Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1150020"
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
With the help of the HA-tag we can proof the protein expression of our device. Through the usage of two NLS we send our fusion construct into the nucleus. Cotransfecting a RNA plasmid (BBa_K1150034) which includes the tracr and a separately integrated, desired crRNA, the Cas9 specifically binds to the requested DNA sequence. With the help of the transactivation domain of VP16 transcription factors are recruited and the pre-initiation complex can be build. Having targeted this device upstream of a promotor region, it is able to activate the gene of interest. | With the help of the HA-tag we can proof the protein expression of our device. Through the usage of two NLS we send our fusion construct into the nucleus. Cotransfecting a RNA plasmid (BBa_K1150034) which includes the tracr and a separately integrated, desired crRNA, the Cas9 specifically binds to the requested DNA sequence. With the help of the transactivation domain of VP16 transcription factors are recruited and the pre-initiation complex can be build. Having targeted this device upstream of a promotor region, it is able to activate the gene of interest. | ||
| − | [[File:Picture1VP16-Cas_Freigem2013.png]] | + | [[File:Picture1VP16-Cas_Freigem2013.png|700px|]] |
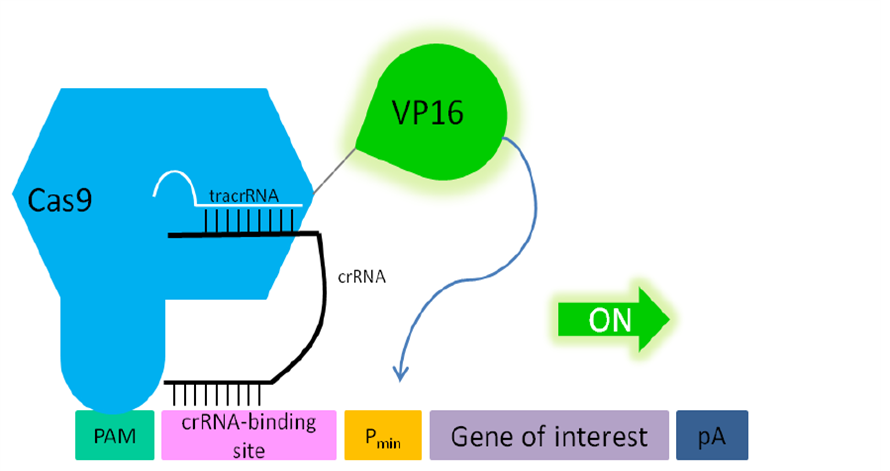
'''Fig. 1: Functionality of the fusion protein Cas9-VP19 (BBa_K1150020) for activating gene expression in mammalian cells.''' The double mutated Cas9 (D10A; H840A) fused to the herpes simplex virus (HSV) derived VP16 activation domain can serve as an crRNA-guided DNA-binding and transactivating protein. If a PAM sequence is present at the 5’ end of crRNA binding site nearly any DNA sequence can be targeted. | '''Fig. 1: Functionality of the fusion protein Cas9-VP19 (BBa_K1150020) for activating gene expression in mammalian cells.''' The double mutated Cas9 (D10A; H840A) fused to the herpes simplex virus (HSV) derived VP16 activation domain can serve as an crRNA-guided DNA-binding and transactivating protein. If a PAM sequence is present at the 5’ end of crRNA binding site nearly any DNA sequence can be targeted. | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
