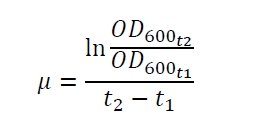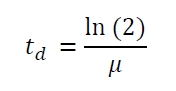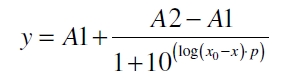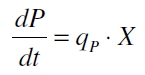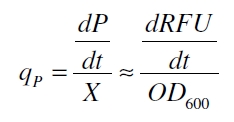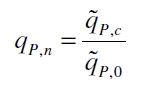Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K389016:Experience"
(→Transfer function of K389016) |
(→Different possible inducers) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
====Transfer function of <partinfo>K389016</partinfo>==== | ====Transfer function of <partinfo>K389016</partinfo>==== | ||
| − | The data for the transfer function was measured and analyzed as [[Part:BBa_K389016:Experience#Data analysis for BBa_K389016 | described below]]. | + | The data for the transfer function was measured and analyzed as [[Part:BBa_K389016:Experience#Data analysis for BBa_K389016 | described below]]. Nelson ''et al'' suggests using a dose response function and fitting it with a logistical equation for the data analysis of receptor systems ([http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v416/n6877/abs/nature726.html Nelson ''et al.'', 2002]). The data was fitted with a function of the form |
| Line 176: | Line 176: | ||
====Different possible inducers==== | ====Different possible inducers==== | ||
| − | A list of | + | A list of tested possible inducers for a VirA/G signaling system is shown in tab. 4. These inducers where tested as a mix. The specific production rate of mRFP q<sub>P</sub> measured as described [[Part:BBa_K389016:Experience#Data analysis for BBa_K389016| above]] for the mix did not significantly differ from the synthesis rate of the uninduced system (t-Test, p < 0.005). So none of the possible inducers listet in tab. 4 induce the VirA/G signaling system significantly in the measured concentration range. In tab. 4 the chemical structures of the tested possible inducers are shown, too. Acetosyringone is also in tab. 4 although it was not tested in the inducer mix to show the chemical similarity of the tested possible inducers to the natural inducer of the VirA/G signaling system. |
<center> | <center> | ||
| − | Table 4: | + | Table 4: Tested possible inducers for a VirA/G signaling system and acetosyringone with concentrations and chemical structure that were tested. |
{|cellpadding="10" style="border-collapse: collapse; border-width: 1px; border-style: solid; border-color: #000" | {|cellpadding="10" style="border-collapse: collapse; border-width: 1px; border-style: solid; border-color: #000" | ||
| Line 251: | Line 251: | ||
Chu D, Zabet NR, Mitavskiy B (2009) [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6WMD-4V42JG5-1&_user=10&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=b6431553217aca1129c5b441f4b78425 Models of transcription factor binding: Sensitivity of activation functions to model assumptions], ''J Theor Biol'' 257(3):419-429. | Chu D, Zabet NR, Mitavskiy B (2009) [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6WMD-4V42JG5-1&_user=10&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=b6431553217aca1129c5b441f4b78425 Models of transcription factor binding: Sensitivity of activation functions to model assumptions], ''J Theor Biol'' 257(3):419-429. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Greg Nelson, Jayaram Chandrashekar, Mark A. Hoon, Luxin Feng, Grace Zhao, Nicholas J. P. Ryba & Charles S. Zuker (2002) ''[http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v416/n6877/abs/nature726.html An amino-acid taste receptor ]'', Nature 416: 199-202. | ||
Pasotti L, Zucca S, Del Fabbro E (2009) Characterization experiment on BBa_J23100, BBa_J23101, BBa_J23118, https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_J23101:Experience. | Pasotti L, Zucca S, Del Fabbro E (2009) Characterization experiment on BBa_J23100, BBa_J23101, BBa_J23118, https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_J23101:Experience. | ||
[http://web.plasmidfactory.com/en/service_CGE.html PlasmidFactory] | [http://web.plasmidfactory.com/en/service_CGE.html PlasmidFactory] | ||
| − | |||
===User Reviews=== | ===User Reviews=== | ||
Latest revision as of 00:36, 28 October 2010
This experience page is provided so that any user may enter their experience using this part.
Please enter
how you used this part and how it worked out.
Applications of BBa_K389016
Growth functions and mRFP expression for BBa_K389016
To characterize this part we performed several cultivations with different concentrations of [http://www.chemblink.com/products/2478-38-8.htm acetosyringone] as inducer and measured the fluorescence emitted by mRFP (Protocol). We used Escherichia coli DB3.1 carrying the pSB1C3::K389016 plasmid. Even without inducer the bacteria carrying the plasmid showed decelerated growth. In addition acetosyringone affected the growth rates (we used a stocksolution of 20 mM acetosyringone solved in 10 % (v/v) DMSO). Growth curves, averaged specific growth rates and doubling times are shown below. It can be observed, that E. coli carrying the pSB1C3::K389016 plasmid growths nearly linear.
The specific growth rates µ and doubling times td are calculated with the OD600 and following formulas:
Table 1: Averaged specific growth rates and doubling times for cultivations of E. coli DB3.1 without plasmid and carrying BBa_K389016 with different acetosyringone concentrations in LB medium with 10 mg ml-1 chloramphenicol.
| E. coli DB3.1 | µ / h-1 | td / h |
|---|---|---|
| without plasmid | 0.35 | 1.98 |
| carrying K389016 | 0.27 | 2.57 |
| carrying K389016 with 150 µM acetosyringone | 0.25 | 2.77 |
| carrying K389016 with 1000 µM acetosyringone | 0.23 | 3.01 |
Exemplary induction curves with the fluorescence normalized to OD600 are shown in fig. 2. We observed a basal transcription, but the induction with acetosyringone is undoubtedly. The detailed data analysis and transfer function is described below.
Transfer function of BBa_K389016
The data for the transfer function was measured and analyzed as described below. Nelson et al suggests using a dose response function and fitting it with a logistical equation for the data analysis of receptor systems ([http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v416/n6877/abs/nature726.html Nelson et al., 2002]). The data was fitted with a function of the form
with the Hill coefficient p, the bottom asymptote A1, the top asymptote A2 and the switch point log(x0). Figure 3 shows the measured normalized specific production rates qP,n (eq. 10) plotted against the logarithm of the concentration of the inductor [http://www.chemblink.com/products/2478-38-8.htm acetosyringone] in µM. The fit has an R2 = 0.99.
The important data from the transfer function is summarized in table 2:
Table 2: Data from the transfer function for the part BBa_K389016.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Hill coefficient | 1.673 |
| Switch point | 26.5 µM |
| Top asymptote | 2.62 |
