Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa B0012"
| (23 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
| − | {| | + | {|width='80%' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width= | + | |width=35% valign='top'| |
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Terminator.png]] |
| − | + | <partinfo>BBa_B0012 parameters</partinfo> | |
| − | | width=50% style='border: 1px solid black'| | + | | width=50% valign='top' style='border: 1px solid black'| |
<partinfo>BBa_B0012 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_B0012 short</partinfo> | ||
* Transcription terminator for the <i>E.coli</i> RNA polymerase. | * Transcription terminator for the <i>E.coli</i> RNA polymerase. | ||
| + | * (This is a bad terminator,) | ||
| + | * (It is a promoter in the reverse direction.) | ||
|} | |} | ||
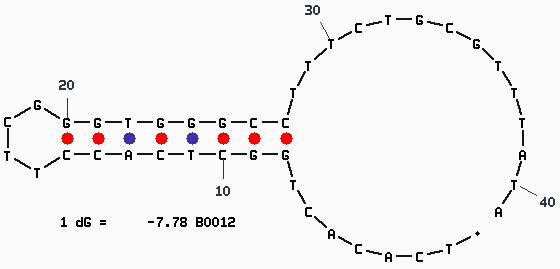
| + | '''Secondary Structure''' | ||
| + | [[Image:Mfold-B0012-1.png]] | ||
| − | + | <hr> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | <partinfo>B0012 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Measurement''' | ||
| + | * [http://openwetware.org/wiki/Cconboy:Terminator_Characterization/Results How these parts were measured] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | >Internal Priming Screening Characterization of BBa_B0012: Has no possible internal priming sites between this BioBrick part and the VF2 or the VR primer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The 2018 Hawaii iGEM team evaluated the 40 most frequently used BioBricks and ran them through an internal priming screening process that we developed using the BLAST program tool. Out of the 40 BioBricks we evaluated, 10 of them showed possible internal priming of either the VF2 or VR primers and sometime even both. The data set has a range of sequence lengths from as small as 12 bases to as large as 1,210 bases. We experienced the issue of possible internal priming during the sequence verification process of our own BBa_K2574001 BioBrick and in the cloning process to express the part as a fusion protein. BBa_K2574001 is a composite part containing a VLP forming Gag protein sequence attached to a frequently used RFP part (BBa_E1010). We conducted a PCR amplification of the Gag-RFP insert using the VF2 and VR primers on the ligation product (pSB1C3 ligated to the Gag + RFP). This amplicon would serve as template for another PCR where we would add the NcoI and BamHI restriction enzyme sites through new primers for ligation into pET14b and subsequent induced expression. Despite gel confirming a rather large, approximately 2.1 kb insert band, our sequencing results with the VR primer and BamHI RFP reverse primer gave mixed results. Both should have displayed the end of the RFP, but the VR primer revealed the end of the Gag. Analysis of the VR primer on the Gag-RFP sequence revealed several sites where the VR primer could have annealed with ~9 - 12 bp of complementarity. Internal priming of forward and reverse primers can be detrimental to an iGEM project because you can never be sure if the desired construct was correctly inserted into the BioBrick plasmid without a successful sequence verification. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Functional Parameters: Austin_UTexas== | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <body> | ||
<partinfo>BBa_B0012 parameters</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_B0012 parameters</partinfo> | ||
| + | <h3><center>Burden Imposed by this Part:</center></h3> | ||
| + | <figure> | ||
| + | <div class = "center"> | ||
| + | <center><img src = "https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/parts/f/fa/T--Austin_Utexas--no_burden_icon.png" style = "width:160px;height:120px"></center> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <figcaption><center><b>Burden Value: -0.5 ± 2.4% </b></center></figcaption> | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | <p> Burden is the percent reduction in the growth rate of <i>E. coli</i> cells transformed with a plasmid containing this BioBrick (± values are 95% confidence limits). This BioBrick did not exhibit a burden that was significantly greater than zero (i.e., it appears to have little to no impact on growth). Therefore, users can depend on this part to remain stable for many bacterial cell divisions and in large culture volumes. Refer to any one of the | ||
| + | <a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3174002">BBa_K3174002</a> - <a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3174007">BBa_K3174007</a> pages for more information on the methods, an explanation of the sources of burden, and other conclusions from a large-scale measurement project conducted by the <a href="http://2019.igem.org/Team:Austin_UTexas">2019 Austin_UTexas team</a>.</p> | ||
| + | <p>This functional parameter was added by the <a href="https://2020.igem.org/Team:Austin_UTexas/Contribution">2020 Austin_UTexas team.</a></p> | ||
