Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2924001"
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
===Characterization=== | ===Characterization=== | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | Note: This data belongs to this basic part, but was collected with the composite part <a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2924010">BBa_K2924010</a> | ||
| + | , containing the promoter <a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_J23119">BBa_J23119</a>, the RBS* <a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K2924009">BBa_K2924009</a> and the double terminator <a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_B0015">BBa_B0015</a>. | ||
| + | |||
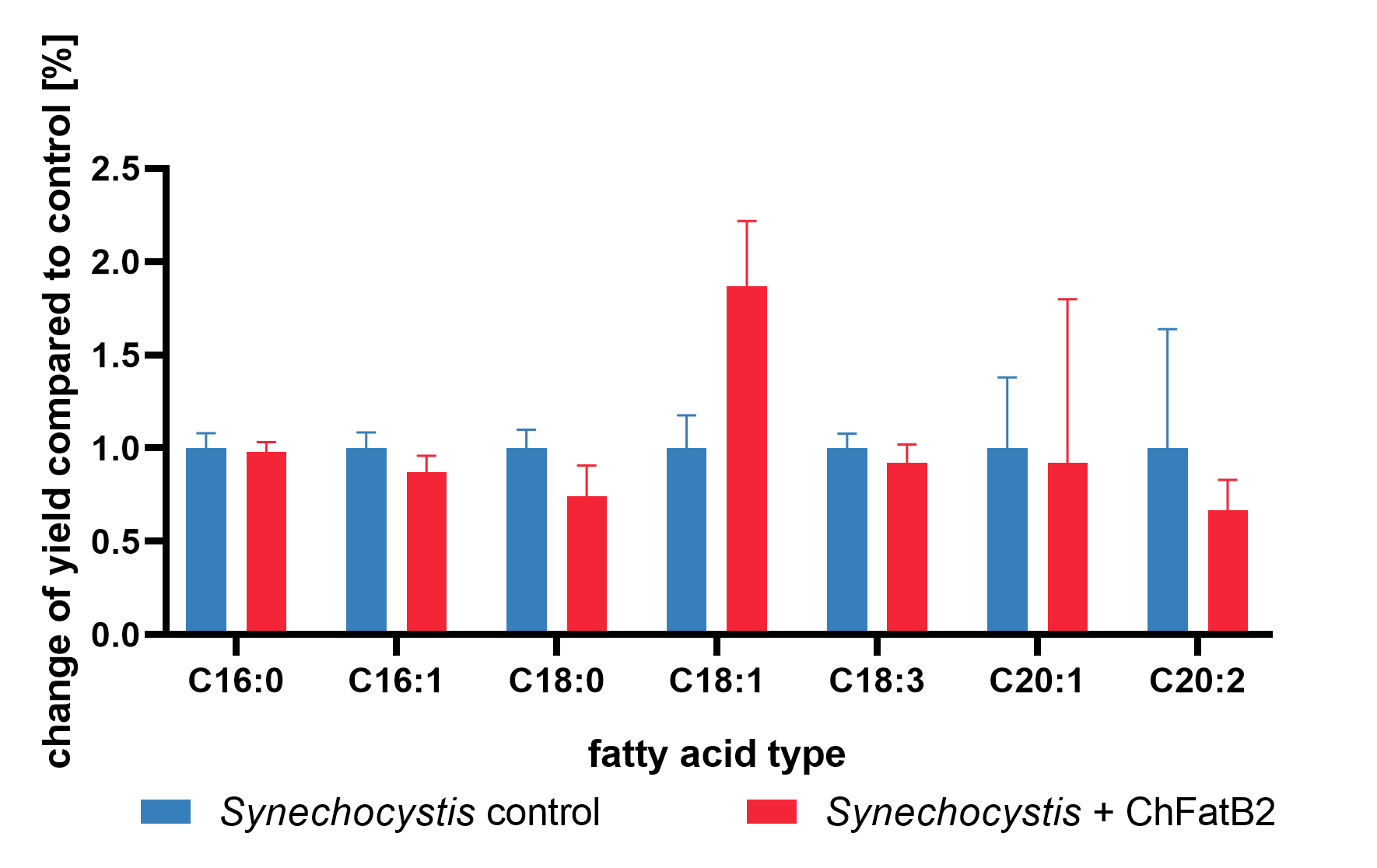
| + | For the fatty acid analysis in <i>Synechocystis sp.</i>, the conjugants and the wild type as control were grown under the same grow conditions. 4 optical density units of the cells, usually, an equivalent of 4 ml at OD<sub>600</sub> = 1, were isolated and used for <a href="https://www.protocols.io/view/fatty-acid-extraction-and-derivatisation-767hrhn/abstract">extraction and derivatization</a> of fatty acids for comparison. The extract was used for gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) to identify different fatty acids compositions in <i>Synechocystis</i> (Fig. 3). | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | [[File:Chfatb2_GC.png|thumb|500px|right|<i><b>Fig. 3:</b> Intracellular levels of a <i>Synechocystis</i> conjugant with the thioesterase ChFatB2 (red) compared to a Synechocystis wildtype (blue). A broad range of free fatty acids are listed and can be compared to the control. </i>]] | ||
Revision as of 09:43, 20 October 2019
Thioesterase from Cuphea hookeriana
Acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] thioesterase (FatB2) from Cuphea hookeriana BBa_K2924001
Usage and Biology
This part contains the (FatB2) gene coding for the Acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] hydrolase of Cuphea hookeriana (cigar plant), which can be found under the UniProt ID: Q39514_CUPHO and shows a thiolester hydrolase activity0.
Background
Fatty acids are long aliphatic chained carboxylic acids, which can be saturated or unsaturated. They have mostly an even number of carbon atoms from 4 to 28. Octanoic acid (Fig. 1) is a saturated fatty acid with 8 carbon atoms, which is also called caprylic acid. It is a colorless 1/light yellow liquid and has a mild to fruity-acid odor 2. It has a molecular mass of 144,21 g/mol.
Decanoic acid (Fig. 2) is a saturated fatty acid with 10 carbon atoms, which is also called capric acid. Capric acid is a white crystalline substance, with a rancid odor 3. It has a molecular weight of 172.27 g/mol.
