Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2323002"
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
| − | [[Image:Bielefeld2012_ECOL3LFermentation.jpg|450px|thumb| | + | [[Image:Bielefeld2012_ECOL3LFermentation.jpg|450px|thumb|right|'''Figure 1:''' Fermentation of ''E. coli'' KRXwith <partinfo>BBa_K863005</partinfo> (ECOL) in an Infors Labfors Bioreactor, scale: 3 L, [http://2012.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Materials#Autoinduction_medium autoinduction medium] + 60 µg/mL chloramphenicol, 37 °C, pH 7, agitation on cascade to hold pO<sub>2</sub> at 50 %, OD<sub>600</sub> measured every 30 minutes.]] |
<p align="justify"> | <p align="justify"> | ||
Revision as of 15:18, 29 October 2017
TEV protease with N-terminal 6x His-Tag under the control of the pT7 promoter
Introduction
TEV protease is a highly specific cysteine protease from the Tobacco Etch Virus. An improvement over BBa_K1319008, the protease can be expressed in strains with T7-polymerase and then purified with the help of the His-TAg for synthetic in-vitro circuits.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 71
Illegal AgeI site found at 803 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Usage and Biology
The (+)-strand RNA genomes are often translated by the host to polyprotein precursors, which are then co-translationally cleaved by therefore provided proteases into the mature proteins. One of these proteases was found in the plant pathogenic Tobacco Etch Virus (TEV). For scientists the TEV protease is a molecular tool to cleave of all sorts of protein tags precisely due to its sequence specificity. It recognizes the amino acid sequence Glu-Asn-Leu-Tyr-Gln-Ser and cleaves then between glutamic acid and serine. In our project, the TEV protease is a main component in the Intein-Extein readout, but also was used in the purification procedure of our Cas13a proteins [http://www.jbc.org/content/277/52/50564.long].
For scientists the TEV protease is a molecular tool to cleave of all sorts of protein tags precisely due to its sequence specificity. It recognizes the amino acid sequence Glu-Asn-Leu-Tyr-Gln-Ser and cleaves then between glutamic acid and serine. In our project, the TEV protease is a main component in the Intein-Extein readout, but also was used in the purification procedure of our Cas13a proteins. We improved the Biobrick BBa_K1319008 by adding a 6x His-tag, which made it possible to purify this protease.
Cloning, expression and Purification
The His-tag was added to pSB1C3-BBa-K1319008 by PCR with overhang primers p-TEV-His-fwd and p-TEV-His-rev.
| Name | 5'-3' primers sequences |
|---|---|
| p-TEV-His-fwd | catcatcaccatcaccacgccggcggcgaaagc |
| p-TEV-His-rev | catctagtatttctcctctttctctagtatctccc |
After PCR we ligated the plasmid using the T4 ligase. This sample was then transformed in E. coli DH5&alpha for plasmid storage and E. coli BL21star for protein expression. We expressed the TEV protease in 2xYT medium and purified it via affinity and size exclusion chromatography.