So the fully induced VirA/G signaling system has a 2.6 fold increased expression compared to the uninduced system. The Hill coefficient is > 1, so a positive cooperation can be observed ([http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6WMD-4V42JG5-1&_user=10&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=b6431553217aca1129c5b441f4b78425 D Chu et al., 2009]). The switch point of the system is at about 25 µM, so this is the concentration at which the device output is 50 % of the maximum output.
Data analysis for BBa_K389016
The data analysis is made in three steps. First step is the processing of the fluorescence raw data gained by the fluorescence plate reader for every sample:
In the second step the RFUcorrected of every sample is plotted against the cultivation time it was drawn. The data is fitted by an exponential fit of the following style:
The accumulation of mRFP in the cells is always exponential. A typical fitted product accumulation curve is shown below:
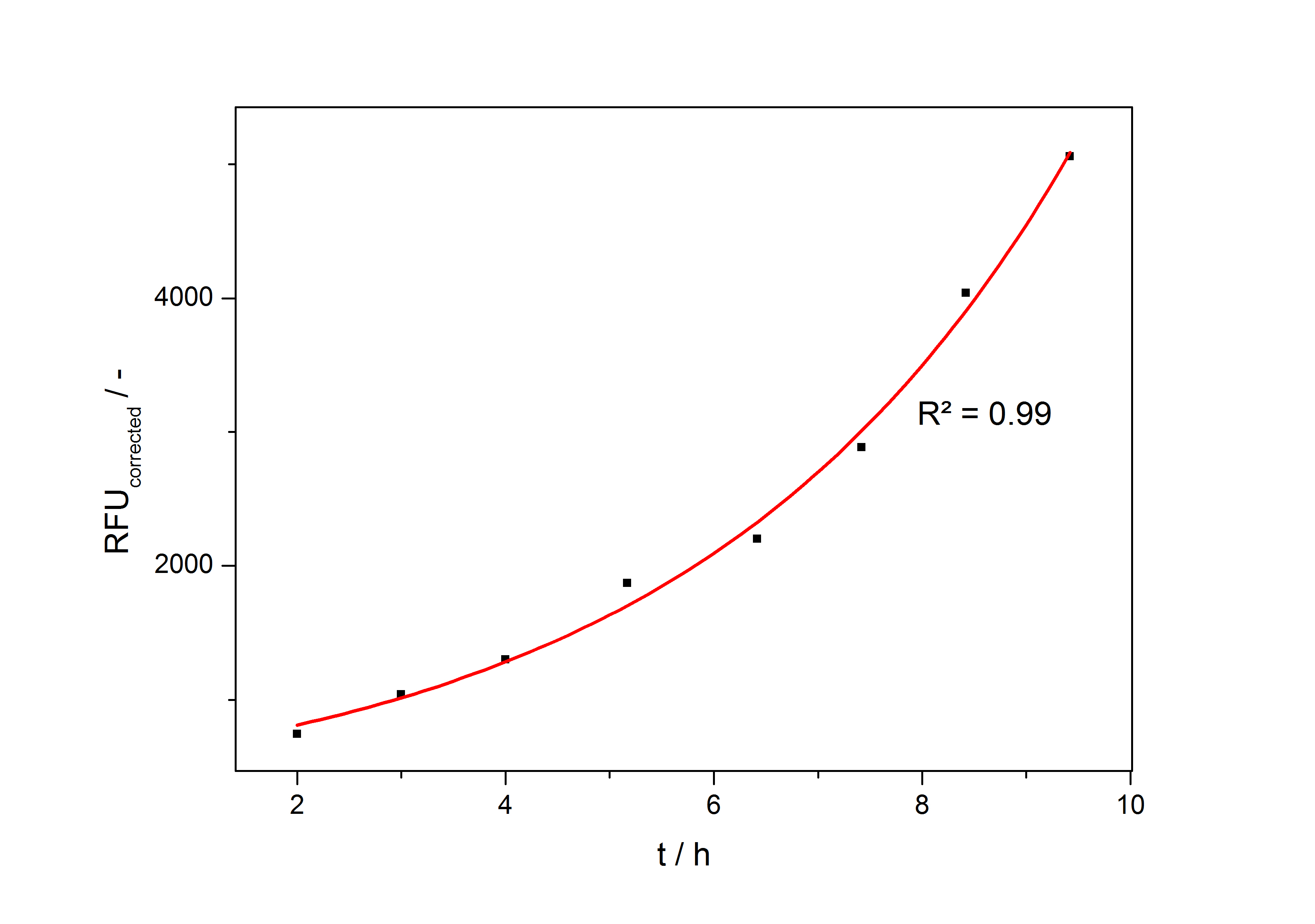
The product accumulation in a cultivation can be described as:
with the amount of product P, the cell count X and the specific production rate qP.
RFU is commensurate to the concentration of mRFP (P) and the OD600 is commensurate to the cell count (X) ( Canton and Labno, 2004):
With these assumptions it is possible to calculate the specific production rate of mRFP qP in the third step: the specific production rate for every sample of a cultivation is calculated by the derivation of the exponential fit line which describes the accumulation of product in the culture (dRFU/dt) and the measured OD600 data:
The specific production rates qP of all samples of all cultivations made with a specific inducer concentration c are averaged and normalized against the specific production rate of the uninduced system qP,0:
This normalized specific production rate we calculated is commensurate to relative promotor units (RPU) which is commensurate to PoPS (polymerase per seconds) (Canton and Labno, 2004; Pasotti et al., 2009):
Plasmid conformation analysis
A plasmid conformation analysis for the BioBrick BBa_K389016 in pSB1C3 was performed by the [http://web.plasmidfactory.com/de/ PlasmidFactory] by Capillary Gel Electrophoresis (CGE). The chromatogram is shown in fig. 5 and the results in tab. 3. The data shows a high percentage of covalently closed circular (ccc) plasmid DNA. This is the biological active shape of plasmids so a high percentage of ccc plasmid DNA indicates a high quality of plasmid DNA ([http://web.plasmidfactory.com/en/service_CGE.html PlasmidFactory]).
Table 3: Data from the CGE of the BioBrick BBa_K389016 in pSB1C3 performed by the [http://web.plasmidfactory.com/de/ PlasmidFactory] (Bielefeld).
| Conformation | Ratio / % |
|---|---|
| ccc monomer | 91.2 |
| ccc dimer | 3.2 |
| oc | 5.6 |
Different possible inducers
A list of tested possible inducers for a VirA/G signaling system is shown in tab. 4. These inducers where tested as a mix. The specific production rate of mRFP qP measured as described above for the mix did not significantly differ from the synthesis rate of the uninduced system (t-Test, p < 0.005). So none of the possible inducers listet in tab. 4 induce the VirA/G signaling system significantly in the measured concentration range. In tab. 4 the chemical structures of the tested possible inducers are shown, too. Acetosyringone is also in tab. 4 although it was not tested in the inducer mix to show the chemical similarity of the tested possible inducers to the natural inducer of the VirA/G signaling system.
Table 4: Tested possible inducers for a VirA/G signaling system and acetosyringone with concentrations and chemical structure that were tested.
| Inducer | Concentration / µM | Chemical structure |
|---|---|---|
| Capsaicin | 200 | 
|
| Dopamine | 200 | 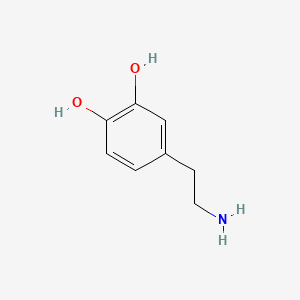
|
| Homovanillic acid | 200 | 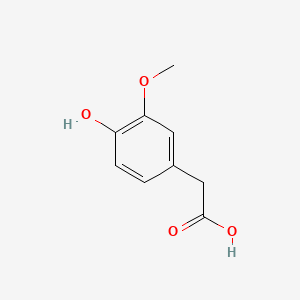
|
| 3-Methoxytyramine | 200 | 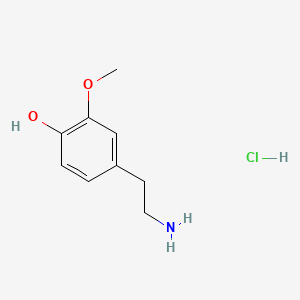
|
| Acetosyringone | 200 | 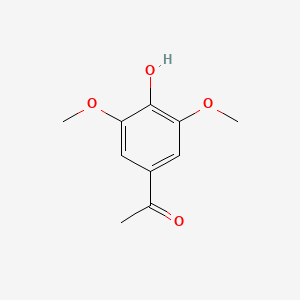
|
Protocols
Cultivation
- Inoculate 10 mL LB containing desired antibiotic with glycerol stock
- Cultivate over night at 37 °C and 175 rpm
- Measure the OD600
- Prepare shake flasks with LB, antibiotic and different concentrations of the inducer acetosyringone
- For mRFP measurement at least 20 mL starting volume
- Inoculate the main culture with a starting OD600 of 0.1
- Cultivate at 37 °C and 175 rpm
- Take a sample at least every hour and measure the OD600
Measurement
- Take at least 500 µL sample for each measurement (200 µL is needed for one measurement) so you can perform a repeat determination
- Freeze samples at -80 °C for storage
- To measure the samples thaw at room temperature and fill 200 µL of each sample in one well of a black, flat bottom 96 well microtiter plate (perform at least a repeat determination)
- Measure the fluorescence in a platereader (we used a Tecan Infinite® m200 platereader ) with following settings
- 20 sec orbital shaking (1 mm amplitude with a frequenzy of 87.6 rpm)
- Measurement mode: Top
- Excitation: 584 nm
- Emission: 620 nm
- Number of reads: 25
- Manual gain: 150
- Integration time: 20 µs
References
Canton B and Labno A (2004) Data processing of Part BBa_F2620.
Chu D, Zabet NR, Mitavskiy B (2009) [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6WMD-4V42JG5-1&_user=10&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=b6431553217aca1129c5b441f4b78425 Models of transcription factor binding: Sensitivity of activation functions to model assumptions], J Theor Biol 257(3):419-429.
Greg Nelson, Jayaram Chandrashekar, Mark A. Hoon, Luxin Feng, Grace Zhao, Nicholas J. P. Ryba & Charles S. Zuker (2002) [http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v416/n6877/abs/nature726.html An amino-acid taste receptor ], Nature 416: 199-202.
Pasotti L, Zucca S, Del Fabbro E (2009) Characterization experiment on BBa_J23100, BBa_J23101, BBa_J23118, https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_J23101:Experience.
[http://web.plasmidfactory.com/en/service_CGE.html PlasmidFactory]
User Reviews
UNIQacd19848e68c7cd1-partinfo-00000014-QINU UNIQacd19848e68c7cd1-partinfo-00000015-QINU