Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3071024"
Heimanleung (Talk | contribs) |
Heimanleung (Talk | contribs) (→Characterization) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K3071024 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K3071024 short</partinfo> | ||
===Description=== | ===Description=== | ||
| − | This composite part is the reporter construct that under the regulation of CBS I & II, which could be activated by pspF TAD-Clp upon DSF ligand binding. The upstream elements RpfC/RpfG (BBa_K3071022) is responsible for the sensing of diffusible signal factor (DSF) from Xanthomonas campestris pv. camperstris and signal transduction through phosphorylation. The co-activator psp TAD-Clp and sigma 54 (BBa_K3071023) are responsible for the activation of this composite part in response to the DSF binding. This part is one of the three parts used to construct our detection system in our part collection, the other two parts include ( | + | This composite part is the reporter construct that under the regulation of CBS I & II, which could be activated by pspF TAD-Clp upon DSF ligand binding. The upstream elements RpfC/RpfG (<html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3071022">BBa_K3071022</a></html>) is responsible for the sensing of diffusible signal factor (DSF) from Xanthomonas campestris pv. camperstris and signal transduction through phosphorylation. The co-activator psp TAD-Clp and sigma 54 (<html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3071023">BBa_K3071023</a></html>) are responsible for the activation of this composite part in response to the DSF binding. This part is one of the three parts used to construct our detection system in our part collection, the other two parts include (<html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3071022">BBa_K3071022</a></html>) and (<html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3071023">BBa_K3071023</a></html>). |
===Biology=== | ===Biology=== | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
<center><u> Figure 1 Basic properties of <i>gumB</i> UAS</u></center> | <center><u> Figure 1 Basic properties of <i>gumB</i> UAS</u></center> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | Clp binding sites (CBSs) ( | + | Clp binding sites (CBSs) (<html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3071011">BBa_K3071011</a></html>) and (<html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3071012">BBa_K3071012</a></html>)have typically been identified by pattern searching of the <i>Xanthomonas campestris</i> pv. <i>camperstris</i> genome using the consensus CRP binding sequence.Clp upregulates the gum operon by binding to two non-consensus sites. CBS I has a high GC content in the central region (6bp) that may be important for binding, and binding may be enhanced if the GC-rich central region is palindromic. |
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
Sigm54-RNA holoenzyme (σ-54 RNAP) ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3071010 BBa_K3071010])forms an inactive transcriptional initiation complex on this promoter, which can be activated in E. coli by the bacterial enhancer-binding protein PspF ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3071006 BBa_K3071006]). PspF functions by binding to the upstream activation sequences (UAS) near the promoter and contacting the promoter-bound σ-54 RNAP via DNA looping stabilized by the binding of integration host factor (IHF). Previous research has demonstrated the property of PspF-dependent and enhancer-specific transcription activation of pspA promoter. | Sigm54-RNA holoenzyme (σ-54 RNAP) ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3071010 BBa_K3071010])forms an inactive transcriptional initiation complex on this promoter, which can be activated in E. coli by the bacterial enhancer-binding protein PspF ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3071006 BBa_K3071006]). PspF functions by binding to the upstream activation sequences (UAS) near the promoter and contacting the promoter-bound σ-54 RNAP via DNA looping stabilized by the binding of integration host factor (IHF). Previous research has demonstrated the property of PspF-dependent and enhancer-specific transcription activation of pspA promoter. | ||
| − | In terms of gene structure, the -24 and -12 region is for the sigma 54-factor binding, with the -60 IHF interaction region and -129 to -89 UAS sequence I and II. The UAS sequence is replaced with the CBS I and CBS II UAS in <i>gumB</i> operon of <i>Xanthomonas campestris pv. camperstris</i>, to create a new synthetic promoter ( | + | In terms of gene structure, the -24 and -12 region is for the sigma 54-factor binding, with the -60 IHF interaction region and -129 to -89 UAS sequence I and II. The UAS sequence is replaced with the CBS I and CBS II UAS in <i>gumB</i> operon of <i>Xanthomonas campestris</i> pv. <i>camperstris</i>, to create a new synthetic promoter (<html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3071014">BBa_K3071014</a></html>)). This promoter is conjugated with the eforRED with RBS (<html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1073023">BBa_K1073023</a></html>) for protein expression and gives a red chromoprotein signal. |
===Usage=== | ===Usage=== | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