Fig. 2: Structural formula of decanoic acid. Gray spheres represent a carbon atom, red spheres represent oxygen atom and the white spheres represent hydrogen atoms.
Octanoic acid and decanoic acid are both naturally found in milk of mammalians.
Biosynthesis
Fatty acids are synthesized and elongated by fatty acid synthases, which is a complex containing multiple enzymes. The determination of its length is controlled by thioesterases, a subgroup of hydrolases. They hydrolyze acetyl-CoA esters or acyl carrier protein esters to the corresponding free fatty acid and the Coenzyme A or the acyl carrier protein. The acyl [ acyl-carrier-protein] thioesterase of Cuphea hookeriana (FatB2) uses 8:0- and 10:0-ACP substrates for hydrolyzing the free fatty acids caprylic acid and capric acid4. In planta two isoform of thioesterases, FatA and FatB, are present. They differ in their specificity and activity for different acp-substrates, which is determined by the N-terminus of the isoforms 5. FatB2 stem from the seed of this plant, which contains a high percentage of short and medium chain fatty acids, especially caprylic, capric, lauric, and myristic acid 6.
Usage of caprylic and capric acid
Caprylic acid is added directly to human food affirmed as generally recognized as safe (GRAS) 7,8. The substance is used as a flavoring agent and adjuvant and occurs normally in various foods, like baked goods, cheeses, fats and oils, frozen dairy desserts, gelatins and puddings, soft candy and snack foods. It is found in milk of various mammals and is a minor component of coconut oil and palm kernel oil 9. Therefore, it has a low toxicity ( oral LD50 for rat: 10.08 g/kg)7.
Capric acid is not only important for milk of mammals, coconut and palm kernel oil, but also in the manufacture for artificial fruit flavors and perfumes and also industrially dyes, plastics, food additives and pharmaceuticals 10.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Characterization
Note: This data belongs to this basic part, but was collected with the composite part BBa_K2924010 , containing the promoter BBa_J23119, the RBS* BBa_K2924009 and the double terminator BBa_B0015. For the fatty acid analysis in Synechocystis sp., the conjugants and the wild type as control were grown under the same grow conditions. 4 optical density units of the cells, usually, an equivalent of 4 ml at OD600 = 1, were isolated and used for extraction and derivatization of fatty acids for comparison. The extract was used for gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) to identify different fatty acids compositions in Synechocystis (Fig. 3).