Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K864401"
(rollbackEdits.php mass rollback) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | __NOTOC__ | |
| + | <partinfo>BBa_K864401 short</partinfo> | ||
| + | |||
| + | aeBlue is a blue chromoprotein extracted from the basal disk of a beadlet anemone ''Actinia equina''. The protein has an absorption maximum at 597nm and a deep blue colour. The protein aeBlue has significant sequence homologies with proteins in the GFP family. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Source=== | ||
| + | The protein was first extracted and characterized by Shkrob et. al. 2005 under the name aeCP597. This version is codon optimized for '' E coli'' by Bioneer Corp. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Below to the left is the expressed aeBlue in ''E coli''. To the right comparison of aeBlue with other chromoproteins available from the registry. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Aeblue_plate_small.jpg.png|360px]] | ||
| + | [[Image:UUChromo.jpg|500px]] | ||
| + | <br>'''iGEM12_Uppsala_University:''' ''Left picture:'' Visual color expression of aeBlue(<partinfo>BBa_K864401</partinfo>). | ||
| + | ''Right picture:'' The Uppsala chromoprotein collection and RFP. Pellets of bacteria expressing chromoproteins eforRed (<partinfo>BBa_K592012</partinfo>), RFP (<partinfo>BBa_E1010</partinfo>), cjBlue (<partinfo>BBa_K592011</partinfo>), aeBlue (<partinfo>BBa_K864401</partinfo>), amilGFP (<partinfo>BBa_K592010</partinfo>) and amilCP (<partinfo>BBa_K592009</partinfo>). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Getting this part=== | ||
| + | All chromoproteins displayed above should be available, but if the registry cannot send them, feel free to contact the Uppsala University team directly via erik.gullberg(at)imbim.uu.se, and we will send them to you. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1316306/]Shkrob, M.A., Yanushevich, Y.G., Chudakov, D.M., Gurskaya, N.G., Labas, Y.A., Poponov, S.Y., Mudrik, N.N., Lukyanov, S., Lukyanov, K.A., 2005. Far-red fluorescent proteins evolved from a blue chromoprotein from Actinia equina. Biochem. J. 392, 649–654. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | ||
| + | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- --> | ||
| + | <span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | ||
| + | <partinfo>BBa_K864401 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- Uncomment this to enable Functional Parameter display | ||
| + | ===Functional Parameters=== | ||
| + | <partinfo>BBa_K864401 parameters</partinfo> | ||
| + | <!-- --> | ||
Revision as of 16:18, 10 May 2013
aeBlue blue chromoprotein
aeBlue is a blue chromoprotein extracted from the basal disk of a beadlet anemone Actinia equina. The protein has an absorption maximum at 597nm and a deep blue colour. The protein aeBlue has significant sequence homologies with proteins in the GFP family.
Source
The protein was first extracted and characterized by Shkrob et. al. 2005 under the name aeCP597. This version is codon optimized for E coli by Bioneer Corp.
Below to the left is the expressed aeBlue in E coli. To the right comparison of aeBlue with other chromoproteins available from the registry.
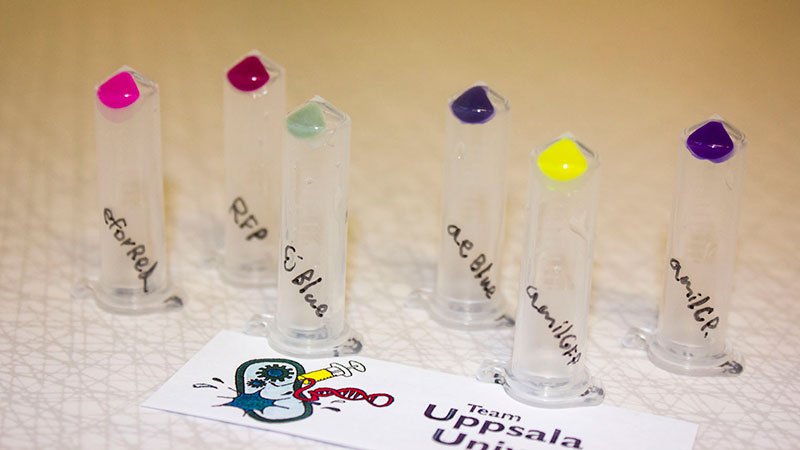
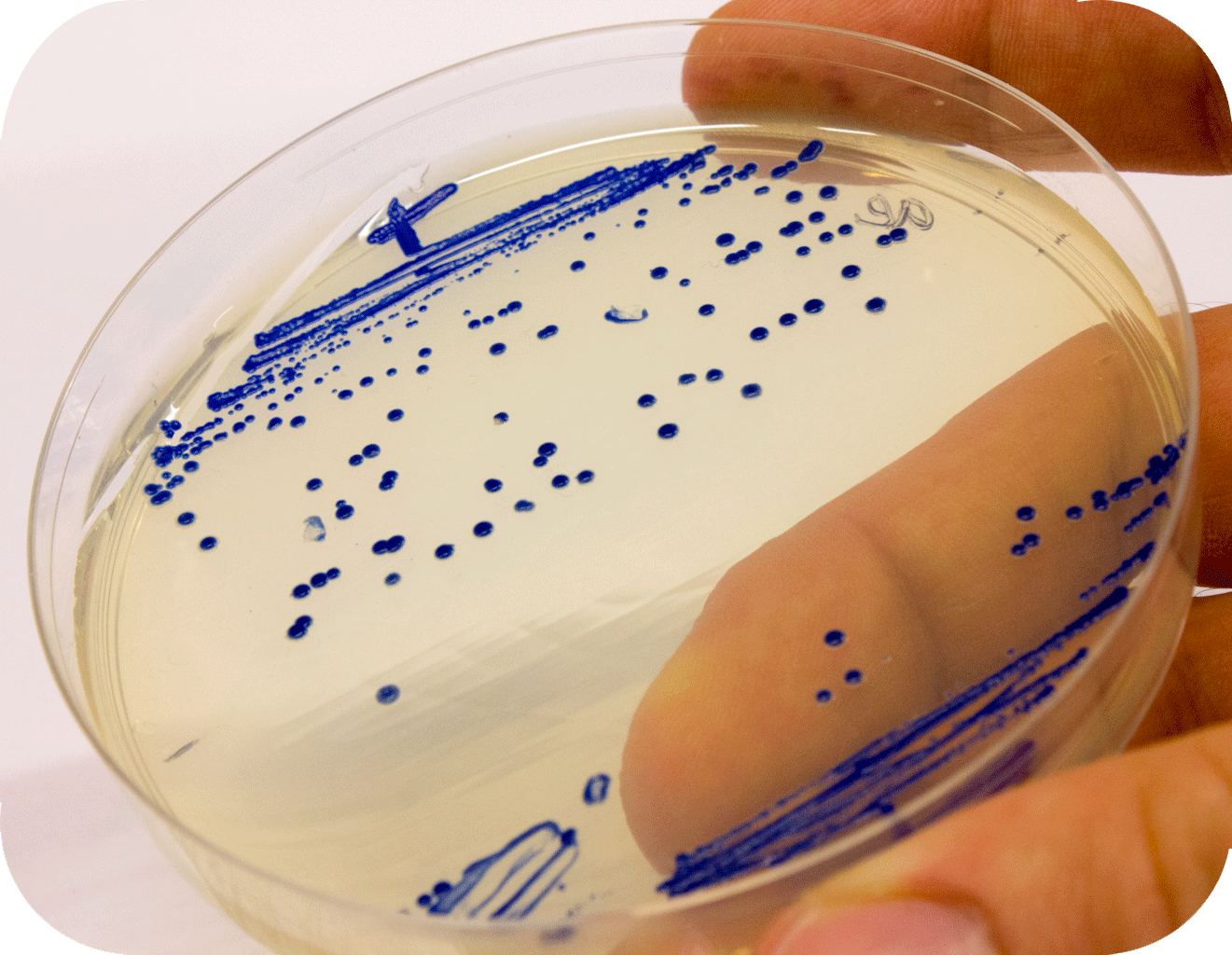

iGEM12_Uppsala_University: Left picture: Visual color expression of aeBlue(BBa_K864401).
Right picture: The Uppsala chromoprotein collection and RFP. Pellets of bacteria expressing chromoproteins eforRed (BBa_K592012), RFP (BBa_E1010), cjBlue (BBa_K592011), aeBlue (BBa_K864401), amilGFP (BBa_K592010) and amilCP (BBa_K592009).
Getting this part
All chromoproteins displayed above should be available, but if the registry cannot send them, feel free to contact the Uppsala University team directly via erik.gullberg(at)imbim.uu.se, and we will send them to you.
References
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1316306/]Shkrob, M.A., Yanushevich, Y.G., Chudakov, D.M., Gurskaya, N.G., Labas, Y.A., Poponov, S.Y., Mudrik, N.N., Lukyanov, S., Lukyanov, K.A., 2005. Far-red fluorescent proteins evolved from a blue chromoprotein from Actinia equina. Biochem. J. 392, 649–654.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
