Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3182100"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K3182100 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K3182100 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | AsPink dropout enabling colour-screening for positive colonies. Using BamHI and SpeI or PstI on both this part assembled in pSB1C3 and the insert of choice will yield a fusion protein between CBDcipA and the insert. The fusion protein can later be cleaved with thrombin to yield two separate proteins. The C-terminal fusion will have one glycine and one serine added to the N-terminal of the protein. | + | A cellulose binding domain (CBDcipA) from Clostridium thermocellum Cellulose scaffolding protein (CipA) which can be used to purify or attach proteins to cellulose, this part has a pCons-AsPink instead of a fusion to the CBDcipA. The part also has a flexible GS-linker (-GGGGSGGGGS-) with a thrombin site (-LVPRGS-, thrombin RS) added at the end, clevage with thrombin will add one glycine and one serine to the N-terminal of the C-terminal fusion protein of the CBDcipA. Also added a BamHI recognition sequence (BamHI RS) to enable changeable fusion protein to the CBDcipA. BamHI was chosen because its RS codes for one glycine and one serine, fitting it to the end of the thrombin site, BamHI is also a cheap enzyme and can be used with methylated DNA. |
| + | |||
| + | The part has a very strong expression with a T7 promotor (<partinfo>BBa_I719005</partinfo>) as well as a 5'-UTR (<partinfo>BBa_K1758100</partinfo>) region which has been shown to further increase expression in E. coli (<partinfo>BBa_K1758106</partinfo>), ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2676996 Olins et al. 1989]), ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23927491 Takahashi et al. 2013]). | ||
| + | |||
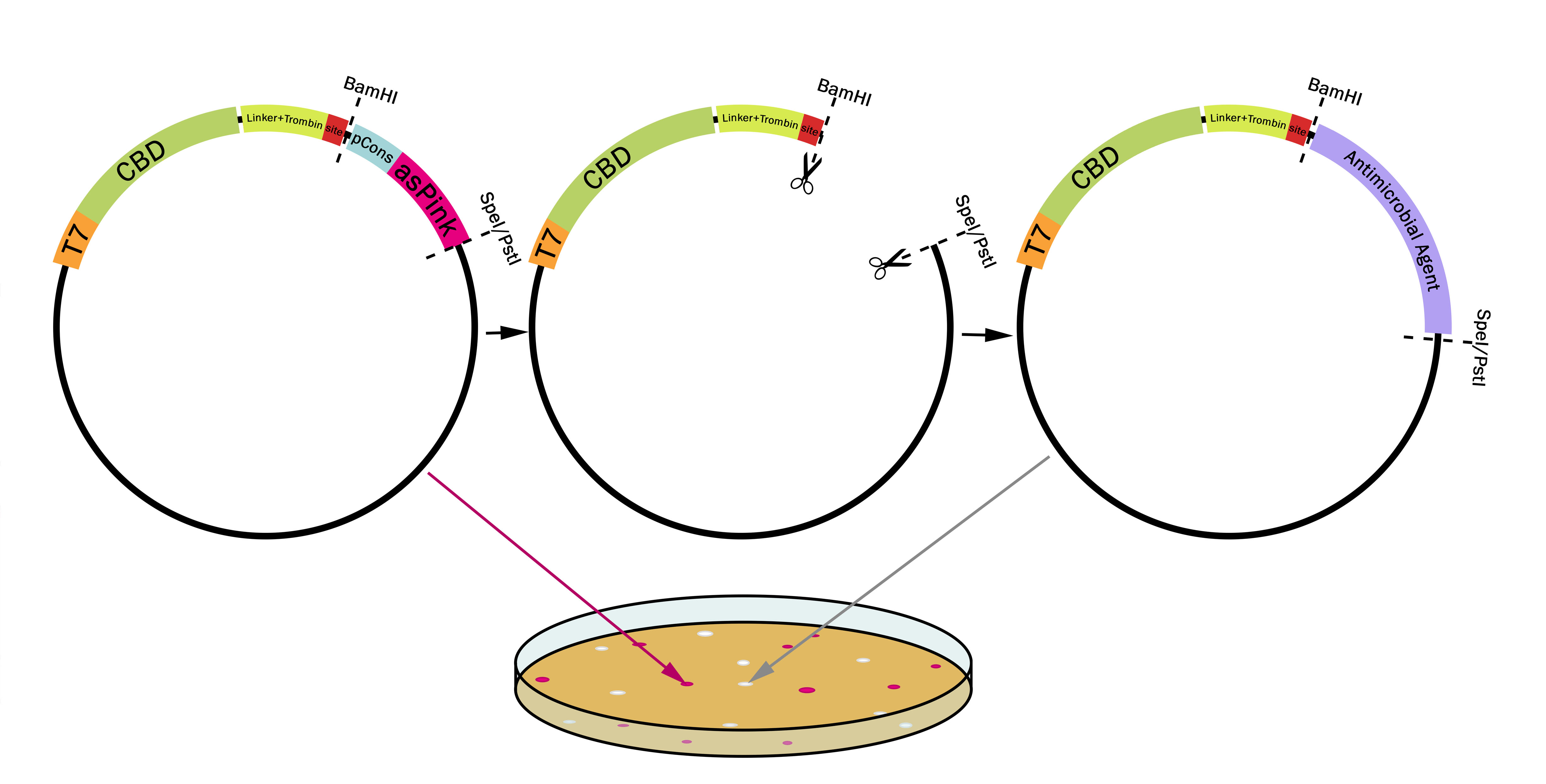
| + | This part utilizes a pCons-AsPink dropout enabling colour-screening for positive colonies. Using BamHI and SpeI or PstI on both this part assembled in pSB1C3 and the insert of choice will yield a fusion protein between CBDcipA and the insert (if designed to correctly). The fusion protein can later be cleaved with thrombin to yield two separate proteins. The C-terminal fusion will have one glycine and one serine added to the N-terminal of the protein. | ||
| − | |||
[[File:T--Linkoping_Sweden--plasmidpstispei.png|800px|thumb|center|<b>Figure 1.</b> The first plasmid (left) contains pCons-AsPink which results in pink colonies. When BamHI is used together with either SpeI or PstI pCons-AsPink is cut out (middle plasmid) and replaced with a compatible biobrick such as an antimicrobial agent (right plasmid). The colonies will then be white due to pCons-AsPink being cleaved from the plasmid. This results in a "pink-white screening". ]] | [[File:T--Linkoping_Sweden--plasmidpstispei.png|800px|thumb|center|<b>Figure 1.</b> The first plasmid (left) contains pCons-AsPink which results in pink colonies. When BamHI is used together with either SpeI or PstI pCons-AsPink is cut out (middle plasmid) and replaced with a compatible biobrick such as an antimicrobial agent (right plasmid). The colonies will then be white due to pCons-AsPink being cleaved from the plasmid. This results in a "pink-white screening". ]] | ||
Revision as of 07:51, 20 July 2019
pT7-CBDcipA-pCons-AsPink
A cellulose binding domain (CBDcipA) from Clostridium thermocellum Cellulose scaffolding protein (CipA) which can be used to purify or attach proteins to cellulose, this part has a pCons-AsPink instead of a fusion to the CBDcipA. The part also has a flexible GS-linker (-GGGGSGGGGS-) with a thrombin site (-LVPRGS-, thrombin RS) added at the end, clevage with thrombin will add one glycine and one serine to the N-terminal of the C-terminal fusion protein of the CBDcipA. Also added a BamHI recognition sequence (BamHI RS) to enable changeable fusion protein to the CBDcipA. BamHI was chosen because its RS codes for one glycine and one serine, fitting it to the end of the thrombin site, BamHI is also a cheap enzyme and can be used with methylated DNA.
The part has a very strong expression with a T7 promotor (BBa_I719005) as well as a 5'-UTR (BBa_K1758100) region which has been shown to further increase expression in E. coli (BBa_K1758106), ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2676996 Olins et al. 1989]), ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23927491 Takahashi et al. 2013]).
This part utilizes a pCons-AsPink dropout enabling colour-screening for positive colonies. Using BamHI and SpeI or PstI on both this part assembled in pSB1C3 and the insert of choice will yield a fusion protein between CBDcipA and the insert (if designed to correctly). The fusion protein can later be cleaved with thrombin to yield two separate proteins. The C-terminal fusion will have one glycine and one serine added to the N-terminal of the protein.
Usage and Biology
Incubating the bacteria, first in 37 degrees Celsius for 16 hours and then 16 degrees for 24 hours gave a very weak color. A protein production host, such as BL21 (DE3) gave the best results, where color development could be seen after the first incubation.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 592
Illegal NheI site found at 615 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 580
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