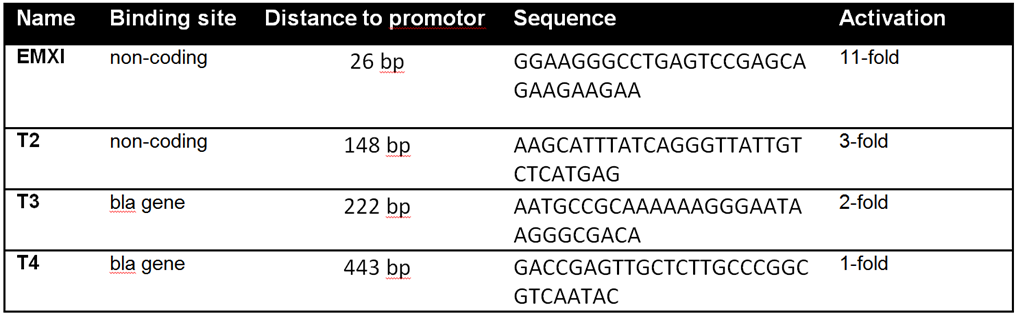
'''Table 1:''' Overview of the tested crRNAs with different binding sites on the SEAP plasmid. | '''Table 1:''' Overview of the tested crRNAs with different binding sites on the SEAP plasmid. | ||
| − | |||
| − | [[File:Activation_targets_on_SEAP_plasmid_Freigem_2013.png]] | + | [[File:CrRNAs_for_activation_Cas-VP16_Freigem2013.png|700px|]] |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Activation_targets_on_SEAP_plasmid_Freigem_2013.png|700px|]] | ||
| + | |||
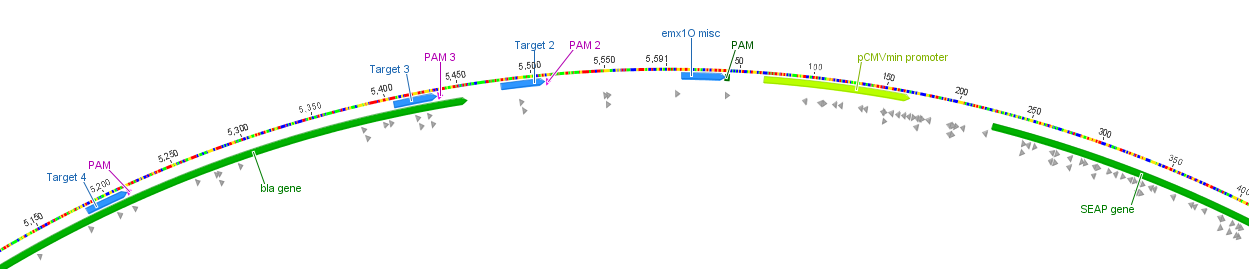
'''Figure 2:''' Position of the target loci on the SEAP plasmid. | '''Figure 2:''' Position of the target loci on the SEAP plasmid. | ||
| Line 54: | Line 56: | ||
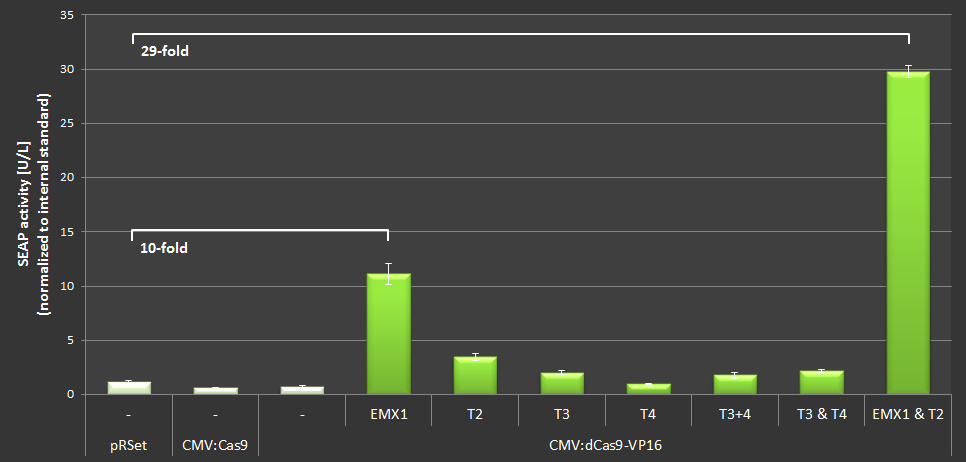
The results are listed in Figure 3. We gained up to 21-fold expression of SEAP in comparison to the basic expression rate using the EMXI and T2 simultaniously. | The results are listed in Figure 3. We gained up to 21-fold expression of SEAP in comparison to the basic expression rate using the EMXI and T2 simultaniously. | ||
| − | [[File:CMV-Cas-VP16_Results_Freigem2013.png]] | + | [[File:CMV-Cas-VP16_Results_Freigem2013.png|900px|]] |
| − | Figure 3: Results of the SEAP-activation with Cas-VP16 under the CMV promotor using different crRNAs. | + | '''Figure 3:''' Results of the SEAP-activation with Cas-VP16 under the CMV promotor using different crRNAs. |
Table | Table | ||
Revision as of 21:59, 30 September 2013
uniCAS Activator (CMV promoter)
| [CMV] Cas9-VP16 | |
|---|---|
| Function | gene activation |
| Use in | Mammalian cells |
| RFC standard | RFC 10, RFC 25 compatible |
| Backbone | pSB1C3 |
| Submitted by | [http://2013.igem.org/Team:Freiburg Freiburg 2013] |
We designed a fusion protein consisting of Cas9 and VP16 in order to gain a sequence-specific transactivation of a desired target locus. Therefore we used our double mutated Cas9 (without any cleavage function) and fused it C’terminal with the transactivation domain of VP16.
The whole device includes the CMV promotor, the HA-tag, one N’-terminal NLS, the double-mutated Cas9, a linker of 3 aminoacids, the activation domain of VP16, one C’-terminal NLS and the BGH terminator.
With the help of the HA-tag we can proof the protein expression of our device. Through the usage of two NLS we send our fusion construct into the nucleus. Cotransfecting a RNA plasmid (BBa_K1150034) which includes the tracr and a separately integrated, desired crRNA, the Cas9 specifically binds to the requested DNA sequence. With the help of the transactivation domain of VP16 transcription factors are recruited and the pre-initiation complex can be build. Having targeted this device upstream of a promotor region, it is able to activate the gene of interest.
Fig. 1: Functionality of the fusion protein Cas9-VP19 (BBa_K1150020) for activating gene expression in mammalian cells. The double mutated Cas9 (D10A; H840A) fused to the herpes simplex virus (HSV) derived VP16 activation domain can serve as an crRNA-guided DNA-binding and transactivating protein. If a PAM sequence is present at the 5’ end of crRNA binding site nearly any DNA sequence can be targeted. Abbr.: Pmin: minimal promoter, containing minimal requirements for binding of transcription factors; Cas9: CRISPR associated protein 9; crRNA: CRISPR RNA; tracrRNA: trans-activating RNA; VP16: Virus protein 16, herpes simplex virus (HSV)-derived transcriptional activator protein; PAM: protospacer adjacent motif.
Usage and Biology
For testing of our standardized device we used HEK394Tcells. We seeded the cells in 24-well plates with 65000 cells/well. After 24 hour we transfected them with a total amount of 0.75 µg DNA and renewed the media 7.5 hours after transfection. 48 hours after transfection we harvested the cells. With the supernatant we measured the expressed and secreted SEAP amount. With the cell lysate we performed a Western blot. Different crRNAs were tested in order to find best activation sides for our used reporter plasmid including SEAP under the control of a CMVmin promotor.
Proof of function
With BBa_K1150020 different target loci has been tested on a SEAP plasmid with a minimal CMV promotor. The target sides were determined through the differently used crRNAs consisting of 30 bp length, respectively. T2 (BBa_K1150035), EMXI (BBa_K1150040), T3 (BBa_K1150041) & T4 (BBa_K1150042) with various distances to the promotor regions were proofed as potential activation sides, see Table 1 and Figure 2.
Table 1: Overview of the tested crRNAs with different binding sites on the SEAP plasmid.
Figure 2: Position of the target loci on the SEAP plasmid.
As read-out we measured the amount of SEAP expression after activation with the BBa_K1150020 and the different crRNAs in comparison to the basis-SEAP-level under the CMVmin Promotor. We performed biological triplicates of each test.
The results are listed in Figure 3. We gained up to 21-fold expression of SEAP in comparison to the basic expression rate using the EMXI and T2 simultaniously.
Figure 3: Results of the SEAP-activation with Cas-VP16 under the CMV promotor using different crRNAs.
Table
Proof of expression
With the help of the HA-tag we performed Western blots to verify the expression of BBa_K1150020 and to estimate its expression rate.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 576
Illegal BglII site found at 900 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]