Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa C0062"
Carolinarp (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
For the biobrick Part BBa_C0062, there was a 0% of identity match and 0% similarity match to the top allergens in the allergen database. This means that the biobrick part is not of potential allergen status. In 80 amino acid alignments by FASTA window, no matches found that are greater than 35% for this biobrick. This also means that there is not of potential allergen status. | For the biobrick Part BBa_C0062, there was a 0% of identity match and 0% similarity match to the top allergens in the allergen database. This means that the biobrick part is not of potential allergen status. In 80 amino acid alignments by FASTA window, no matches found that are greater than 35% for this biobrick. This also means that there is not of potential allergen status. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | >Internal Priming Screening Characterization of BBa_C0062: Has 1 possible internal priming site between this BioBrick part and the VR primer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The 2018 Hawaii iGEM team evaluated the 40 most frequently used BioBricks and ran them through an internal priming screening process that we developed using the BLAST program tool. Out of the 40 BioBricks we evaluated, 10 of them showed possible internal priming of either the VF2 or VR primers and sometime even both. The data set has a range of sequence lengths from as small as 12 bases to as large as 1,210 bases. We experienced the issue of possible internal priming during the sequence verification process of our own BBa_K2574001 BioBrick and in the cloning process to express the part as a fusion protein. BBa_K2574001 is a composite part containing a VLP forming Gag protein sequence attached to a frequently used RFP part (BBa_E1010). We conducted a PCR amplification of the Gag-RFP insert using the VF2 and VR primers on the ligation product (pSB1C3 ligated to the Gag + RFP). This amplicon would serve as template for another PCR where we would add the NcoI and BamHI restriction enzyme sites through new primers for ligation into pET14b and subsequent induced expression. Despite gel confirming a rather large, approximately 2.1 kb insert band, our sequencing results with the VR primer and BamHI RFP reverse primer gave mixed results. Both should have displayed the end of the RFP, but the VR primer revealed the end of the Gag. Analysis of the VR primer on the Gag-RFP sequence revealed several sites where the VR primer could have annealed with ~9 - 12 bp of complementarity. Internal priming of forward and reverse primers can be detrimental to an iGEM project because you can never be sure if the desired construct was correctly inserted into the BioBrick plasmid without a successful sequence verification. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For the BioBrick part BBa_C0062, the first location of the internal priming site is on the 628-634 base number of the BioBrick and on the 14-20 base number of the VR primer. | ||
| + | |||
==Contribution: SiCAU-China 2017== | ==Contribution: SiCAU-China 2017== | ||
Revision as of 03:20, 18 October 2018
luxR repressor/activator, (no LVA?)
In complex with HSL, LuxR binds to the Lux promoter, activating transcription from Pr BBa_R0062, and repressing transcription from Pl BBa_R0063.
The lux cassette of V. fischeri contains a left and a right promoter. The right promoter gives weak constitutive expression of downstream genes.This expression is up-regulated by the action of the Lux activator, LuxR complexed to HSL. Two molecules of LuxR protein form a complex with two molecules the signalling compound homoserine lactone (HSL). This complex binds to a palindromic site on the promoter, increasing the rate of transcription.
Usage and Biology
We improved this part by using it in a part which allows for the constitutive expression of LuxR (BBa_K1893004). This part also includes the pLux promoter, so that genes placed downstream the promoter will be expressed when induced with 3OC6-AHL. We also made a part which allows for the characterisation of LuxR, as we placed GFP downstream the pLux promoter (BBa_K1893005). The part is currently being characterised.
Unspecified.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
- Allergen characterization of BBa_C0062: Not a potential allergen
The Baltimore Biocrew 2017 team discovered that proteins generated through biobrick parts can be evaluated for allergenicity. This information is important to the people using these parts in the lab, as well as when considering using the protein for mass production, or using in the environment. The allergenicity test permits a comparison between the sequences of the biobrick parts and the identified allergen proteins enlisted in a data base.The higher the similarity between the biobricks and the proteins, the more likely the biobrick is allergenic cross-reactive. In the full-length alignments by FASTA, 30% or more amount of similarity signifies that the biobrick has a Precaution Status meaning there is a potential risk with using the part. A 50% or more amount of identity signifies that the biobrick has a Possible Allergen Status. In the sliding window of 80 amino acid segments, greater than 35% signifies similarity to allergens. The percentage of similarity implies the potential of harm biobricks’ potential negative impact to exposed populations. For more information on how to assess your own biobrick part please see the “Allergenicity Testing Protocol” in the following page http://2017.igem.org/Team:Baltimore_Bio-Crew/Experiments
For the biobrick Part BBa_C0062, there was a 0% of identity match and 0% similarity match to the top allergens in the allergen database. This means that the biobrick part is not of potential allergen status. In 80 amino acid alignments by FASTA window, no matches found that are greater than 35% for this biobrick. This also means that there is not of potential allergen status.
