Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K316005"
(rollbackEdits.php mass rollback) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | __NOTOC__ | |
| + | <partinfo>BBa_K316005 short</partinfo> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Enables characterization and comparison with alternative promoters e.g. <bbpart>BBa_J23101</bbpart> Designed for characterisation of XylE in ''Bacillus subtilis'' where Pveg is a useful constitutive promoter. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For more information about XylE, it's substrate and spectrophotometric assays, please see <bbpart>BBa_K316003</bbpart> or our [http://2010.igem.org/Team:Imperial_College_London/Results wiki results section] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Safety''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | The substrate XylE works on is a chemical called catechol. It is classed as irritant in the EU but as toxic in the USA, as well as being a possible carcinogen. It should therefore be handled with care and proper safety equipment. More information is available on the [http://www.sciencelab.com/msds.php?msdsId=9927131 Material Safety Data Sheet]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | ||
| + | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- --> | ||
| + | <span class='h3bb'><big>'''Sequence and Features'''</big></span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <partinfo>BBa_K316005 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- Uncomment this to enable Functional Parameter display | ||
| + | ===Functional Parameters=== | ||
| + | <partinfo>BBa_K316005 parameters</partinfo> | ||
| + | <!-- --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | ==Part Characterisation == | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| | ||
| + | |colspan="2"| | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | <span class='h3bb'><big>'''Characterization in r.p.u. of Pveg promoter'''</big></span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Aims of experiment | Measuring the activity of BioBrick promoters using an in vivo reference standard. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Results | pVeg promoter in pSB1C3 vector, a high copy plasmid, has an 1.62 r.p.u value and in 3K3 vector, a low copy plasmid an 0.79 r.p.u. value. These values were derived by dividing signal from the production of HMS by the pVeg promoter population of cells by signal from the standard promoter J23101 (r.p.u value of 1) | ||
| + | |||
| + | See experience page for more information. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <span class='h3bb'><big>'''Optimum absorbtion wavelength for catechol assays'''</big></span> | ||
| + | |||
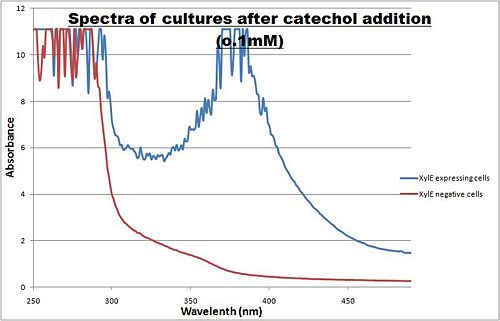
| + | [[Image:SpectraXylE.PNG|thumb|right|400px| Peak absorbance of catechol breakdown product (2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The enzymatic reaction catalysed by XylE can also serve as a powerful reporter. The substrate - catechol - is colourless. However within seconds of its addition, the colonies or suspended cultures of XylE-expressing cells become clearly yellow<cite>3</cite> to the naked eye. This reaction allows direct measurement of XylE activity by measuring product concentrations, which absorbs light in the visible spectrum, at 380nm. In contrast to other common reporters like GFP, LacZ or Luciferase which do easily express correctly in thermophile environments, a XylE assay has also been shown to be functional in here. The spectrophotometric assay compared the spectra of two cultures of E.coli (one XylE gene transformed and the other not) were compared on addition of 0.1mM Catechol substrate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A spectrophotometric assay of two cultures of E.coli (Blue: contains <bbpart>BBa_K316004</bbpart>, Red: not expressing XylE ) were compared on addition of 0.1mM Catechol substrate. The spectra show that in XylE transformed cells, a broad peak appears at about 380nm. The absorbance at this particular wavelength is due to the yellow product of the reaction (2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde (HMS)). | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | |colspan="2"| | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | <span class='h3bb'><big>'''''In VItro'' Assay'''</big></span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Experiment6.PNG|thumb|right|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Due to technical limitations, to measure kinetic parameters of XylE is to lyse cells and . In this experiment cell lysate was assayed with increasing catechol concentrations. The rate at which the yellow product appears is directly proportional to the velocity of the reaction. The rate reaction was monitored by measuring color output of the reaction in the plate reader. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cell lysate was tested for dioxygenase activity to determine appropriate dilutions for the assay. The cell lysate was obtained from a 100ml overnight culture and diluted by a factor of 20 to obtain a suitable concentration of total enzyme for the plate reader assay. The concentrations of catechol used were 1, 2, 5, 10, 25, 50 mM. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Data collected was used to construct the Michaelis-Menten curve for the in vitro kinetics of XylE in cell lysate. | ||
| + | Michaelis-Menten curve was drawn using velocity values calculated from the slope at the initial stages of the reaction, as this is the only time when substrate concentration values are accurate. The plot was delineated by non-linear regression analysis using GraFit software tool[http://www.erithacus.com/grafit/]. The calculated Km is 0.71mM catechol (with a Vmax of 3.37 in O.D. arbitrary units for this dilution of cell lysate). | ||
| + | |||
| + | For more detailed information, please check our wiki [http://2010.igem.org/Team:Imperial_College_London/Results/Exp6] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | |colspan="2"| | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | <span class='h3bb'><big>'''Cytotoxicity of Catechol'''</big></span> | ||
| + | |||
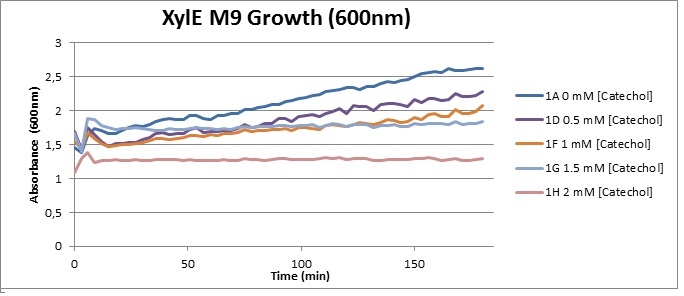
| + | [[Image:XylE M9 Growth (600).jpg|thumb|right|400px|O.D. at 600 over 3h for XylE-transformed Top10 cells in presence of different catechol concentrations, growing in M9 medium.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The addition of catechol had distinctive deleterious effects on XylE expressing cells. While at 0% catechol growth-behavior did not show a significant change (dark blue), even the lowest concentration of 0.25% catechol appeared to drastically reduce cell-survival (red). In contrast, CMR-control cells did not change their growing behavior in the presence of catechol. From this we conclude that the breakdown product of catechol, 2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde, and not Catechol itself, has strong cytotoxic effects | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | Characterisation data was obtained for XylE <bbpart>BBa_K316003</bbpart>. In addition constructs under two different promoters: J23101-XylE <bbpart>BBa_K316004</bbpart> from ''E. coli'' was used to categorise ''B. subtilis'' derived Pveg-XylE <bbpart>BBa_K316005</bbpart>. Also GFP-XylE constructs <bbpart>BBa_K316007</bbpart> were tested to determine the effectiveness of repression. These are described on our wiki[http://2010.igem.org/Team:Imperial_College_London/Results] and the aforementioned parts pages. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | <biblio> | ||
| + | #1 pmid=10368270 | ||
| + | #2 pmid=12519074 | ||
| + | #3 pmid=6405380 | ||
| + | |||
| + | </biblio> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | Characterisation data was obtained for XylE <bbpart>BBa_K316003</bbpart>. In addition constructs under two different promoters: J23101-XylE <bbpart>BBa_K316004</bbpart> from ''E. coli'' was used to categorise ''B. subtilis'' derived Pveg-XylE <bbpart>BBa_K316005</bbpart>. Also GFP-XylE constructs <bbpart>BBa_K316007</bbpart> were tested to determine the effectiveness of inhibition of XylE activity by attachment of GFP. These are described on our wiki[http://2010.igem.org/Team:Imperial_College_London/Results] and the aforementioned parts pages. | ||
Latest revision as of 16:17, 10 May 2013
Functional XylE under Pveg promoter, with double terminator
Enables characterization and comparison with alternative promoters e.g. BBa_J23101 Designed for characterisation of XylE in Bacillus subtilis where Pveg is a useful constitutive promoter.
For more information about XylE, it's substrate and spectrophotometric assays, please see BBa_K316003 or our [http://2010.igem.org/Team:Imperial_College_London/Results wiki results section]
Safety
The substrate XylE works on is a chemical called catechol. It is classed as irritant in the EU but as toxic in the USA, as well as being a possible carcinogen. It should therefore be handled with care and proper safety equipment. More information is available on the [http://www.sciencelab.com/msds.php?msdsId=9927131 Material Safety Data Sheet].
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 442
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 614
Illegal AgeI site found at 965 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Part Characterisation
|
Characterization in r.p.u. of Pveg promoter
Results | pVeg promoter in pSB1C3 vector, a high copy plasmid, has an 1.62 r.p.u value and in 3K3 vector, a low copy plasmid an 0.79 r.p.u. value. These values were derived by dividing signal from the production of HMS by the pVeg promoter population of cells by signal from the standard promoter J23101 (r.p.u value of 1) See experience page for more information.
The enzymatic reaction catalysed by XylE can also serve as a powerful reporter. The substrate - catechol - is colourless. However within seconds of its addition, the colonies or suspended cultures of XylE-expressing cells become clearly yellow3 to the naked eye. This reaction allows direct measurement of XylE activity by measuring product concentrations, which absorbs light in the visible spectrum, at 380nm. In contrast to other common reporters like GFP, LacZ or Luciferase which do easily express correctly in thermophile environments, a XylE assay has also been shown to be functional in here. The spectrophotometric assay compared the spectra of two cultures of E.coli (one XylE gene transformed and the other not) were compared on addition of 0.1mM Catechol substrate. A spectrophotometric assay of two cultures of E.coli (Blue: contains BBa_K316004, Red: not expressing XylE ) were compared on addition of 0.1mM Catechol substrate. The spectra show that in XylE transformed cells, a broad peak appears at about 380nm. The absorbance at this particular wavelength is due to the yellow product of the reaction (2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde (HMS)). |
|
|
In VItro Assay Due to technical limitations, to measure kinetic parameters of XylE is to lyse cells and . In this experiment cell lysate was assayed with increasing catechol concentrations. The rate at which the yellow product appears is directly proportional to the velocity of the reaction. The rate reaction was monitored by measuring color output of the reaction in the plate reader. Cell lysate was tested for dioxygenase activity to determine appropriate dilutions for the assay. The cell lysate was obtained from a 100ml overnight culture and diluted by a factor of 20 to obtain a suitable concentration of total enzyme for the plate reader assay. The concentrations of catechol used were 1, 2, 5, 10, 25, 50 mM. Data collected was used to construct the Michaelis-Menten curve for the in vitro kinetics of XylE in cell lysate. Michaelis-Menten curve was drawn using velocity values calculated from the slope at the initial stages of the reaction, as this is the only time when substrate concentration values are accurate. The plot was delineated by non-linear regression analysis using GraFit software tool[http://www.erithacus.com/grafit/]. The calculated Km is 0.71mM catechol (with a Vmax of 3.37 in O.D. arbitrary units for this dilution of cell lysate). For more detailed information, please check our wiki [http://2010.igem.org/Team:Imperial_College_London/Results/Exp6] |
|
|
Cytotoxicity of Catechol The addition of catechol had distinctive deleterious effects on XylE expressing cells. While at 0% catechol growth-behavior did not show a significant change (dark blue), even the lowest concentration of 0.25% catechol appeared to drastically reduce cell-survival (red). In contrast, CMR-control cells did not change their growing behavior in the presence of catechol. From this we conclude that the breakdown product of catechol, 2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde, and not Catechol itself, has strong cytotoxic effects |
|
Characterisation data was obtained for XylE BBa_K316003. In addition constructs under two different promoters: J23101-XylE BBa_K316004 from E. coli was used to categorise B. subtilis derived Pveg-XylE BBa_K316005. Also GFP-XylE constructs BBa_K316007 were tested to determine the effectiveness of repression. These are described on our wiki[http://2010.igem.org/Team:Imperial_College_London/Results] and the aforementioned parts pages.
References
<biblio>
- 1 pmid=10368270
- 2 pmid=12519074
- 3 pmid=6405380
</biblio>
Characterisation data was obtained for XylE BBa_K316003. In addition constructs under two different promoters: J23101-XylE BBa_K316004 from E. coli was used to categorise B. subtilis derived Pveg-XylE BBa_K316005. Also GFP-XylE constructs BBa_K316007 were tested to determine the effectiveness of inhibition of XylE activity by attachment of GFP. These are described on our wiki[http://2010.igem.org/Team:Imperial_College_London/Results] and the aforementioned parts pages.