| + | </body> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =SUSTech_Shenzhen 2020 characterization= | ||
| + | |||
| + | Protein anti-CRISPR-associated 1 (Aca1) is expressed by T7 promoter, Aca1 will subsequently inhibit the anti-CRISPR promoter, so the gene expression downstream anti-CRISPR will be inhibited until Navitoclax (a compound that can inhibit Aca1 found by SUSTech_Shenzhen) is added artificially. Without the inhibition from Aca1, the expression of genes downstream anti-CRISPR promoter will increase significantly. Therefore, protein expression can be regulated artificially. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We characterised the efficiency of this part of terminating an inhibitor and a report gene in a protein regulation system, the transcription was terminated and it did not affect our composite part [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3423005 BBa_K3423005].The green fluorescence intensity in the composite part using this terminator is measured: https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/parts/3/33/SUSTech_ShenzhenGFP.png | ||
Latest revision as of 11:08, 23 October 2020
|
TE from coliphageT7
|
Secondary Structure
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Measurement
- [http://openwetware.org/wiki/Cconboy:Terminator_Characterization/Results How these parts were measured]
>Internal Priming Screening Characterization of BBa_B0012: Has no possible internal priming sites between this BioBrick part and the VF2 or the VR primer.
The 2018 Hawaii iGEM team evaluated the 40 most frequently used BioBricks and ran them through an internal priming screening process that we developed using the BLAST program tool. Out of the 40 BioBricks we evaluated, 10 of them showed possible internal priming of either the VF2 or VR primers and sometime even both. The data set has a range of sequence lengths from as small as 12 bases to as large as 1,210 bases. We experienced the issue of possible internal priming during the sequence verification process of our own BBa_K2574001 BioBrick and in the cloning process to express the part as a fusion protein. BBa_K2574001 is a composite part containing a VLP forming Gag protein sequence attached to a frequently used RFP part (BBa_E1010). We conducted a PCR amplification of the Gag-RFP insert using the VF2 and VR primers on the ligation product (pSB1C3 ligated to the Gag + RFP). This amplicon would serve as template for another PCR where we would add the NcoI and BamHI restriction enzyme sites through new primers for ligation into pET14b and subsequent induced expression. Despite gel confirming a rather large, approximately 2.1 kb insert band, our sequencing results with the VR primer and BamHI RFP reverse primer gave mixed results. Both should have displayed the end of the RFP, but the VR primer revealed the end of the Gag. Analysis of the VR primer on the Gag-RFP sequence revealed several sites where the VR primer could have annealed with ~9 - 12 bp of complementarity. Internal priming of forward and reverse primers can be detrimental to an iGEM project because you can never be sure if the desired construct was correctly inserted into the BioBrick plasmid without a successful sequence verification.
Functional Parameters: Austin_UTexas
Burden Imposed by this Part:

Burden is the percent reduction in the growth rate of E. coli cells transformed with a plasmid containing this BioBrick (± values are 95% confidence limits). This BioBrick did not exhibit a burden that was significantly greater than zero (i.e., it appears to have little to no impact on growth). Therefore, users can depend on this part to remain stable for many bacterial cell divisions and in large culture volumes. Refer to any one of the BBa_K3174002 - BBa_K3174007 pages for more information on the methods, an explanation of the sources of burden, and other conclusions from a large-scale measurement project conducted by the 2019 Austin_UTexas team.
This functional parameter was added by the 2020 Austin_UTexas team.
SUSTech_Shenzhen 2020 characterization
Protein anti-CRISPR-associated 1 (Aca1) is expressed by T7 promoter, Aca1 will subsequently inhibit the anti-CRISPR promoter, so the gene expression downstream anti-CRISPR will be inhibited until Navitoclax (a compound that can inhibit Aca1 found by SUSTech_Shenzhen) is added artificially. Without the inhibition from Aca1, the expression of genes downstream anti-CRISPR promoter will increase significantly. Therefore, protein expression can be regulated artificially.
We characterised the efficiency of this part of terminating an inhibitor and a report gene in a protein regulation system, the transcription was terminated and it did not affect our composite part BBa_K3423005.The green fluorescence intensity in the composite part using this terminator is measured: