Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3182100"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| − | <span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | + | <span class='h3bb'><h1>Sequence and Features</h1></span> |
<partinfo>BBa_K3182100 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K3182100 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <h1>Introduction</h1> | ||
| − | + | <partinfo>BBa_K3182100 short</partinfo> | |
| − | + | [[File:T--Linkoping_Sweden--fusionproteinillustration.jpg|420px|thumb|right|<b>Figure 1.</b> Mechanism of action. The CBDcipA-fusion is attached to cellulose. By adding thrombin from any source the fusion protein will be cleaved and the C-terminal fusion protein will be released into the solution. By changing the fusion protein to an antimicrobial peptide/enzyme, and using the cellulose as a bandage, the peptide/enzyme can be released into a wound by native human thrombin.]] | |
| − | <partinfo>BBa_K3182100 short</partinfo>[[File:T--Linkoping_Sweden-- | + | |
This part consists of a cellulose binding domain (CBD) from Clostridium thermocellum (C. thermocellum) cellulose scaffolding protein (CipA) and is a central part Clostridium thermocellum's cellusome. The CBD was fused to sfGFP in this part to easily track the binding capacities and to test our release mechanism. The CBD-sfGFP were fused using a flexible GS-linker (-GGGGSGGGGS-). A thrombin cleavage site (-LVPRGS-) was added to the end of the linker and its breakage will leave a glycine and serine attached to the N-terminal of the sfGFP fusion protein. | This part consists of a cellulose binding domain (CBD) from Clostridium thermocellum (C. thermocellum) cellulose scaffolding protein (CipA) and is a central part Clostridium thermocellum's cellusome. The CBD was fused to sfGFP in this part to easily track the binding capacities and to test our release mechanism. The CBD-sfGFP were fused using a flexible GS-linker (-GGGGSGGGGS-). A thrombin cleavage site (-LVPRGS-) was added to the end of the linker and its breakage will leave a glycine and serine attached to the N-terminal of the sfGFP fusion protein. | ||
| Line 14: | Line 15: | ||
An internal BamHI recognition sequence (RS) has been added to enable changeable fusion proteins. BamHI was chosen because its RS codes for glycine and serine, fitting it to the end of the thrombin site. It is also cost-effective enzyme and is unaffected by methylated DNA. | An internal BamHI recognition sequence (RS) has been added to enable changeable fusion proteins. BamHI was chosen because its RS codes for glycine and serine, fitting it to the end of the thrombin site. It is also cost-effective enzyme and is unaffected by methylated DNA. | ||
| − | < | + | This part can be used to track purification, measure CBD binding ability and report cleavage at the thrombin site. |
| − | < | + | |
| + | <br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h2>CBDcipA crystal structure</h2> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:T--Linkoping_Sweden--rotatingcbdanimationloop.gif|420px|thumb|left|<b>Figure 1.</b> Crystal structure of CBDcipA with a resolution of 1.75 Å which were solved by [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/PMC452321 Tormo et al. 1989]. PDB code 1NBC. In red from the left, W118, R112, D56, H57 and Y67, thought to be the surface which interacts strongly with cellulose.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h3>Important molecular faces</h3> | ||
| + | CBDcipA is composed of a nine-stranded beta sandwich with a jelly roll topology and binds a calcium ion. It further contains conserved residues exposed on the surface which map into two clear surfaces on each side of the molecule. One of faces mainly contains planar strips of aromatic and polar residues which may be the cellulose binding part. Further aspect are unknown and unique with this CBD such as the other conserved residues which are contained in a groove. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h3>The choice of cellulose binding domain</h3> | ||
| + | iGEM Linköping 2019 choose CBDcipA due to many other iGEM teams exploring the possibilities of this domain. Our basic design was influenced by iGEM14 Imperial, iGEM15 Edinburgh and iGEM18 Ecuador. Purification and where to place the fusion protein (N- or C-terminal) was determined by studying the former projects. CBDcipA also originates from a thermophilic bacteria which further increases the domains applications. | ||
| + | |||
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
<h2>Expression system</h2> | <h2>Expression system</h2> | ||
