:00, 10 September 2008
Plasmids are circular, double-stranded DNA molecules typically containing a few thousand base pairs that replicate within the cell independently of the chromosomal DNA. Plasmid DNA is easily purified from cells, manipulated using common lab techniques and incorporated into cells. Most BioBrick parts in the Registry are maintained and propagated on plasmids. Thus, construction of BioBrick parts, devices and systems usually requires working with plasmids.
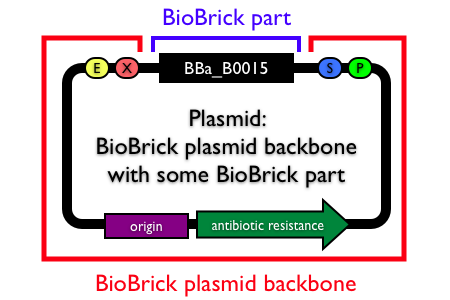
Note: In the Registry, plasmids are made up of two distinct components:
- the BioBrick part, device or system that is located in the BioBrick cloning site, between (and excluding) the BioBrick prefix and suffix.
- the plasmid backbone which propagates the BioBrick part. The plasmid backbone is defined as the sequence beginning with the BioBrick suffix, including the replication origin and antibiotic resistance marker, and ending with the BioBrick prefix. [Note that the plasmid backbone itself can be composed of BioBrick parts.]
Many BioBrick parts in the Registry are maintained on more than one plasmid backbone!
There are many different types of plasmids backbones and parts that compose plasmid backbones in the Registry. Here we've tried to collect all the plasmid backbones and plasmid parts into one place for easy browsing and retrieval.
| Assembly: Are you trying to assemble two BioBrick® parts together? There are a set of plasmid backbones available designed to make assembly of BioBrick® parts easier. | |
| Assembly of protein fusions: Are you trying to do an in-frame assembly of two protein domains? There are a set of plasmid backbones available designed to make assembly of protein domains easier. | |
| Measurement: Are you interested in measuring the behavior of a BioBrick® promoter, ribosome binding site, or transcriptional inverter? Jason Kelly has designed various plasmid backbones to streamline the process of part characterization so that you can compare your results to those that others have gotten. | |
| System operation: Oftentimes, it pays to use a different set of plasmid backbones for operating or running your BioBrick® device or system than you use for assembly. For example, high copy plasmid backbones are great for getting good DNA yields when doing plasmid purification. High DNA yields are helpful when assembling parts. However, some BioBrick® devices and systems consume too many resources when operated on a high copy plasmid backbone and significantly impact cell growth. In those cases, you might want to switch to a low or medium copy plasmid backbone. | |
| Building new BioBrick® vectors: Sometimes there just isn't a plasmid backbone already available that has the replication origin and antibiotic resistance marker that you want. In that case, you might need to build a new BioBrick® plasmid backbone. But you don't need to start from scratch. Here are a set of BioBrick® parts that might help you in building a new BioBrick® plasmid backbone. | |
| BioBrick® friendly plasmids: Some Registry contributors have built plasmids that don't strictly comply with the BioBrick® assembly standard, but still can accept BioBrick® parts. Therefore, they might be useful to you. Check out those plasmids here. | |
| Non-BioBrick® plasmids: Some Registry contributors have built plasmids that do not comply with the BioBrick® standard, but still might be useful to you. Check out those plasmids here. | |
| Archive: Older plasmid backbones that have been replaced by new versions of BioBrick® plasmid backbones. | |
| Help: Have questions about plasmid backbones? Want to know how to enter new plasmid backbones into the Registry, how to build new BioBrick® plasmid backbones, or how to name new BioBrick® plasmid backbones? See the help pages for more information. |
References
<biblio>
- MolecularCloning isbn=0-87969-577-3
- Anderson-Annu-Rev-Microbiol-1968 pmid=4879515
- Cohen-Proc-Natl-Acad-Sci-USA-1973a pmid=4576014
- Cohen-Proc-Natl-Acad-Sci-USA-1973b pmid=4594039
</biblio>
(This page is a work in progress. Thank you for your patience. If you have comments or questions, contact [http://openwetware.org/wiki/User:Reshma_P._Shetty Reshma Shetty])