| − | Using the RpfC-RpfG system as a foundation, we fused the PspF protein with Clp to enhance binding specificity and prevent expression leakage. The DNA binding domain in the C-terminus of pspF (BBa_K3071006) is replaced by Clp to construct a fusion transcription activator for our reporter construct (BBa_K3071024). This transcription activator can activate the CBSI & II-regulated pspA promoter (BBa_K3071014) upon diffusable signal factor (DSF) appearance. | + | Using the RpfC-RpfG system as a foundation, we fused the PspF protein with Clp to enhance binding specificity and prevent expression leakage. The DNA binding domain in the C-terminus of pspF (BBa_K3071006) is replaced by Clp to construct a fusion transcription activator for our reporter construct (<html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3071024">BBa_K3071024</a></html>). This transcription activator can activate the CBSI & II-regulated pspA promoter (<html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3071014">BBa_K3071014</a></html>) upon diffusable signal factor (DSF) appearance. |
| − | pspA promoter is a sigma-54 (σ-54) regulated activator depending on promoter. sigm54-RNA holoenzyme (σ-54 RNAP) forms an inactive transcriptional initiation complex on this promoter, which can be activated in E. coli by the bacterial enhancer-binding protein PspF (BBa_K3071006). PspF transcription activation domain (pspF TAD) functions by binding to upstream activation sequences (UAS) near the promoter and contacting the promoter-bound σ-54 RNAP via DNA looping stabilized by integration host factor (IHF). Previous research has demonstrated the property of pspF-dependent and enhancer-specific transcription activation of pspA promoter. | + | pspA promoter is a sigma-54 (σ-54) regulated activator depending on promoter. sigm54-RNA holoenzyme (σ-54 RNAP) forms an inactive transcriptional initiation complex on this promoter, which can be activated in E. coli by the bacterial enhancer-binding protein PspF (<html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3071006">BBa_K3071006</a></html>). PspF transcription activation domain (pspF TAD) (<html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3071008">BBa_K3071008</a></html>) functions by binding to upstream activation sequences (UAS) near the promoter and contacting the promoter-bound σ-54 RNAP via DNA looping stabilized by integration host factor (IHF). Previous research has demonstrated the property of pspF-dependent and enhancer-specific transcription activation of pspA promoter. |
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
<center><u>Figure 4 rt-qPCR data Azathioprine treatment on the eforRED mRNA expression level </u></center> | <center><u>Figure 4 rt-qPCR data Azathioprine treatment on the eforRED mRNA expression level </u></center> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | Azathioprine is an indirect supressor to cyclic-di-GMP, treatment of azathioprine to bacteria culture can reduce the cyclic-di-GMP level and lead to activation of the pspF-Clp and by-pass the RpfC/RpfG two-component system.The result from rt-qPCR data shows that the above | + | Azathioprine is an indirect supressor to cyclic-di-GMP, treatment of azathioprine to bacteria culture can reduce the cyclic-di-GMP level and lead to activation of the pspF-Clp and by-pass the RpfC/RpfG two-component system.The result from rt-qPCR data shows that the above synthetic biological system is functional with significant up-regulation of reporter mRNA. |
<br> | <br> | ||
<center>[[file:T--Hong_Kong-CUHK--DSF_assay.png]]</center> | <center>[[file:T--Hong_Kong-CUHK--DSF_assay.png]]</center> | ||
<center><u>Figure 5 rt-qPCR data DSF treatment on the eforRED mRNA expression level</u></center> | <center><u>Figure 5 rt-qPCR data DSF treatment on the eforRED mRNA expression level</u></center> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | The result from rt-qPCR data shows that the above | + | The result from rt-qPCR data shows that the above synthetic biological system is functional with significant up-regulation of reporter mRNA upon DSF activation. |
<!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | ||
Latest revision as of 16:44, 21 October 2019
Reporter construct in response to diffusible signal factor (DSF) with sequencing part
Description
This composite part is the reporter construct that under the regulation of CBS I & II, which could be activated by pspF TAD-Clp upon DSF ligand binding. The upstream elements RpfC/RpfG (BBa_K3071022) is responsible for the sensing of diffusible signal factor (DSF) from Xanthomonas campestris pv. camperstris and signal transduction through phosphorylation. The co-activator psp TAD-Clp and sigma 54 (BBa_K3071023) are responsible for the activation of this composite part in response to the DSF binding. This part is one of the three parts used to construct our detection system in our part collection, the other two parts include (BBa_K3071022) and (BBa_K3071023).
Biology
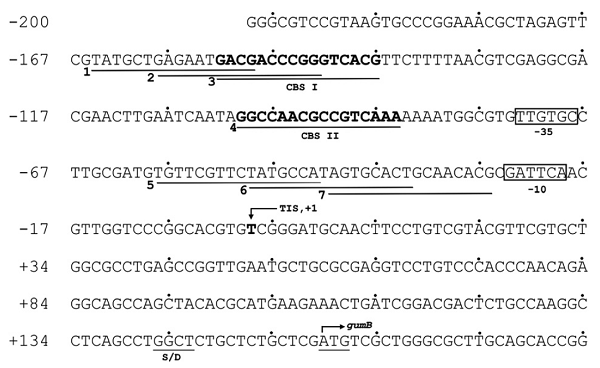
Clp binding sites (CBSs) (BBa_K3071011) and (BBa_K3071012)have typically been identified by pattern searching of the Xanthomonas campestris pv. camperstris genome using the consensus CRP binding sequence.Clp upregulates the gum operon by binding to two non-consensus sites. CBS I has a high GC content in the central region (6bp) that may be important for binding, and binding may be enhanced if the GC-rich central region is palindromic.

pspA promoter (BBa_K3071013) is a sigma-54 (σ-54) regulated activator dependent promoter. In the original pspA promoter upstream region, it contains σ-54 consensus sequence 5' of the start contains a GG doublet as -24 and a consensus GG doublet at -12, the high-affinity IHF site (-25 to -60), as well as the UAS sites (UAS I: -89 to -107; UAS II:-111 to -129).
Sigm54-RNA holoenzyme (σ-54 RNAP) (BBa_K3071010)forms an inactive transcriptional initiation complex on this promoter, which can be activated in E. coli by the bacterial enhancer-binding protein PspF (BBa_K3071006). PspF functions by binding to the upstream activation sequences (UAS) near the promoter and contacting the promoter-bound σ-54 RNAP via DNA looping stabilized by the binding of integration host factor (IHF). Previous research has demonstrated the property of PspF-dependent and enhancer-specific transcription activation of pspA promoter.
In terms of gene structure, the -24 and -12 region is for the sigma 54-factor binding, with the -60 IHF interaction region and -129 to -89 UAS sequence I and II. The UAS sequence is replaced with the CBS I and CBS II UAS in gumB operon of Xanthomonas campestris pv. camperstris, to create a new synthetic promoter (BBa_K3071014)). This promoter is conjugated with the eforRED with RBS (BBa_K1073023) for protein expression and gives a red chromoprotein signal.
Usage

The responsible sensor kinase system detecting DSF in the environment compose of RpfC-RpfG phosphorylation relay. After a series of auto-phosphorylation in RpfC, phosphotransfer from RpfC to RpfG occurs. This leads to the activation of the phosphodiesterase domain in RpfG, which will degrade the second messenger cyclic-di-GMP. As one of the downstream results, Clp binds to its target CBS I and CBS II. Without the DSF induction, cyclic di-GMP will not be degraded but bind to the Clp. The binding between Clp and c-di-GMP prevents Clp from binding CBS.
Using the RpfC-RpfG system as a foundation, we fused the PspF protein with Clp to enhance binding specificity and prevent expression leakage. The DNA binding domain in the C-terminus of pspF (BBa_K3071006) is replaced by Clp to construct a fusion transcription activator for our reporter construct (BBa_K3071024). This transcription activator can activate the CBSI & II-regulated pspA promoter (BBa_K3071014) upon diffusable signal factor (DSF) appearance.
pspA promoter is a sigma-54 (σ-54) regulated activator depending on promoter. sigm54-RNA holoenzyme (σ-54 RNAP) forms an inactive transcriptional initiation complex on this promoter, which can be activated in E. coli by the bacterial enhancer-binding protein PspF (BBa_K3071006). PspF transcription activation domain (pspF TAD) (BBa_K3071008) functions by binding to upstream activation sequences (UAS) near the promoter and contacting the promoter-bound σ-54 RNAP via DNA looping stabilized by integration host factor (IHF). Previous research has demonstrated the property of pspF-dependent and enhancer-specific transcription activation of pspA promoter.
Activation of PspA promoter leads to mRNA expression of the reporter eforRed chromoprotein as an output signal after detecting the existence of DSF.
Characterization
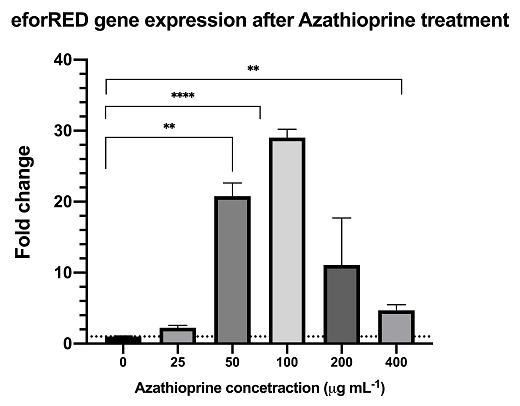
Azathioprine is an indirect supressor to cyclic-di-GMP, treatment of azathioprine to bacteria culture can reduce the cyclic-di-GMP level and lead to activation of the pspF-Clp and by-pass the RpfC/RpfG two-component system.The result from rt-qPCR data shows that the above synthetic biological system is functional with significant up-regulation of reporter mRNA.

The result from rt-qPCR data shows that the above synthetic biological system is functional with significant up-regulation of reporter mRNA upon DSF activation.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 105
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
