Difference between revisions of "AHL"
(→Acyl-HSL's in different species) |
Macampbell (Talk | contribs) (→Acyl-HSL's in different species) |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
"Although the target genes regulated by AIs are extremely varied, the basic mechanism of AIs biosynthesis and gene regulation seems to be conserved in different bacteria. The general feature of gene regulation by AIs is cell-density dependence, also known as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quorum_sensing "quorum sensing"]. | "Although the target genes regulated by AIs are extremely varied, the basic mechanism of AIs biosynthesis and gene regulation seems to be conserved in different bacteria. The general feature of gene regulation by AIs is cell-density dependence, also known as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quorum_sensing "quorum sensing"]. | ||
| − | At low cell densities, the AIs are at low concentrations, and, at high cell densities, the AIs can accumulate to a concentration sufficient for activation of related regulatory genes. Because the concentration of AHL's is a key factor in determining virulence gene expression in several pathogenic bacteria, it is possible to develop a strategy for disease control by controlling production of AIs or eliminating AIs produced by pathogenic bacteria." | + | At low cell densities, the AIs are at low concentrations, and, at high cell densities, the AIs can accumulate to a concentration sufficient for activation of related regulatory genes. Because the concentration of AHL's is a key factor in determining virulence gene expression in several pathogenic bacteria, it is possible to develop a strategy for disease control by controlling production of AIs or eliminating AIs produced by pathogenic bacteria."<cite>Dong</cite> |
==Acyl-HSL's in different species== | ==Acyl-HSL's in different species== | ||
| − | "In recent years, AIs have been identified in several Gram-negative bacteria. AIs are involved in the regulation of a range of biological functions, including Ti plasmid conjugal transfer in Agrobacterium tumefaciens, induction of virulence genes in Erwinia carotovora, Erwinia chrysanthemi, Erwinia stewartii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas solanacearum, and Xenorhabdus nematophilus, regulation of antibiotic production in Pseudomonas aureofaciens and E. carotovora, regulation of swarming motility in Serratia liquefaciens, and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens and P. aeruginosa. Many more bacterial species are known to produce AIs, but the relevant biological functions have not yet been established." | + | "In recent years, AIs have been identified in several Gram-negative bacteria. AIs are involved in the regulation of a range of biological functions, including Ti plasmid conjugal transfer in Agrobacterium tumefaciens, induction of virulence genes in Erwinia carotovora, Erwinia chrysanthemi, Erwinia stewartii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas solanacearum, and Xenorhabdus nematophilus, regulation of antibiotic production in Pseudomonas aureofaciens and E. carotovora, regulation of swarming motility in Serratia liquefaciens, and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens and P. aeruginosa. Many more bacterial species are known to produce AIs, but the relevant biological functions have not yet been established."<cite>Dong</cite> |
{|{{Table}} | {|{{Table}} | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
|Butanoyl-homoserine lactone | |Butanoyl-homoserine lactone | ||
|C4HSL | |C4HSL | ||
| − | |'' | + | |''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' |
| | | | ||
|[http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/09945 Sigma Aldrich (#09945)] | |[http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/09945 Sigma Aldrich (#09945)] | ||
|align='center'|[[Image:Butryl-homoserine lactone.GIF|100px]] | |align='center'|[[Image:Butryl-homoserine lactone.GIF|100px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |N-(3-oxododecanoyl) homoserine lactone ([http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pubmed&pubmedid=8278364 Reference]) | ||
| + | |3OC12HSL | ||
| + | |''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' | ||
| + | |Las system signaling molecule [[Part:BBa_C0078]] | ||
| + | |[http://www.caymanchem.com/app/template/Product.vm/catalog/10007895/tab/data/a/z Cayman Chemicals (#10007895)] | ||
| + | |align='center'|[[Image:3OC12HSL.jpg|100px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[3OC6HSL|3-oxohexanoyl-homoserine lactone]] | |[[3OC6HSL|3-oxohexanoyl-homoserine lactone]] | ||
| Line 37: | Line 44: | ||
|Hexanoyl-homoserine lactone | |Hexanoyl-homoserine lactone | ||
|C6HSL | |C6HSL | ||
| − | | | + | |''C. violaceum'' |
|Very similar to 3OC6HSL | |Very similar to 3OC6HSL | ||
|[http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/09926 Sigma Aldrich (#09926)] | |[http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/09926 Sigma Aldrich (#09926)] | ||
| Line 44: | Line 51: | ||
|Heptanoyl-homoserine lactone | |Heptanoyl-homoserine lactone | ||
|C7HSL | |C7HSL | ||
| − | | | + | |''E. psidii'' R. IBSBF 435T |
| | | | ||
|[http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/10939 Sigma Aldrich (#10939)] | |[http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/10939 Sigma Aldrich (#10939)] | ||
| Line 51: | Line 58: | ||
|Octanoyl-homoserine lactone | |Octanoyl-homoserine lactone | ||
|C8HSL | |C8HSL | ||
| − | | | + | |''B. cepacia'', ''V. fischeri'' |
| | | | ||
|[http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/10940 Sigma Aldrich (#10940)] | |[http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/10940 Sigma Aldrich (#10940)] | ||
|align='center'|[[Image:Octanoyl-homoserine lactone.GIF|100px]] | |align='center'|[[Image:Octanoyl-homoserine lactone.GIF|100px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |3-oxoctanoyl-homoserine lactone | ||
| + | |3OC8HSL | ||
| + | |''A. tumefaciens'' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |[http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/SIGMA/O1764 Sigma Aldrich (#O1764)] | ||
| + | |align='center'|[[Image:3-Oxooctanoyl-L-homoserine lactone2.GIF|125px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Decanoyl-homoserine lactone | |Decanoyl-homoserine lactone | ||
|C10HSL | |C10HSL | ||
| − | | | + | |''B. pseudomallei '' |
| | | | ||
|[http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/17248 Sigma Aldrich (#17248)] | |[http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/17248 Sigma Aldrich (#17248)] | ||
| Line 65: | Line 79: | ||
|Dodecanoyl-homoserine lactone | |Dodecanoyl-homoserine lactone | ||
|C12HSL | |C12HSL | ||
| − | | | + | |Synthetic |
| | | | ||
|[http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/17247 Sigma Aldrich (#17247)] | |[http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/17247 Sigma Aldrich (#17247)] | ||
|align='center'|[[Image:Dodecanoyl-homoserine lactone.GIF|100px]] | |align='center'|[[Image:Dodecanoyl-homoserine lactone.GIF|100px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Tetradecanoyl-homoserine lactone |
| − | | | + | |C14HSL |
| − | | | + | |Synthetic |
| | | | ||
|[http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/10937 Sigma Aldrich (#10937)] | |[http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/10937 Sigma Aldrich (#10937)] | ||
| Line 82: | Line 96: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | # Dong | + | <biblio> |
| − | # Collins | + | #Engebrecht pmid=6377310 |
| + | #Dong pmid=10716724 | ||
| + | #Collins pmid=15660998 | ||
| + | </biblio> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:55, 18 June 2008
Full name: [N-]acyl-homoserine lactones
These are small signalling molecules which are employed in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quorum_sensing "quorum sensing"] systems.
They are also known as autoinducers (AIs) and are present in many Gram-negative bacteria.
"Although the target genes regulated by AIs are extremely varied, the basic mechanism of AIs biosynthesis and gene regulation seems to be conserved in different bacteria. The general feature of gene regulation by AIs is cell-density dependence, also known as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quorum_sensing "quorum sensing"].
At low cell densities, the AIs are at low concentrations, and, at high cell densities, the AIs can accumulate to a concentration sufficient for activation of related regulatory genes. Because the concentration of AHL's is a key factor in determining virulence gene expression in several pathogenic bacteria, it is possible to develop a strategy for disease control by controlling production of AIs or eliminating AIs produced by pathogenic bacteria."Dong
Acyl-HSL's in different species
"In recent years, AIs have been identified in several Gram-negative bacteria. AIs are involved in the regulation of a range of biological functions, including Ti plasmid conjugal transfer in Agrobacterium tumefaciens, induction of virulence genes in Erwinia carotovora, Erwinia chrysanthemi, Erwinia stewartii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas solanacearum, and Xenorhabdus nematophilus, regulation of antibiotic production in Pseudomonas aureofaciens and E. carotovora, regulation of swarming motility in Serratia liquefaciens, and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens and P. aeruginosa. Many more bacterial species are known to produce AIs, but the relevant biological functions have not yet been established."Dong
| Full Name | Molecule abbreviation | Species | Notes | Source | Images (from Sigma Aldrich) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Butanoyl-homoserine lactone | C4HSL | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | [http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/09945 Sigma Aldrich (#09945)] | 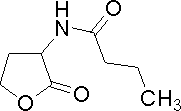
| |
| N-(3-oxododecanoyl) homoserine lactone ([http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pubmed&pubmedid=8278364 Reference]) | 3OC12HSL | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Las system signaling molecule Part:BBa_C0078 | [http://www.caymanchem.com/app/template/Product.vm/catalog/10007895/tab/data/a/z Cayman Chemicals (#10007895)] | |
| 3-oxohexanoyl-homoserine lactone | 3OC6HSL | V. fischeri | Lux system signaling molecule | [http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/SIGMA/K3007 Sigma Aldrich (#K3007)] | |
| Hexanoyl-homoserine lactone | C6HSL | C. violaceum | Very similar to 3OC6HSL | [http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/09926 Sigma Aldrich (#09926)] | 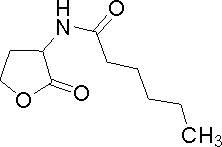
|
| Heptanoyl-homoserine lactone | C7HSL | E. psidii R. IBSBF 435T | [http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/10939 Sigma Aldrich (#10939)] | 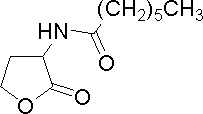
| |
| Octanoyl-homoserine lactone | C8HSL | B. cepacia, V. fischeri | [http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/10940 Sigma Aldrich (#10940)] | 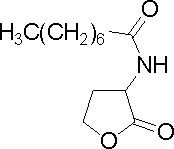
| |
| 3-oxoctanoyl-homoserine lactone | 3OC8HSL | A. tumefaciens | [http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/SIGMA/O1764 Sigma Aldrich (#O1764)] | 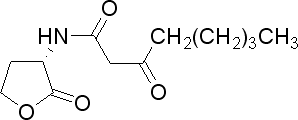
| |
| Decanoyl-homoserine lactone | C10HSL | B. pseudomallei | [http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/17248 Sigma Aldrich (#17248)] | 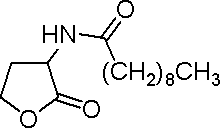
| |
| Dodecanoyl-homoserine lactone | C12HSL | Synthetic | [http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/17247 Sigma Aldrich (#17247)] | 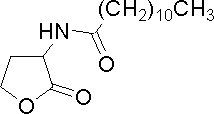
| |
| Tetradecanoyl-homoserine lactone | C14HSL | Synthetic | [http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search/ProductDetail/FLUKA/10937 Sigma Aldrich (#10937)] | 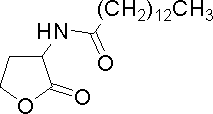
|
Related Pages
- Featured Parts:Cell-Cell-Signaling - A listing of parts relating to the Lux operon's signalling system
References
<biblio>
- Engebrecht pmid=6377310
- Dong pmid=10716724
- Collins pmid=15660998
</biblio>
