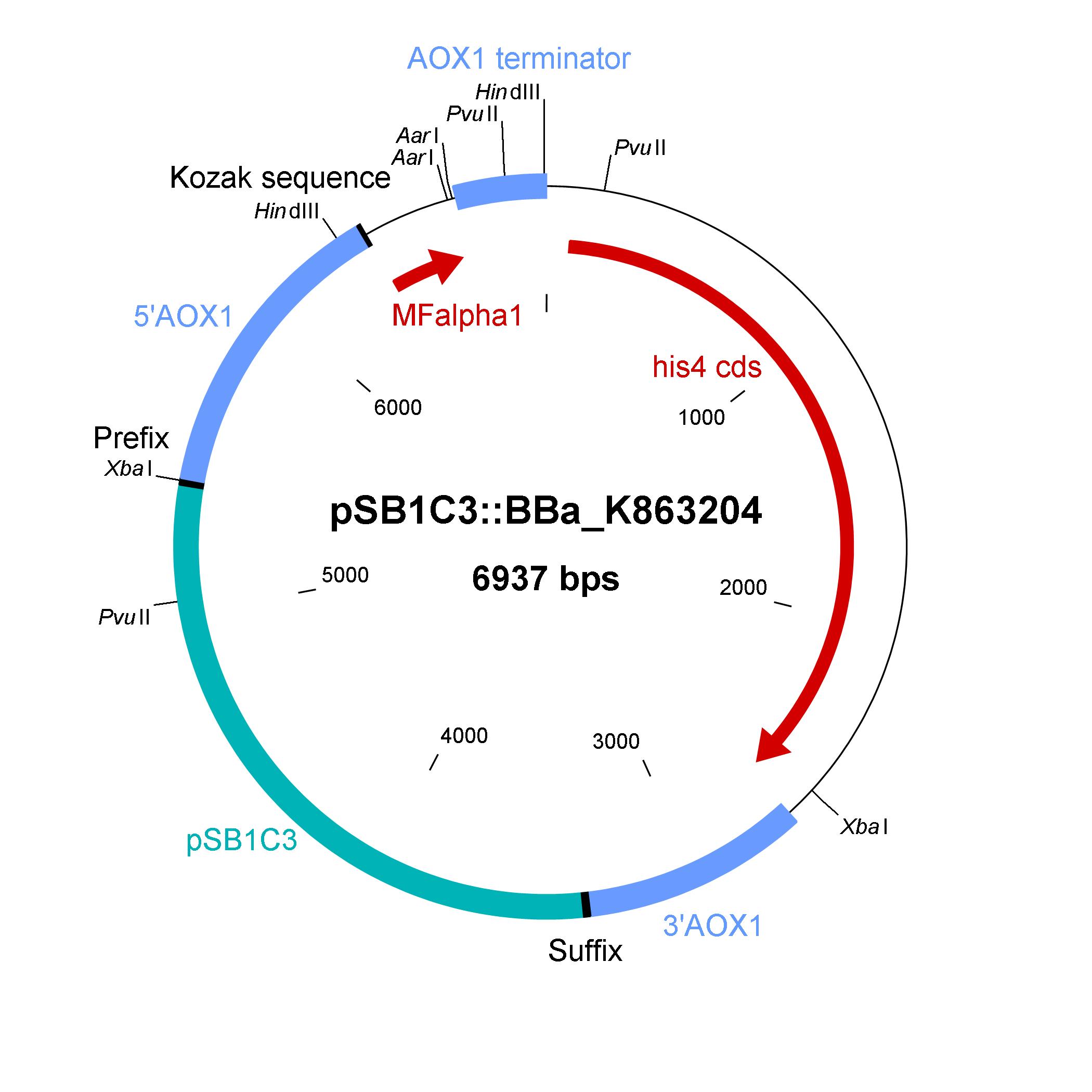
Part:BBa_K863204
shuttle vector pECPP11JS for recombination of genes of interest in yeast
The design of a minimal shuttle vector system with defined regions (or better DNA fragments) for expression and secretion of proteins of interest (POI), like laccase, which needed glycolisation is the basic concept. The shuttle vector needs a bacterial part for cloning in bacteria (like E. coli) and an eucaryotic part for genomic integration and selection in yeast (like P. pastoris). An other team will be able to clime in frame their gene of interest via the AarI restriction site. With only one restriction ligation cloning step the shuttle vector will be ready to use and integrate in the eucaryote P. pastoris.
The shuttle vector consists of the plasmid pSB1C3, 5' UTR of alcohol oxidase 1 gene (aox1) containing the aox1 promoter region, Kozak sequence, mating factor alpha 1 (MFalpha1), AarI restriction site, aox1 terminator, his4 gene and 3' UTR of aox1 gene. Cloning and plasmid replication in E. coli are able via the pSB1C3 part. The gene of interest (like laccase) can be included in frame with MFalpha1 via AarI restriction site. With the N-terminal MFalpha1 the POI could be secreted in the media. Genomic integation of MFalpha1-taged POI is able via the 5' UTR and 3' UTR of the aox1 gene. This allows a double cross over and the genomic integration without any bacterial proportion of DNA which could be a decisive point for industrial application. The complementation of histidine auxotrophie via his4 gene was chosen instead of a zeocine resistance. This selection strategy is chosen because we want to avoid the application of antibiotics.
Gibson assembly was used for building the shuttle vector and the fragments with 5' overlap were amplified via PCR. In addition, the fragments were designed as basic BioBrick parts for different applications by the community.
Sequence and Features
- 10INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]Illegal XbaI site found at 4086
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 3381
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 1
Illegal BglII site found at 1532
Illegal BamHI site found at 1889
Illegal XhoI site found at 1196 - 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal XbaI site found at 4086
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal XbaI site found at 4086
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI site found at 4242
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 2041
Shuttle vector in E. coli
The developed shuttle vector could be transformed in E. coli and analyzed by restriction with the enzymes PvuII and HindIII. The restriction pattern is positive. A sequencing was also done.
Shuttle vector in P. pastoris
After linearization by restriction with EcoRI and SpeI the shuttle vector could be transformed in competent P. pastoris cells. Transformants grow on selective media plates because of complementation of histidine auxotrophy. For differentiation between the M+ and Ms genotype a PCR with the Primer 5AOX-Genotyp-FW (5'-GACTGGTTCCAATTGACAAGC-3') and TT-Genotyp-RV (5'-GCAAATGGCATTCTGACATCC-3') have to be done. The M+ phenotype means that a single cross over recombination took place and the cultivation with methanol have no effect on the growth of the cells. The Ms phenotype means that a double cross over recombination took place and the gene aox1 was removed from the genome. During cultivation and induction with methanol the cells grow slow, because now only the gene aox2 exist in the genome.
//chassis/eukaryote/yeast
| None |