Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1065102"
(→Characterization) |
(→Usage and Biology) |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K1065102 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1065102 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | This was the device employed in the project <i>B. Fruity</i> to inhibit the ripening maturation with the production of Methyl Salicylate by the UNITN-Trento 2013 iGEM team. The device includes the enzyme PCHBA under the control of pLac promoter and BSMT1 under the control of an arabinose inducible promoter <html><a href="#ref2" id="ret_ref2">[ | + | This was the device employed in the project <i>B. Fruity</i> to inhibit the ripening maturation with the production of Methyl Salicylate by the UNITN-Trento 2013 iGEM team. The device includes the enzyme PCHBA under the control of pLac promoter and BSMT1 under the control of an arabinose inducible promoter <html><a href="#ref2" id="ret_ref2">[1]</a></html>. |
===Usage and Biology=== | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
| − | The chorismate, a metabolic intermediate of the Shikimate pathway | + | The chorismate, a metabolic intermediate of the Shikimate pathway present in many plants and bacteria, undergoes at first a reaction of isomerization by the isochorismate synthase PchA. Salicylate is then obtained by the action of PchB, an isochorismate pyruvate lyase. Both enzymes are from the microorganism <i>Pseudomonas aeruginosa</i> <html><a href="#ref1" id="ret_ref1">[2]</a></html> . In the final part of the reaction, BSMT1, a methyltransferase, transfers a methyl group from the S-adenosyl-L-methionine, synthesized by the SAM synthetase (in<i> E. coli</i> there's already a basal expression of the enzyme) <html><a href="#ref1" id="ret_ref1">[3]</a></html> . |
To improve methyl salicylate production, iGEM UniTN Trento 2013 created another device containing also SAM synthetase: <partinfo>BBa_K1065106</partinfo>. | To improve methyl salicylate production, iGEM UniTN Trento 2013 created another device containing also SAM synthetase: <partinfo>BBa_K1065106</partinfo>. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
===Characterization=== | ===Characterization=== | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
| − | <h3>MeSA detection</h3> | + | <h3>MeSA detection in liquid phase</h3> |
<p> | <p> | ||
MeSA is an highly volatile liquid with a distinct minty fragrance. We exploited the physical properties of MeSA to quantify its production by gas chromatography using a Finnigan Trace GC ULTRA connected to a <b>flame ionization detector</b> (FID). This kind of instrument, is able to detect ions formed during combustion in a hydrogen flame. The generation of these ions is proportional to MeSA concentration in the sample stream. A calibration curve was initially created using samples with a well known pure MeSA concentration (0 mM, 0.2 mM, 0.5 mM, 1.0 mM, 2 mM). | MeSA is an highly volatile liquid with a distinct minty fragrance. We exploited the physical properties of MeSA to quantify its production by gas chromatography using a Finnigan Trace GC ULTRA connected to a <b>flame ionization detector</b> (FID). This kind of instrument, is able to detect ions formed during combustion in a hydrogen flame. The generation of these ions is proportional to MeSA concentration in the sample stream. A calibration curve was initially created using samples with a well known pure MeSA concentration (0 mM, 0.2 mM, 0.5 mM, 1.0 mM, 2 mM). | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
<center><p style="width:600px; margin-bottom:60px;text-align:justify;"><b>Figure 2:</b> Left panel: calibration curve obtained with different concentrations of pure MeSA in ethanol. Right panel: Quantification of MeSA by GC-FID. NEB10β cells transformed with <a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1065102">BBa_K1065102</a> supplemented with salycilic acid produce around 0.4 mM of MeSA. Non transformed cells and non induced cells did not produce any MeSA. Cells induced with arabinose and not supplemented with salycilic acid did not show any significant MeSA concentration (data not shown).</p></center> | <center><p style="width:600px; margin-bottom:60px;text-align:justify;"><b>Figure 2:</b> Left panel: calibration curve obtained with different concentrations of pure MeSA in ethanol. Right panel: Quantification of MeSA by GC-FID. NEB10β cells transformed with <a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1065102">BBa_K1065102</a> supplemented with salycilic acid produce around 0.4 mM of MeSA. Non transformed cells and non induced cells did not produce any MeSA. Cells induced with arabinose and not supplemented with salycilic acid did not show any significant MeSA concentration (data not shown).</p></center> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
<h3>MeSA detection in gas phase</h3> | <h3>MeSA detection in gas phase</h3> | ||