>Internal Priming Screening Characterization of BBa_C0062: Has 1 possible internal priming site between this BioBrick part and the VR primer.
The 2018 Hawaii iGEM team evaluated the 40 most frequently used BioBricks and ran them through an internal priming screening process that we developed using the BLAST program tool. Out of the 40 BioBricks we evaluated, 10 of them showed possible internal priming of either the VF2 or VR primers and sometime even both. The data set has a range of sequence lengths from as small as 12 bases to as large as 1,210 bases. We experienced the issue of possible internal priming during the sequence verification process of our own BBa_K2574001 BioBrick and in the cloning process to express the part as a fusion protein. BBa_K2574001 is a composite part containing a VLP forming Gag protein sequence attached to a frequently used RFP part (BBa_E1010). We conducted a PCR amplification of the Gag-RFP insert using the VF2 and VR primers on the ligation product (pSB1C3 ligated to the Gag + RFP). This amplicon would serve as template for another PCR where we would add the NcoI and BamHI restriction enzyme sites through new primers for ligation into pET14b and subsequent induced expression. Despite gel confirming a rather large, approximately 2.1 kb insert band, our sequencing results with the VR primer and BamHI RFP reverse primer gave mixed results. Both should have displayed the end of the RFP, but the VR primer revealed the end of the Gag. Analysis of the VR primer on the Gag-RFP sequence revealed several sites where the VR primer could have annealed with ~9 - 12 bp of complementarity. Internal priming of forward and reverse primers can be detrimental to an iGEM project because you can never be sure if the desired construct was correctly inserted into the BioBrick plasmid without a successful sequence verification.
For the BioBrick part BBa_C0062, the first location of the internal priming site is on the 628-634 base number of the BioBrick and on the 14-20 base number of the VR primer.
Contribution: SiCAU-China 2017
Authors:Wenwen Lin
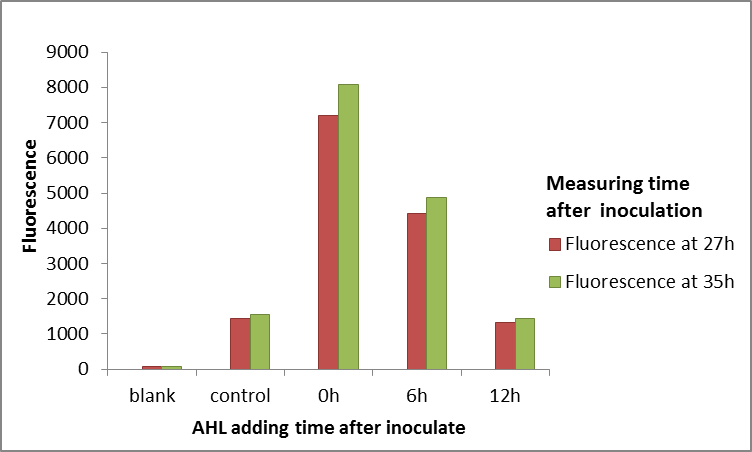
Summary:The QS system LuxR/LuxI has been widely used in kinds of logic circuit. But this year we find that LuxR can not always work well in E.coli. The LuxR, in E.coli, will not work when E.coli enter into stationary phase. This characteristic may be useful to users who will use LuxR as an activating transcription. (more details)
Contribution
Group: Valencia_UPV iGEM 2018
Author: Adrián Requena Gutiérrez, Carolina Ropero
Summary:
We adapted the part to be able to assemble transcriptional units with the Golden Gate assembly method
Documentation: