Difference between revisions of "Recombination/Saccharomyces cerevisiae-derived Flp-FRT"
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
===Recombinases=== | ===Recombinases=== | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | [[Part:BBa_K313002|BBa_K313002]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
<!-- <parttable>flp_recombinase_protein_coding_sequence </parttable> --> | <!-- <parttable>flp_recombinase_protein_coding_sequence </parttable> --> | ||
<!-- To include a part in this table, include the categories "//cds/enzyme/recombinase/flp" and set the part type to Coding under the Hard Information tab of the part. --> | <!-- To include a part in this table, include the categories "//cds/enzyme/recombinase/flp" and set the part type to Coding under the Hard Information tab of the part. --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Composite parts=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <parttable>flp_frt_recombination_composite_parts</parttable> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- To include a part in this table, include the categories "//function/recombination/flp" and make it a composite part under the Hard Information tab of the part. --> | ||
===References=== | ===References=== | ||
Latest revision as of 10:05, 3 November 2010
< Back to Recombination systems, DNA recombination sites, or Recombinases
| Chris Anderson, a professor of bioengineering at UC Berkeley, constructed the FRT recombination site BBa_J61020. |
The following text is excerpted from Huang et al. Huang. It has been edited for clarity.
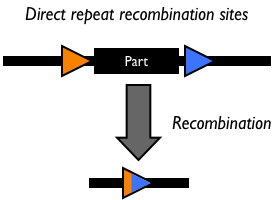
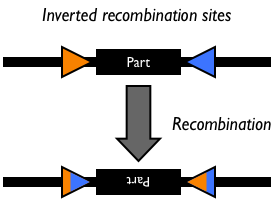
The FLP system of the yeast 2mm plasmid is one of the most attractive for genomic manipulation because of its efficiency, simplicity, and demonstrated in vivo activity in a wide range of organisms. The Flp system has been used to construct specific genomic deletions and gene duplications, study gene function, promote chromosomal translocations, promote site-specific chromosome cleavage, and facilitate the construction of genomic libraries in organisms including bacteria, yeast, insects, plants, mice, and humans. Site-specific recombination catalyzed by the FLP recombinase occurs readily in bacterial cells.
The yeast FLP system has been studied intensively (7, 8, 22, 36). The only requirements for FLP recombination are the FLP protein and the FLP recombination target (FRT) sites on the DNA substrates. The minimal functional FRT site contains only 34 bp. The FLP protein can promote both inter- and intramolecular recombination.
Recombination sites
| Name | Description | Sequence | Recombinase | Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBa_J61020 | [FRT] | . . . ttcctatactttttagagaataggaacttc | 34 | |
| BBa_J72001 | {FRT} recombination site for flp recombinase in BBb | . . . ttcctatactttctagagaataggaacttc | 36 |
Recombinases
Composite parts
| Name | Type | Description | Length | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBa_K551000 | Composite | FRT-CM-FRT | 837 | It's complicated |
| BBa_J61024 | Composite | [CmR][FRT] | 936 | It's complicated |
| BBa_J61025 | Composite | [FRT][CmR][FRT] | 978 | It's complicated |
| BBa_J61026 | Composite | [FRT][R6K] | 448 | It's complicated |
| BBa_J61027 | Composite | [FRT][R6K][CmR][FRT] | 1392 | It's complicated |
References
<biblio>
- Schweizer pmid=12736528
- Huang pmid=9324255
- Cherepanov pmid=7789817
- Cox pmid=6308608
- Fiering pmid=8378321
- Golic pmid=2509077
- Morris pmid=1945877
- Sadowski pmid=7659779
- Senecoff pmid=2997780
</biblio>