| − | NEB10β cells transformed with Bba_K1065102, were grown in M9 medium, induced with 5 mM arabinose and in some cases supplemented with 2mM of salicylic acid. After 4 hours we performed the gas chromatographyc analyis with a column optimized for the fast analysis of volatile compounds (J&W GC Column Performance Summary-Agilent Tecnologies). Peak corresponding to MeSA eluted at a ritension time of 5.5 min. The quantitative analysis done by integration of the peak area showed that small amounts of MeSA are released in the gas phase under this experimental condition: | + | NEB10β cells transformed with Bba_K1065102, were grown in M9 medium, induced with 5 mM arabinose and in some cases supplemented with 2mM of salicylic acid. After 4 hours we performed the gas chromatographyc analyis with a column optimized for the fast analysis of volatile compounds (J&W GC Column Performance Summary-Agilent Tecnologies). Peak corresponding to MeSA eluted at a ritension time of 5.5 min. The quantitative analysis done by integration of the peak area showed that small amounts of MeSA are released in the gas phase under this experimental condition: 1.3 ppm for BBa_K1065102. Non induced cells did not produce any MeSA. |
<center><img style="width:800px;"src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/parts/7/7a/Unitn2013_k02.jpg"></center> | <center><img style="width:800px;"src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/parts/7/7a/Unitn2013_k02.jpg"></center> | ||
<center><p style="width:600px; margin-bottom:60px; text-align:justify"><b>Figure 3</b> Quantification of MeSA by gas chromatography. a)NEB10β cells transformed with Bba_K1065102 and induced with 5mM arabinose, b) 15 ppm reference point. | <center><p style="width:600px; margin-bottom:60px; text-align:justify"><b>Figure 3</b> Quantification of MeSA by gas chromatography. a)NEB10β cells transformed with Bba_K1065102 and induced with 5mM arabinose, b) 15 ppm reference point. | ||
| − | </p></center> </html> | + | </p></center> |
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Summary=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Our MeSA device BBa_K1065102 was able to produce a significant concentration of MeSA only in the presence of salycilic acid. This finding was also previously observed by the MIT team in 2006 with their device (<partinfo>BBa_J45700</partinfo>). Additionally, it seems that more MeSA is present in the liquid phase than in the gas phase. <br> | ||
| + | After we received the DNA sequencing results of the MIT part (<partinfo>BBa_J45300</partinfo>) and of our complete device (built with MIT parts) we realised that the pLAC promoter was missing the -35 box, thus generating a less strong promoter. We believe that this problem can significantly affect the correct functioning of the device. We are now in the process of improving this part by mutagenesis to rebuild a full functional pLAC promoter. | ||
| + | |||
| Line 48: | Line 50: | ||
<span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | <span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K1065102 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1065102 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | <html><ol> | ||
| + | <li><a id="ref1"></a>Chang-Kui Ding, Chien Yi Wang (2003). The dual effects of methyl salicylate on ripening and expression of ethylene biosynthetic genes in tomato fruit, Plant Science Volume 164, Pages 589–596.</li> | ||
| + | <li><a id="ref2"></a>Marianne C. Verberne at al., (1999). Salicylic acid biosynthesis, Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Plant Hormones, 295–312.</li> | ||
| + | <li><a id="ref3"></a>Florence Negre at al., Novel S-adenosyl-l-methionine:salicylic acid carboxyl methyltransferase, an enzyme responsible for biosynthesis of methyl salicylate and methyl benzoate, is not involved in floral scent production in snapdragon flowers, Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, Volume 406, Issue 2, 15 October 2002, Pages 261–270.</li> | ||
| + | </lo></html> | ||
Latest revision as of 23:14, 4 October 2013
Wintergreen device: Plac + PchBA + AraCpBAD + BSMT1
This was the device employed in the project B. Fruity to inhibit the ripening maturation with the production of Methyl Salicylate by the UNITN-Trento 2013 iGEM team. The device includes the enzyme PCHBA under the control of pLac promoter and BSMT1 under the control of an arabinose inducible promoter [1].
Usage and Biology
The chorismate, a metabolic intermediate of the Shikimate pathway present in many plants and bacteria, undergoes at first a reaction of isomerization by the isochorismate synthase PchA. Salicylate is then obtained by the action of PchB, an isochorismate pyruvate lyase. Both enzymes are from the microorganism Pseudomonas aeruginosa [2] . In the final part of the reaction, BSMT1, a methyltransferase, transfers a methyl group from the S-adenosyl-L-methionine, synthesized by the SAM synthetase (in E. coli there's already a basal expression of the enzyme) [3] .
To improve methyl salicylate production, iGEM UniTN Trento 2013 created another device containing also SAM synthetase: BBa_K1065106.

Characterization
MeSA detection in liquid phase
MeSA is an highly volatile liquid with a distinct minty fragrance. We exploited the physical properties of MeSA to quantify its production by gas chromatography using a Finnigan Trace GC ULTRA connected to a flame ionization detector (FID). This kind of instrument, is able to detect ions formed during combustion in a hydrogen flame. The generation of these ions is proportional to MeSA concentration in the sample stream. A calibration curve was initially created using samples with a well known pure MeSA concentration (0 mM, 0.2 mM, 0.5 mM, 1.0 mM, 2 mM).
