Part:BBa_K259007
AraC Promoter fused with RBS
This part has the arabinose regulated promoter (AraC/pBAD) upstream of a ribosome binding site. This is ideal for inserting a protein to be expressed downstream of this part as it's expression can be regulated by the presence of the concentration of arabinose in the growing environment/media of the cells.
What this part actually does
This composite part includes the AraC/pBAD promoter and a strong ribosome binding site designed from the Anderson family of RBS.
The AraC/pBAD promoter can be used with prokaryotic chassis to regulate expresion of proteins.
When the AraC/pBAD promoter is placed upstream of your canditate translational unit (protein to be expressed) it allows control of the trancription of the said protein. This is done via controlling the concentration of arabinose sugar in the environment/solution of bacterial growth.
Controlling the transcription will not ensure translation. The ribosome binding site is ideally placed a small distance away from the promoter site to ensure that the ribosome will bind and start translating the protein coding sequence found downstream.
Part assessment
The AraC-RBS was tested by promoter induction at various concentrations of L-Arabinose sugar. Concentrations used were 0.05% 0.1% 0.2% 0.5% and 1.0% . Two constructs were tested:
1.AraC-RBS-FhuA-GFP
2.AraC-RBS-GFP(E0040)-Terminator(B0014)
Construct 1. This causes reduction in optical density at A600 after promoter induction with L-Arabinose.
Construct 2. This does not cause reduction in optical density at A600 after promoter induction with L-Arabinose.
Optical density at A600nm is indicative of cell density. L-Arabinose concentration is in weight per volume. A drop in cell density might be indicative of cell growth inhibition and partial cell lysis. In this case construct 1 probably lyses the cells partially as a protein fusion involving two membrane protein could cause cell lysis.
The graph below illustrates that the part can induce promoter with as little as 0.05%(w/v) [L-Arabinose].

Characterization - Team:UFRGS_Brazil 2019
Measurement BioBrick
To test this part (1), we combined it with a mRFP translation unit fused with a terminator (RBS + CDS + Terminator) (7). To do so, we digested the former (1) with EcoRI and SpeI, and the latter (7) with XbaI and PstI in an overnight cleavage reaction.
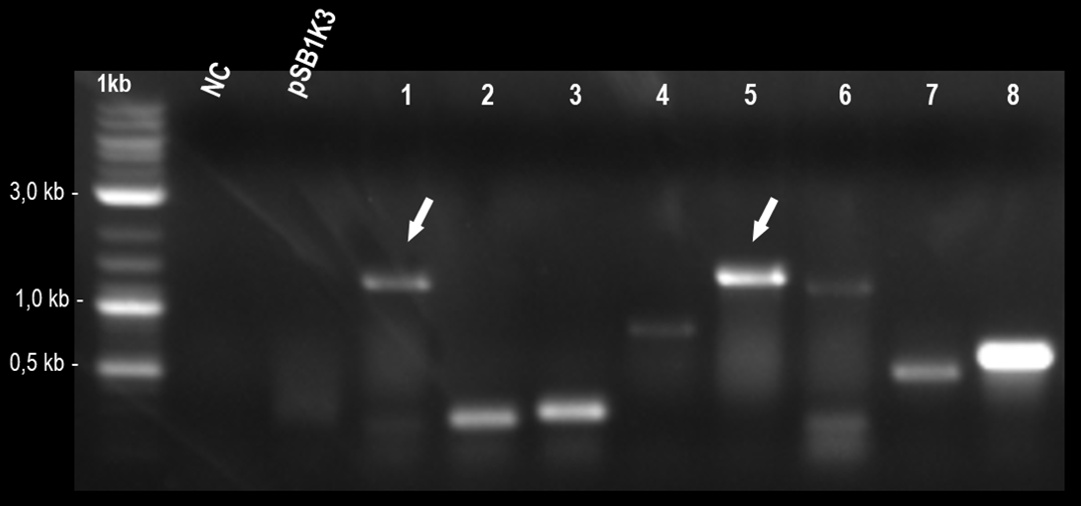
After this, we made a ligation reaction overnight, to unite these fragments, generating the part BBa_K3215011, which was designed to measure the efficiency of part "AraC promoter fused with RBS" (BBa_K259007). This construction was inserted into pSB1K3, that was previously cleaved overnight with PstI and EcoRI, in another overnight ligation reaction. The colony PCR is showed bellow.
Fig. 1. Colony PCR indicating positive colonies
Part characterization
To add new data to this part, we made an arabinose curve according to data showed in our model simulations, which can be accessed in our Modelling page in our Wiki: Team 2019 UFRGS_Brazil
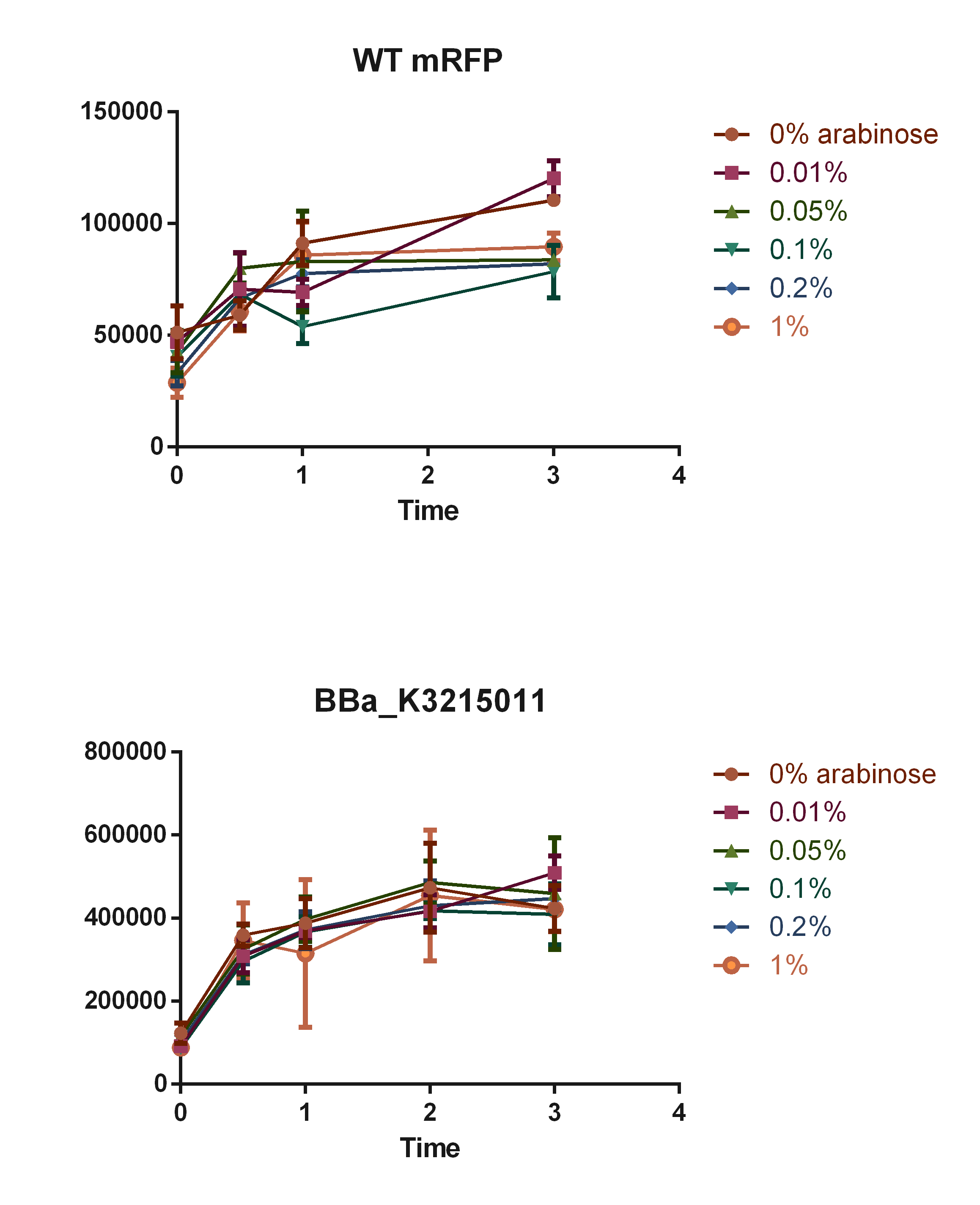
The concentrations used were of 0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2 and 1% of arabinose. The mRFP expression was measured overtime using the imaging system SpectraMax i3, with excitation in 558 nm and excitation at 607 nm, and the measures were compared with WT E. coli K-12.
Fig. 2. Curve of mRFP expression in different arabinose percentages.
As observed in the graph, E. coli with BBa_K3215011 part was able to produce fluorescence signals stronger than the observed in the WT (background signal), although concentrations of arabinose did not show impact in mRFP expression, going in contrast with the predictions made by our in silico kinetic study of the promoter induction.
To show mRFP fluorescence, we plated the cells with arabinose and made images of microscopy with an inverted microscope of fluorescence Axiovert 200:
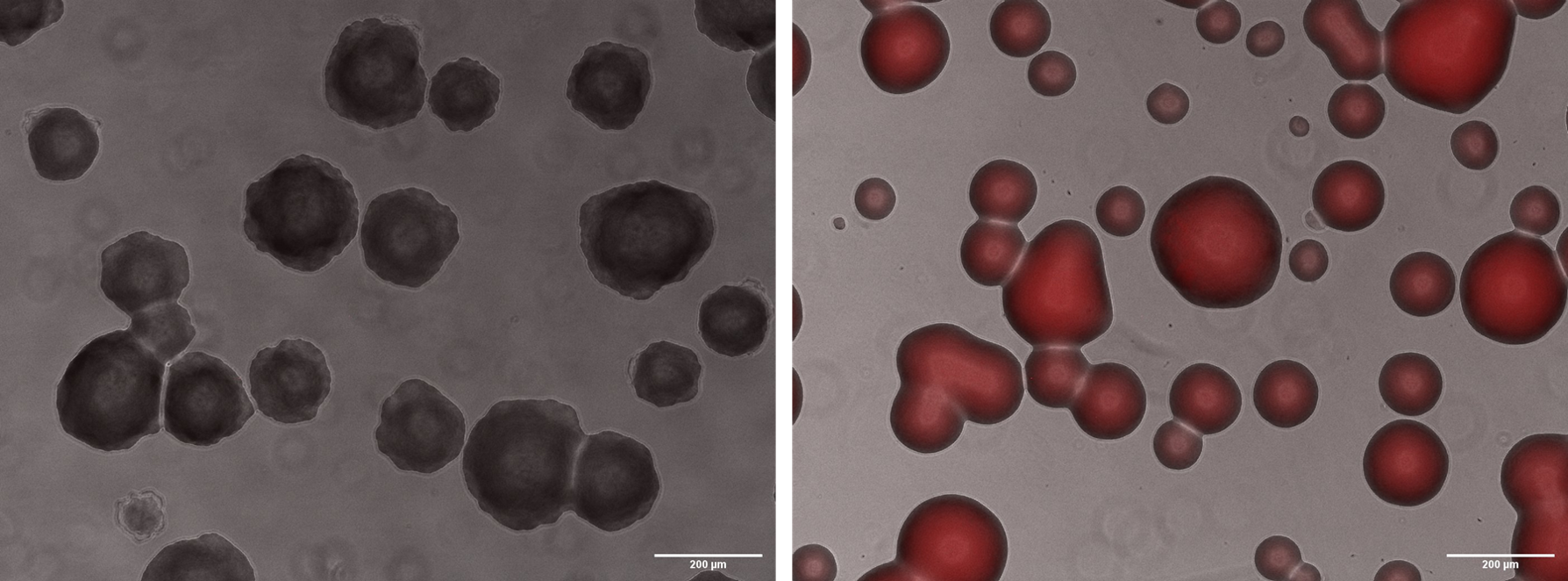
Fig. 3. Microscopy with 10x magnification. A) WT colonies. B) BBa_K3215011 containing colonies.
As we can observe, only colonies with the BBa_K3215011 plated in arabinose media were able to express mRFP, evidencing that our constructions were correct.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 294
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 125
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal SapI site found at 107
//direction/forward
//promoter
//rbs/prokaryote/constitutive/anderson
//rbs/prokaryotic/constitutive/miscellaneous
//regulation/multiple
//regulation/negative
//regulation/positive
//rnap/prokaryote/ecoli/sigma70
regulator
transcriptional
| biology | |
| control | araC |
| direction | Forward |
| negative_regulators | |
| o_h | |
| o_l | |
| positive_regulators | |
| rbs |