Part:BBa_K2586011
Palf4-RBS-gltT: Palf4 linked to a RBS linked to gltT
This part is a composite part made from (BBa_K2586000) ; (BBa_K2586008) and (BBa_K2586001).
It connects the Palf4 Promoter to a RBS and also makes a connection to the gltT gene. This composite part was used within the soil bacterium Bacillus subtilis.
Sequence and Features
- 10INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]Illegal PstI site found at 163
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal PstI site found at 163
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal PstI site found at 163
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal PstI site found at 163
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 799
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 1180 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
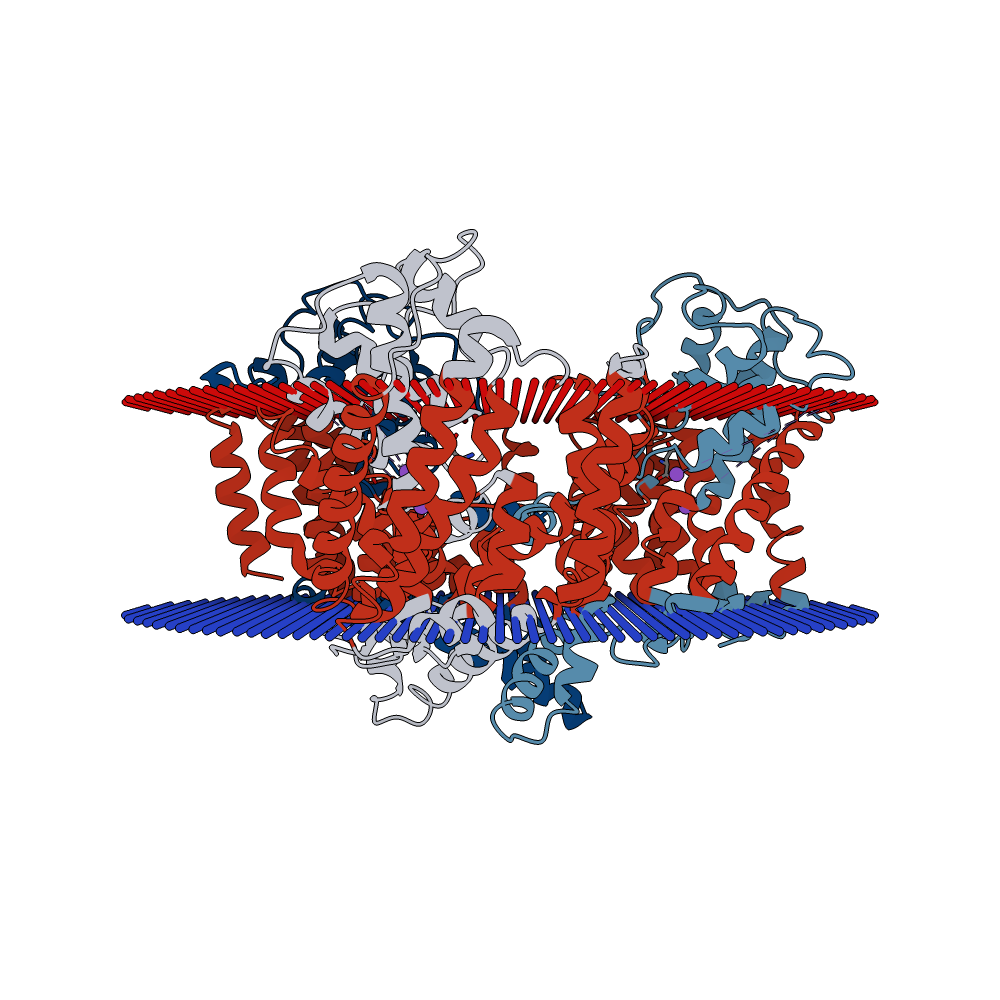
GltT: glutamate and glyphosate transporter in B. subtilis
This part is coding for a glutamate and glyphosate transporter.
The DNA sequence of the gltT gene is coding for the GltT transporter, which is responsible for glutamate uptake into the cell. We found that GltT is also involved in glyphosate uptake in the Gram-positive model bacterium Bacillus subtilis.