NEB10β cells transformed with BBa_K1065102 were grown in M9 medium, induced with 5 mM arabinose and in some cases supplemented with salicylic acid. All the gas chromatography measures here reported were done in liquid phase, by injecting 1 ul of pre-filtered culture in the instrument.
Figure 1: induced sample produces MeSA. A culture of cells transformed with BBa_K1065102 was grown until O.D. 0.6 was reached. The culture was then splitted in 2 samples and one was induced with 5 mM arabinose. 2 mM salycilic acid was added to these samples. After about 4 h the samples were connected to the Gas Chromatograph. The induced sample (blue trace) shows the characteristic peak of methyl salicylate, as opposed to non induced cells (red trace).

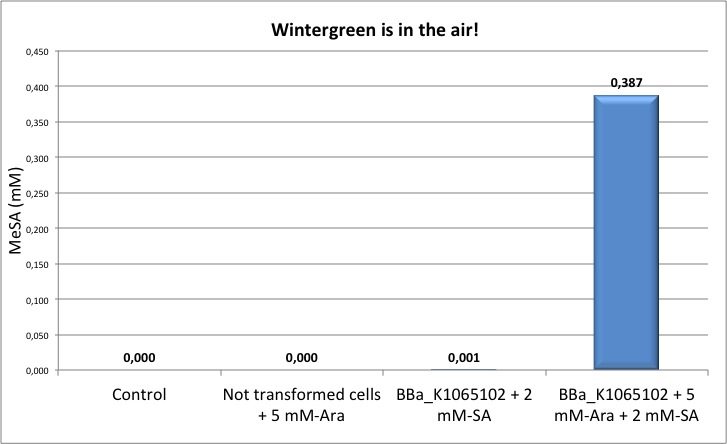
Figure 2: Left panel: calibration curve obtained with different concentrations of pure MeSA in ethanol. Right panel: Quantification of MeSA by GC-FID. NEB10β cells transformed with BBa_K1065102 supplemented with salycilic acid produce around 0.4 mM of MeSA. Non transformed cells and non induced cells did not produce any MeSA. Cells induced with arabinose and not supplemented with salycilic acid did not show any significant MeSA concentration (data not shown).
MeSA detection in gas phase
NEB10β cells transformed with Bba_K1065102, were grown in M9 medium, induced with 5 mM arabinose and in some cases supplemented with 2mM of salicylic acid. After 4 hours we performed the gas chromatographyc analyis with a column optimized for the fast analysis of volatile compounds (J&W GC Column Performance Summary-Agilent Tecnologies). Peak corresponding to MeSA eluted at a ritension time of 5.5 min. The quantitative analysis done by integration of the peak area showed that small amounts of MeSA are released in the gas phase under this experimental condition: 1.3 ppm for BBa_K1065102. Non induced cells did not produce any MeSA.
Figure 3 Quantification of MeSA by gas chromatography. a)NEB10β cells transformed with Bba_K1065102 and induced with 5mM arabinose, b) 15 ppm reference point.
Summary
Our MeSA device BBa_K1065102 was able to produce a significant concentration of MeSA only in the presence of salycilic acid. This finding was also previously observed by the MIT team in 2006 with their device (BBa_J45700). Additionally, it seems that more MeSA is present in the liquid phase than in the gas phase.
After we received the DNA sequencing results of the MIT part (BBa_J45300) and of our complete device (built with MIT parts) we realised that the pLAC promoter was missing the -35 box, thus generating a less strong promoter. We believe that this problem can significantly affect the correct functioning of the device. We are now in the process of improving this part by mutagenesis to rebuild a full functional pLAC promoter.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 3107
Illegal BamHI site found at 3856 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 389
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 793
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 918
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 929
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 1210
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 1678
Illegal AgeI site found at 2942 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI site found at 3397
Illegal SapI site found at 2924
References
- Chang-Kui Ding, Chien Yi Wang (2003). The dual effects of methyl salicylate on ripening and expression of ethylene biosynthetic genes in tomato fruit, Plant Science Volume 164, Pages 589–596.
- Marianne C. Verberne at al., (1999). Salicylic acid biosynthesis, Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Plant Hormones, 295–312.
- Florence Negre at al., Novel S-adenosyl-l-methionine:salicylic acid carboxyl methyltransferase, an enzyme responsible for biosynthesis of methyl salicylate and methyl benzoate, is not involved in floral scent production in snapdragon flowers, Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, Volume 406, Issue 2, 15 October 2002, Pages 261–270.
