Part:BBa_K3158006
LPPGFP
A signal peptide (sometimes referred to as signal sequence, targeting signal, localization signal, localization sequence, transit peptide, leader sequence or leader peptide) is a short (5-30 amino acids long) peptide present at the N-terminus of the majority of newly synthesized proteins that are destined towards the secretory pathway. If we found the protein(s) which are able to degrade m-phenylenediamine, we would try to secret the protein(s) out of the cell to improve the efficiency of degradation. We use these signal peptides infusion with GFP: LPPGFP, LTBGFP, OmpAGFP, OmpCGFP, OmpFGFP, OmpTGFP, PelBGFP, PhoAGFP, PhoEGFP.
Usage and Biology
BBa_K3158006 LPPGFP
Methods:
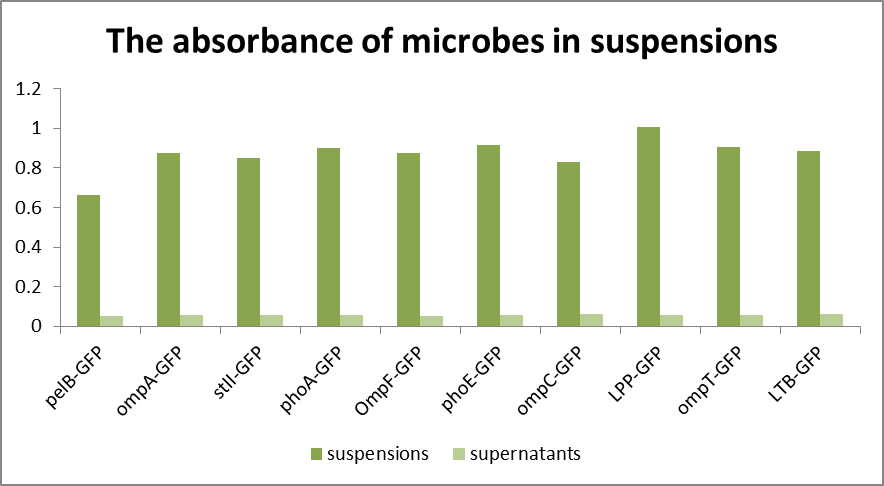
1. 20 bacteria culture 20ul were absorbed and put into the microtitration plate.
2. Entrifuge the remaining bacteria solution at 12000g for 1 min.
3. Draw 20ul of supernatant from 20 bottles after centrifugation and put it into the microtitration plate.
4. Put the plate into the instrument to measure the absorbance and fluorescence.
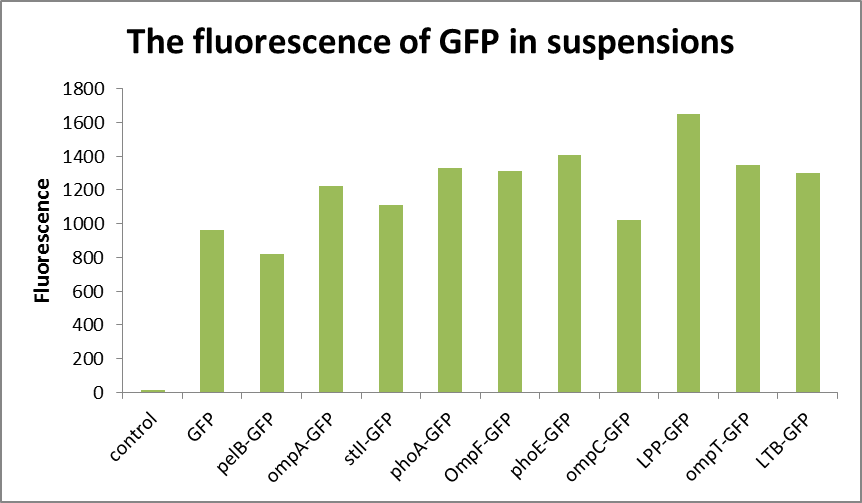
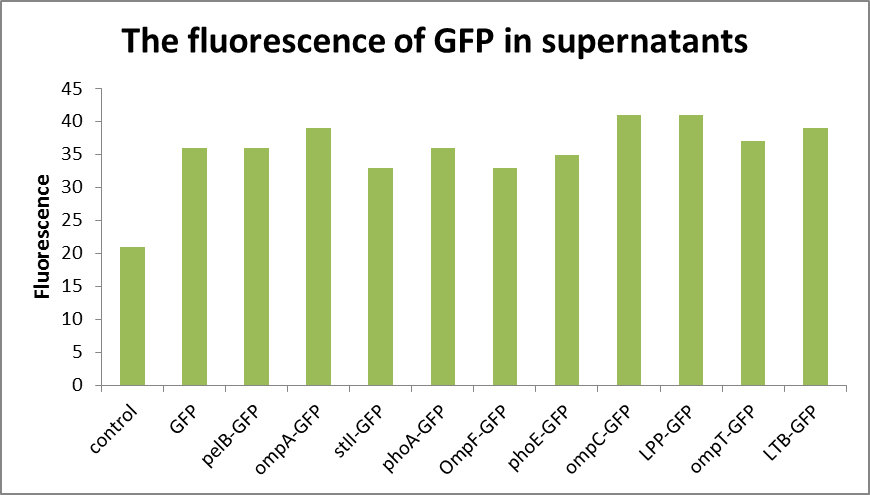
Results:
As can be seen from Fig1, the absorbance of the bacterial solution is generally higher than that of the supernatant, while the fluorescence measurement shows that the value of the supernatant is relatively small, generally 30-40, compared with the value of about 1000 of the bacterial solution(Fig2 and Fig3). The fluorescence of pelB-GFP was higher than the control. It turned out that the protein pelB-GFP was expressed successfully and secreted to the extracellular environment.
the low fluorescence of supernatant indicates that E. coli can only secrete a small amount of fluorescent substances to the extracellular environment. And liken to the control group, it is easy to confirm the specific amount of fluorescent substances secreted.
Next Day
Methods:
1. Take out the E. coli cultured in a shaker yesterday (6 in total) and divide them into three groups: no GFP gene, GFP gene without signal peptide and GFP gene with signal peptide. Proper amount of bacterial suspensions and supernatant samples after centrifugation were successively extracted for absorbance detection.
2. Extract appropriate amount of bacteria solution: extract 200 microliters of bacteria solution from each tube and put it into group A 1-6 Wells of 96-well plate
3. Supernatant extraction: again, extract 500 microliters of bacterial liquid from each tube, place them in the labeled EP tube, and put them into a centrifuge for centrifugation. After centrifugation, 200 microliters of supernatant were extracted from each tube and put into group B Wells 1-6 of the 96-well plate.
4. Put the 96-well plates into the microplate reader and test their absorbance.
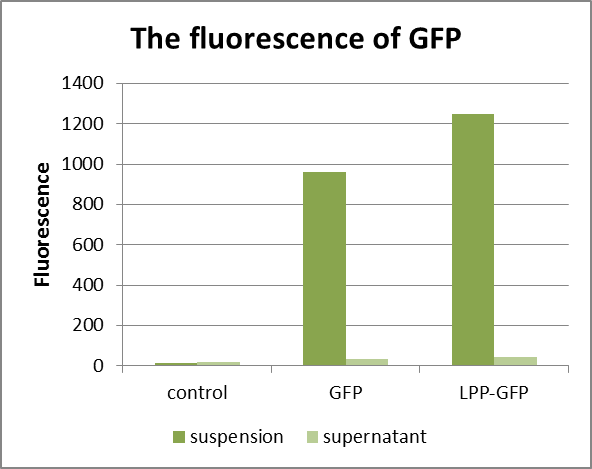
Results:
In suspension, GFP containing E. coli have high value of fluorescence, while adding signal peptide has a little effect. So the signal peptide can improve the absorbance a little.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
| None |