Bacteria lacking the gltT gene are highly resistant to glyphosate because the herbicide is not transported into the cell. This part could be useful to engineer bacteria for the uptake and degradation of the weedkiller.
This biobrick is closely related to BBa_K2586002.
| Locus | BSU10220 |
| Isoelectric point | 9.03 |
| Molecular weight | 45.76 |
| Protein length | 429 aa |
| Gene length | 1287 bp |
| Function | glutamate and aspartate uptake |
| Product | major Na+-couples glutamate/aspartate symport protein |
| Essential | no |
| Synonyms | yhfG |
Characterization
Deletion of gltT confers glyphosate tolerance
We tested whether the clean deletion of the gltT gene sufficient to confer high-level resistance of B. subtilis to glyphosate. For this purpose, we constructed the mutant strain BP233 (gltT). To assess the glyphosate resistance of the gltT mutant, we cultivated the bacteria in CS-Glc minimal medium supplemented with increasing amounts of glyphosate. As shown in Figure 1A, growth of the wild type was inhibited by 5 mM glyphosate. The transporter with a high-affinity for glyphosate seems to be in fact GltT because the deletion of the gltT gene conferred high-level resistance to the herbicide (Figure 1C). Moreover, the growth rates of the strain BP233 (gltT) were reduced by 50% at herbicide concentrations of 6.1 mM (Figure 1B). Thus, in comparison to the wild type strain, 6-fold higher glyphosate concentration is needed to reduce the growth rate of the strain BP233 (gltT) by 50%.
Double mutant gltT gltP shows even higher glyphosate tolerance
In order to test whether the deletion of both gltT and gltP confers an even higher glyphosate tolerance, we constructed the mutant strain BP235 (gltT gltP). We cultivated the bacteria in CS-Glc minimal medium supplemented with increasing amounts of glyphosate. As shown in Figure 1D, the double deletion increased the glyphosate tolerance to 8.0 mM. Therefore, an 8-fold higher glyphosate concentration is needed to reduce the growth rate of the strain BP235 (gltT gltP) by 50%.
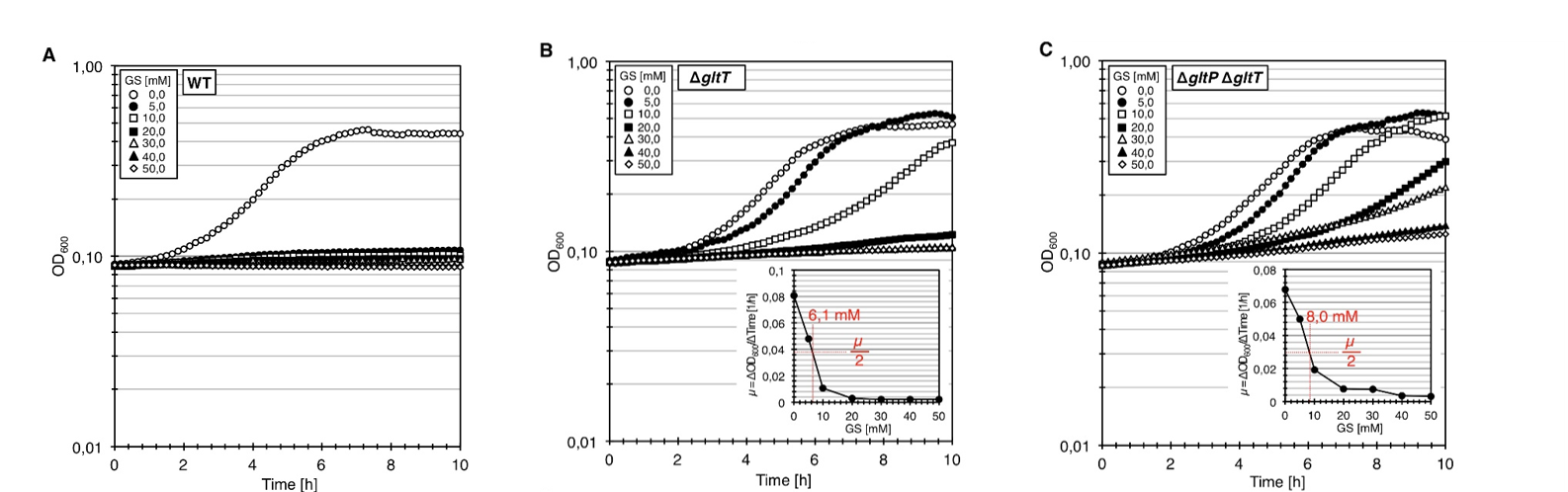
Fig. 1. Inactivation of the glutamate transporters confers high-level resistance to glyphosate. (A) Growth of the B. subtilis wild type (WT) strain 168 in CS-Glc minimal medium supplemented with increasing amounts of glyphosate (GS). (B) Growth of the Δ(gltT) mutant strain BP233 in CS-Glc minimal medium supplemented with increasing amounts of glyphosate (GS). The figure inlay shows the relationship between the growth rate (µ) and the glyphosate (GS) concentration.(C) Growth of the Δ(gltT) Δ(gltP) mutant strain BP235 in CS-Glc minimal medium supplemented with increasing amounts of glyphosate (GS). The figure inlay shows the relationship between the growth rate (µ) and the glyphosate (GS) concentration.
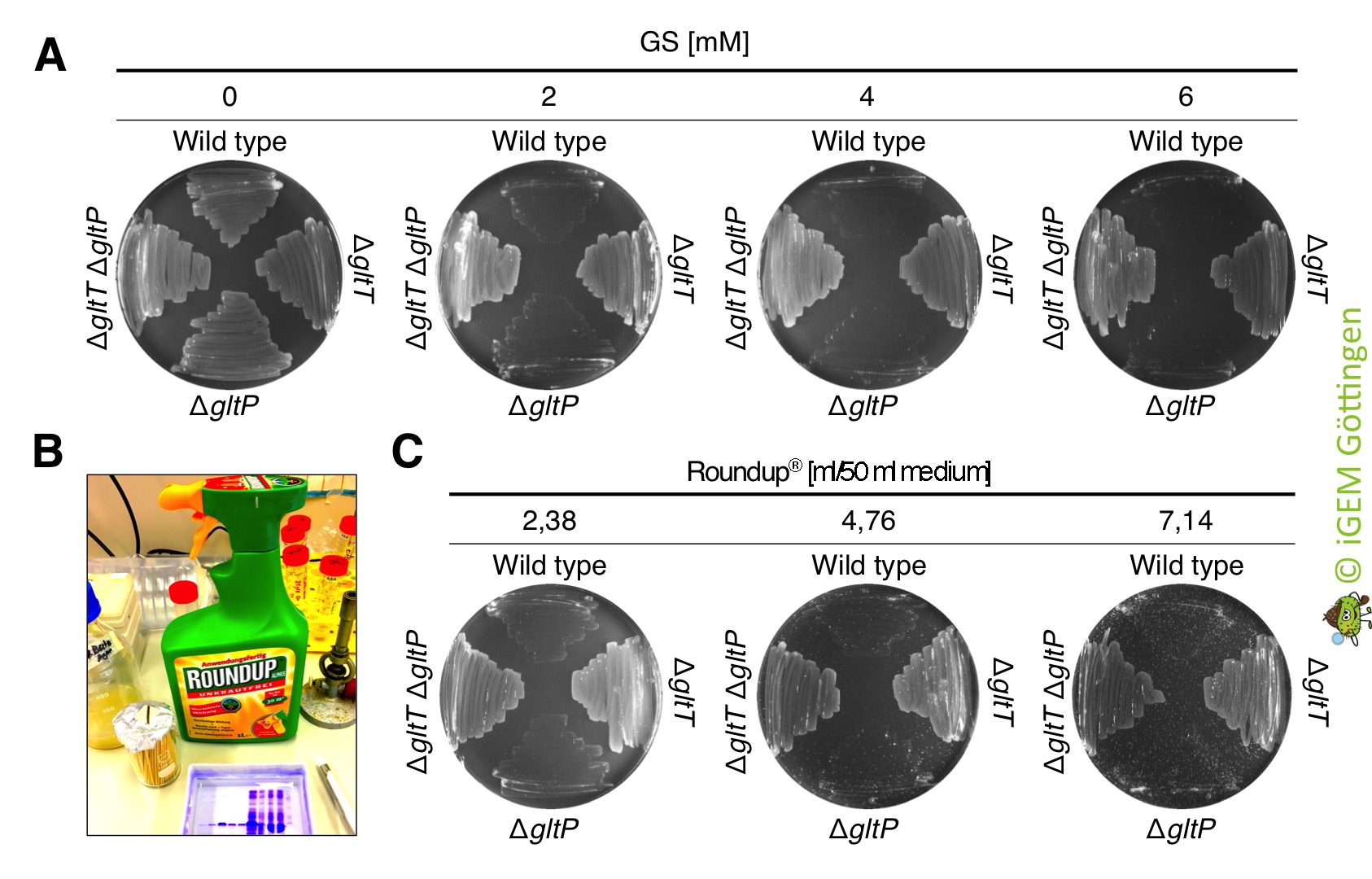
The deletion strains show also high resistance to commercially available RoundUp
We also tested whether the glyphosate that is present in commercially available Roundup® is toxic for B. subtilis. Roundup® was ordered from the german company Westfalia . 1 l of Roundup® Alphee contains 9.4 g of the isopropylamine salt of glyphosate (which corresponds to 7.2 g/l pure glyphosate), 5 g surfactant (undefined) and water. To test the effect of Roundup® Alphee on growth of the bacteria, we propagated the B. subtilis strains 168 (wild type ), BP233 (ΔgltT), BP234 (ΔgltP) and BP235 (ΔgltT ΔgltP) on CS-Glc minimal medium agar plates that were supplemented with glyphosate (control) and with equimolar amounts of glyphosate present in Roundup (test conditions). As shown in Figure 9, Roundup® Alphee killed the B. subtilis wild type strain and the strain lacking the low-affinity glutamate transporter GltP already at a concentration of 2 mM. By contrast, all strains lacking the high-affinity transporter GltT grew in the presence of 2 - 6 mM glyphosate that is present in Roundup.
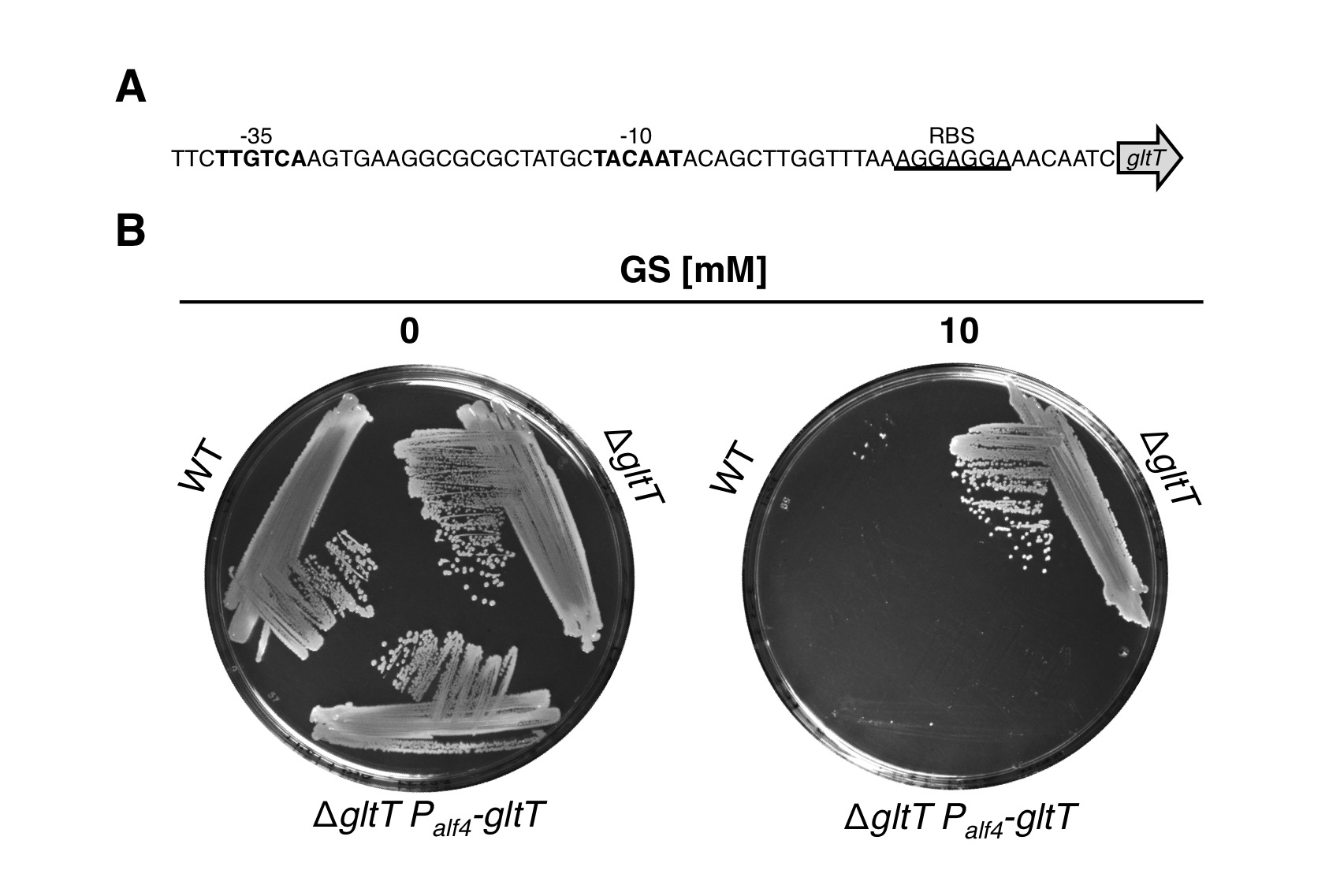
Complementation of the gltT mutation
We also performed a complementation experiment to provide further evidence that GltT is the major glyphosate transporter in B. subtilis. For this purpose, we fused the artificial Palf4 promoter ( BBa_K2586000) together with the gapA ribosome-binding site ( BBa_K2586008) to the gltT gene and integrated the construct into the amyE locus of the gltT mutant (Figure 3A). Next, we propagated the strains BP233 (gltT) and BP237 (gltT Palf4-gltT) together with the wild type strain 168 on agar plates without and with glyphosate (Figure 3B). As expected, all strains grew in the absence of glyphosate. By contrast, only the gltT mutant strain BP233 grew with glyphosate. Thus, like the wild type also the complementation strain BP237 take up glyphosate via GltT. To conclude, under the tested growth conditions the high-affinity glutamate transporter GltT is the major entryway of glyphosate into B. subtilis!