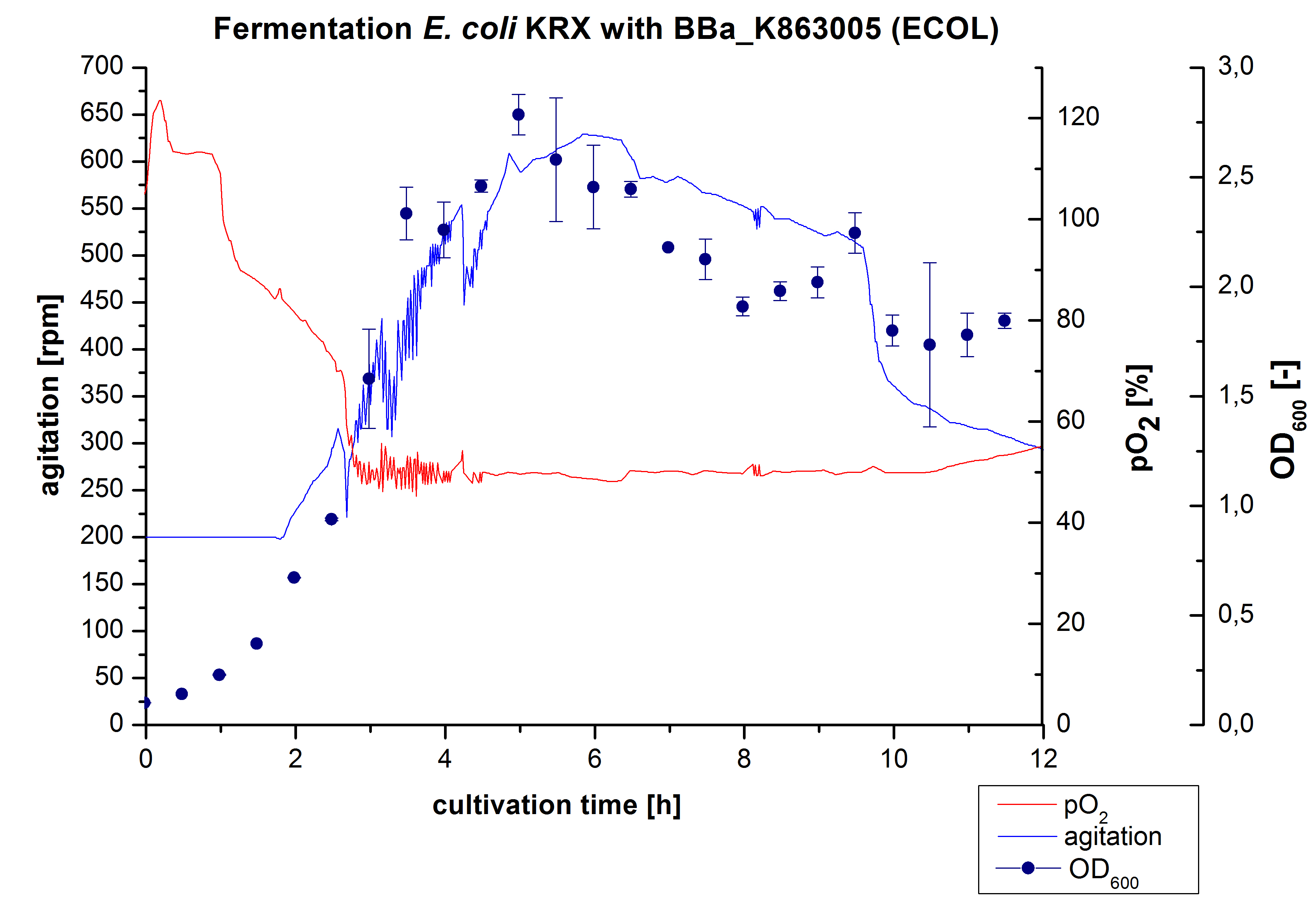
After the positive measurement of activity of ECOL we made a scale-up and fermented E. coli KRX with BBa_K863005 in an Infors Labfors fermenter with a total volume of 3 L. Agitation speed, pO2 and OD600 were determined and illustrated in Figure 1. The exponential phase started after 1.5 hours of cultivation. The cell growth caused a decrease in pO2. After 2 hours of cultivation the agitation speed increased up to 629 rmp (5.9 hours) to hold the minimal pO2 level of 50 %. Then, after 4 hours there was a break in cell growth due to induction of protein expression. The maximal OD600 of 2.78 was reached after 5 hours. In comparison to E. coli KRX (OD600,max =4.86 after 8.5 hours) and to E. coli KRX with BBa_K863000 (OD600,max =3.53 after 10 hours, time shift due to long lag phase) the OD600 max is lower. In the following hours, the OD600 and the agitation speed decreased and the pO2 increased, which indicates the death phase of the cells. This is caused by the cell toxicity of ECOL (reference: [http://www.dbu.de/OPAC/ab/DBU-Abschlussbericht-AZ-13191.pdf DBU final report]). Hence, cells were harvested after 12 hours.