| − | The part has a very strong expression with a T7 promotor (<partinfo>BBa_I719005</partinfo>) as well as a 5'-UTR (<partinfo>BBa_K1758100</partinfo>) region which has been shown to further increase expression in E. coli (<partinfo>BBa_K1758106</partinfo>), ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2676996 Olins et al. 1989]), ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23927491 Takahashi et al. 2013]). Both this part and the part were sfGFP was changed for AsPink (<partinfo>BBa_K3182000</partinfo>) showed great expression. | + | The part has a very strong expression with a T7-RNA-polymerase promotor (<partinfo>BBa_I719005</partinfo>) as well as a 5'-UTR (<partinfo>BBa_K1758100</partinfo>) region which has been shown to further increase expression in E. coli (<partinfo>BBa_K1758106</partinfo>), ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2676996 Olins et al. 1989]), ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23927491 Takahashi et al. 2013]). Both this part and the part were sfGFP was changed for AsPink (<partinfo>BBa_K3182000</partinfo>) showed great expression. |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:T--Linkoping_Sweden--expression.png|900px|thumb|center|<b>Figure B.</b> Benchling screenshot of the expression system. The T7-RNA-polymerase promotor is followed by a T7 g10 leader sequence which enhances the binding to the 16S ribosomal RNA. After the leader sequence a poly A spacer is found, which has been shown to increase translation in vitro. Before the start codon a strong RBS, g10-L, followed by an AT-rich spacer can be seen, which will slightly increase translation of the following gene.]] | ||
| − | |||
<h3>Theoretical usage of this part</h3> | <h3>Theoretical usage of this part</h3> | ||
This part utilizes a pCons-AsPink dropout enabling colour-screening for positive colonies. Using BamHI and PstI or SpeI on both this part assembled in pSB1C3 (or vector of choice) and the insert of choice will yield a fusion protein between CBDcipA and the insert. The fusion protein can later be cleaved with thrombin to yield two separate proteins. The C-terminal fusion will have one glycine and one serine added to the N-terminal of the protein. | This part utilizes a pCons-AsPink dropout enabling colour-screening for positive colonies. Using BamHI and PstI or SpeI on both this part assembled in pSB1C3 (or vector of choice) and the insert of choice will yield a fusion protein between CBDcipA and the insert. The fusion protein can later be cleaved with thrombin to yield two separate proteins. The C-terminal fusion will have one glycine and one serine added to the N-terminal of the protein. | ||
Revision as of 08:33, 6 September 2019
Contents
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 592
Illegal NheI site found at 615 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 580
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Introduction
pT7-CBDcipA-pCons-AsPink

This part consists of a cellulose binding domain (CBD) from Clostridium thermocellum (C. thermocellum) cellulose scaffolding protein (CipA) and is a central part Clostridium thermocellum's cellusome. The CBD was fused to sfGFP in this part to easily track the binding capacities and to test our release mechanism. The CBD-sfGFP were fused using a flexible GS-linker (-GGGGSGGGGS-). A thrombin cleavage site (-LVPRGS-) was added to the end of the linker and its breakage will leave a glycine and serine attached to the N-terminal of the sfGFP fusion protein.
Assembly compabilities
An internal BamHI recognition sequence (RS) has been added to enable changeable fusion proteins. BamHI was chosen because its RS codes for glycine and serine, fitting it to the end of the thrombin site. It is also cost-effective enzyme and is unaffected by methylated DNA.
This part can be used to track purification, measure CBD binding ability and report cleavage at the thrombin site.
CBDcipA crystal structure
Important molecular faces
CBDcipA is composed of a nine-stranded beta sandwich with a jelly roll topology and binds a calcium ion. It further contains conserved residues exposed on the surface which map into two clear surfaces on each side of the molecule. One of faces mainly contains planar strips of aromatic and polar residues which may be the cellulose binding part. Further aspect are unknown and unique with this CBD such as the other conserved residues which are contained in a groove.
The choice of cellulose binding domain
iGEM Linköping 2019 choose CBDcipA due to many other iGEM teams exploring the possibilities of this domain. Our basic design was influenced by iGEM14 Imperial, iGEM15 Edinburgh and iGEM18 Ecuador. Purification and where to place the fusion protein (N- or C-terminal) was determined by studying the former projects. CBDcipA also originates from a thermophilic bacteria which further increases the domains applications.
Expression system
The part has a very strong expression with a T7-RNA-polymerase promotor (BBa_I719005) as well as a 5'-UTR (BBa_K1758100) region which has been shown to further increase expression in E. coli (BBa_K1758106), ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2676996 Olins et al. 1989]), ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23927491 Takahashi et al. 2013]). Both this part and the part were sfGFP was changed for AsPink (BBa_K3182000) showed great expression.

Theoretical usage of this part
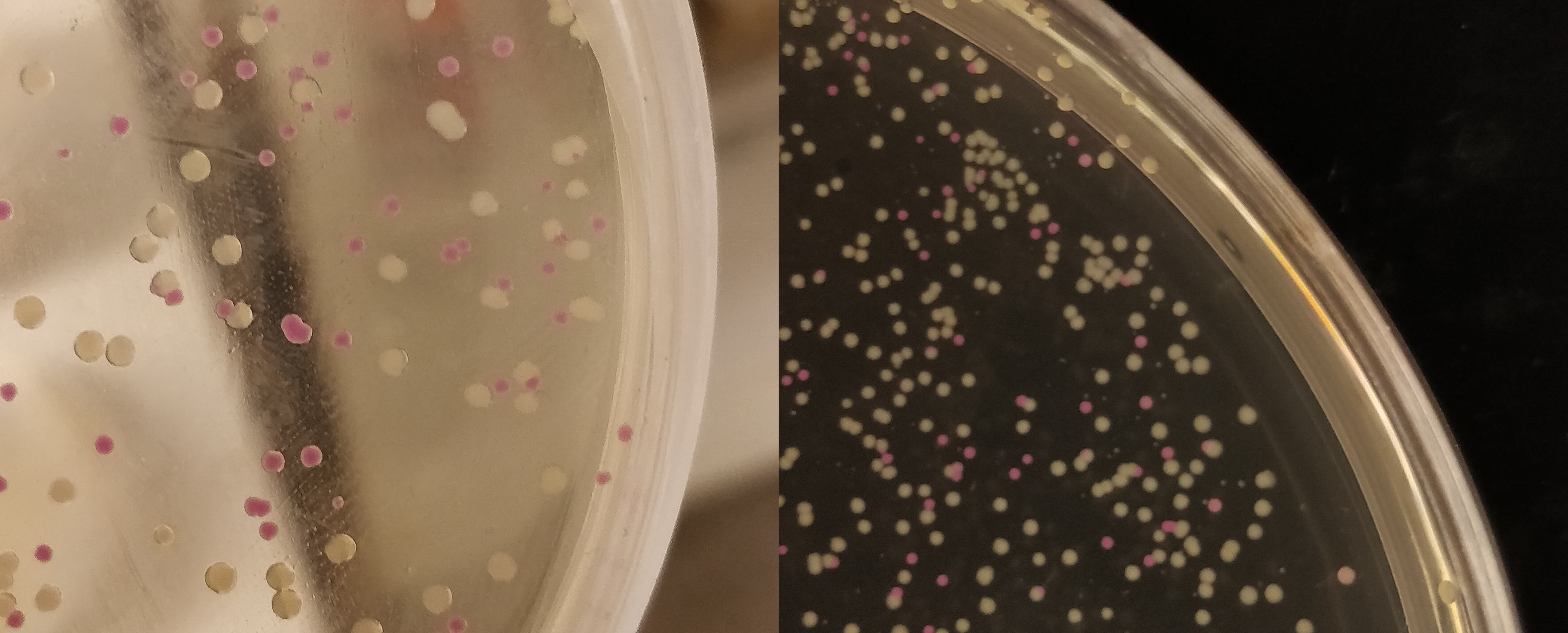
This part utilizes a pCons-AsPink dropout enabling colour-screening for positive colonies. Using BamHI and PstI or SpeI on both this part assembled in pSB1C3 (or vector of choice) and the insert of choice will yield a fusion protein between CBDcipA and the insert. The fusion protein can later be cleaved with thrombin to yield two separate proteins. The C-terminal fusion will have one glycine and one serine added to the N-terminal of the protein.
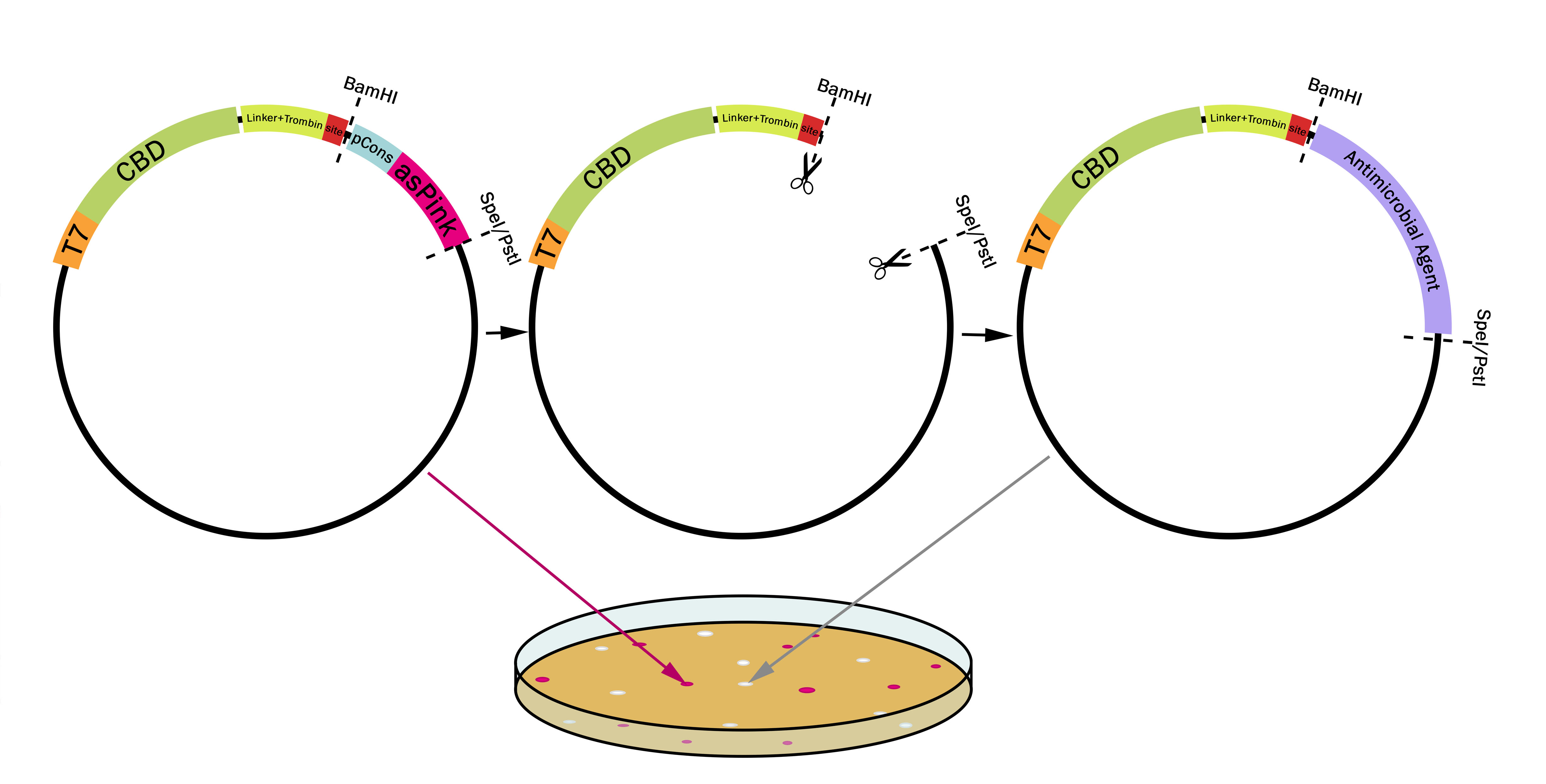
Examples of biobricks assembled with this method
This method was used to assemble: BBa_K3182103, BBa_K3182104, BBa_K3182105, BBa_K3182106, BBa_K3182107, BBa_K3182108.
Usage and Biology
Design any gene which you want to be fused to the CBDcipA with a BamHI recognition sequence in the 5'-end. The biobrick suffix can be used in the 3'-end. Cut the vector and insert with BamHI and PstI (SpeI also works), remove enzymes and mix, no need for gel purification. Using very high molar ratios might not yield any pink colonies at all, a molar ratio insert to vector of 7-20:1 will yield some pink colonies. Transform the host (BL21 (DE3) for quickest results) and incubate at 37 degrees Celsius overnight, if the color is weak or can't be seen, incubate in 24-37 degrees for an additional 16-24 hours.
INSERT AGAROSE GEL HERE

