Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K729008"
(→Modelling) |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K729008 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K729008 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | This starvation sensitive device was used by the | + | This starvation sensitive device was used by the [http://2012.igem.org/Team:University_College_London UCL’s 2012 iGem team] to increase the expression of a reporter gene (GFP) under low glucose concentrations. During carbon starvation cAMP binds the cAMP receptor protein, the complex formed activates the expression of the downstream gene (T7 RNA polymerase), which promotes the expression of GFP under the control of the T7 promoter. |
This device comprises the ligation of the parts ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K729007 BBa_K729007]) and ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I746909 BBa_I746909]). | This device comprises the ligation of the parts ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K729007 BBa_K729007]) and ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I746909 BBa_I746909]). | ||
| − | + | ||
<!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
<span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | <span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K729008 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K729008 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Characterisation== | ||
| + | [[Image:System2.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Normalized expression levels were plotted as relative fluorescent units per optical density at 600 nm. Transformed E. coli was grown overnight in LB media and then transferred into minimal M9 media supplemented with different glucose concentrations (0%, 0.2%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 3%, 5%) to induce the activation of the cstA promoter. | ||
| + | BBa_K729008 integrates the T7 RNA polymerase and T7 promoter in order to increase the expression of the reporter gene. Once the bacteria is exposed to carbon starvation stress, cstA promoter is activated, as a results it can be seen from the chart that GFP was expressed reaching higher accumulation in cultures with M9 media supplemented with less than 0.5% of glucose. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 27: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K729008 parameters</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K729008 parameters</partinfo> | ||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Modelling == | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | For the simbiology model was to investigate if the addition of T7 RNA Polymerase as well as T7 promoter woud increase the expression levels for the GFP. The aim for the mathematical model is to predict the number of E.coli cells required to maintain buoyancy in a mass of aggregated plastics. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
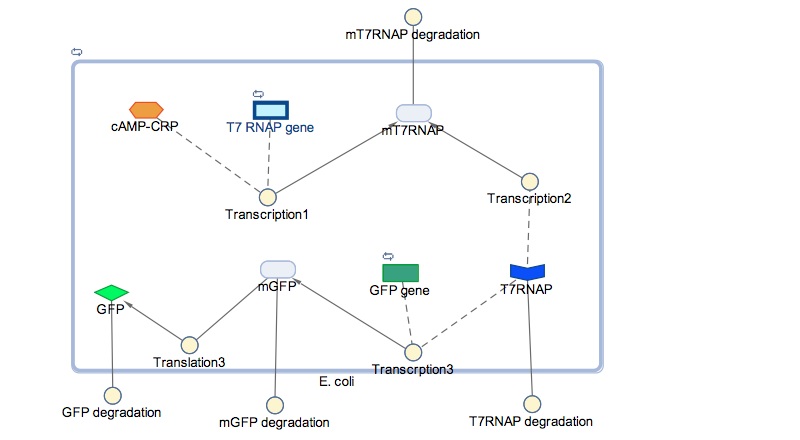
| + | The block diagram shows the module where GFP expression is control by cstA promoter; the expression is triggered under low glucose concentrations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:UniversityCollegeLondon_ bla4.png|600px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the models the environmental sensitive promoters (cstA) is activated by carbon starvation stress, then the mRNA encoding T7 RNA polymerase is transcribed, whose protein binds the T7 promoter driving the expression of the the reporter output (GFP). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:UniversityCollegeLondon_ bla5.png|600px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
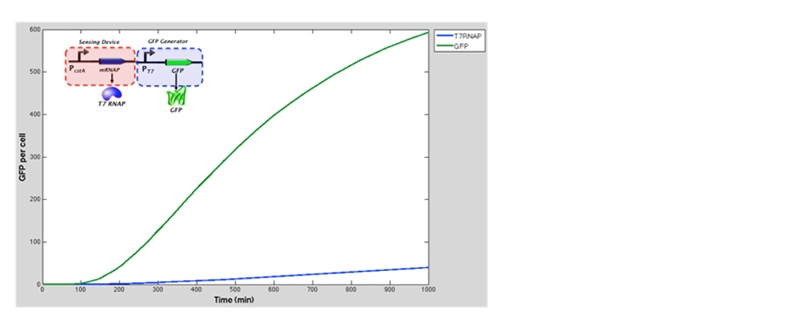
| + | The green line represents GFP expression levels and the blue line shows the T7 RNAP concentration over time. GFP production is considerably higher than in the previous model. | ||
| + | Conclusion and influence to our experimental work: From the results obtained above our model suggests that there was a 10 fold increase in GFP expression when the T7 RNA Polymerase as well as T7 promoter are added to the original construct (which was cstA + GFP). We expect that our experimental data fill follow this. | ||
Latest revision as of 01:55, 2 October 2012
pCstA+RBS+T7RNAP+pT7+RBS+GFP+TT
This starvation sensitive device was used by the [http://2012.igem.org/Team:University_College_London UCL’s 2012 iGem team] to increase the expression of a reporter gene (GFP) under low glucose concentrations. During carbon starvation cAMP binds the cAMP receptor protein, the complex formed activates the expression of the downstream gene (T7 RNA polymerase), which promotes the expression of GFP under the control of the T7 promoter.
This device comprises the ligation of the parts (BBa_K729007) and (BBa_I746909).
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 2793
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal SapI.rc site found at 2887
Characterisation
Normalized expression levels were plotted as relative fluorescent units per optical density at 600 nm. Transformed E. coli was grown overnight in LB media and then transferred into minimal M9 media supplemented with different glucose concentrations (0%, 0.2%, 0.5%, 1.0%, 3%, 5%) to induce the activation of the cstA promoter. BBa_K729008 integrates the T7 RNA polymerase and T7 promoter in order to increase the expression of the reporter gene. Once the bacteria is exposed to carbon starvation stress, cstA promoter is activated, as a results it can be seen from the chart that GFP was expressed reaching higher accumulation in cultures with M9 media supplemented with less than 0.5% of glucose.
Modelling
For the simbiology model was to investigate if the addition of T7 RNA Polymerase as well as T7 promoter woud increase the expression levels for the GFP. The aim for the mathematical model is to predict the number of E.coli cells required to maintain buoyancy in a mass of aggregated plastics.
The block diagram shows the module where GFP expression is control by cstA promoter; the expression is triggered under low glucose concentrations.
In the models the environmental sensitive promoters (cstA) is activated by carbon starvation stress, then the mRNA encoding T7 RNA polymerase is transcribed, whose protein binds the T7 promoter driving the expression of the the reporter output (GFP).
The green line represents GFP expression levels and the blue line shows the T7 RNAP concentration over time. GFP production is considerably higher than in the previous model.
Conclusion and influence to our experimental work: From the results obtained above our model suggests that there was a 10 fold increase in GFP expression when the T7 RNA Polymerase as well as T7 promoter are added to the original construct (which was cstA + GFP). We expect that our experimental data fill follow this.