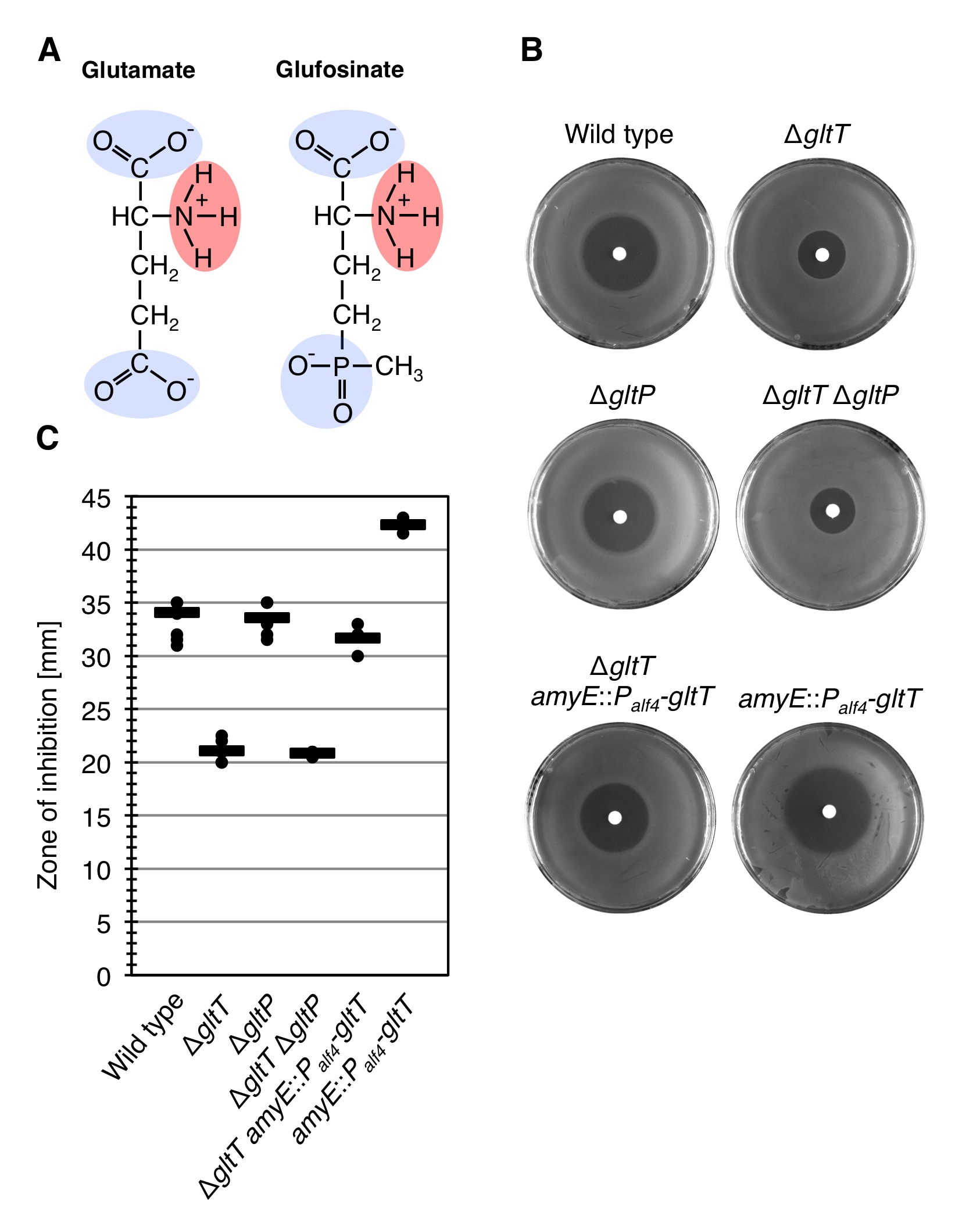
GltT is also involved in the uptake of the herbicide glufosinate
Our structural comparison of glutamate and glyphosate revealed that the two molecules resemble each other because they contain negatively charged groups encompassing positively charged groups. However, the structural similarity of glutamate and glyphosate is not very high. During a scientific discussion with our collaborator Dr. Till Ischebeck from the Department of Plant Biochemistry at the University of Göttingen, we came up with the idea that GltT may also transport the herbicide glufosinate, which is structurally more similar to glutamate than glyphosate and inhibits the glutamine synthetase (Figure 5) (Fraser and Ridley, 1984). Glufosinate (phosphinothricin) is a naturally occurring broad-spectrum systemic herbicide produced by several species of Streptomyces soil bacteria. Plants may also metabolize bialaphos (L-Alanyl-L-alanyl-phosphinothricin), another naturally occurring herbicide, directly into glufosinate (Fraser and Ridley, 1984).
The compound irreversibly inhibits glutamine synthetase, an enzyme necessary for the de novo synthesis of glutamine from ammonia and glutamate, giving it antibacterial, antifungal and herbicidal properties. Application of glufosinate to plants leads to reduced glutamine and elevated ammonia levels in tissues, halting photosynthesis, resulting in plant death. In the 1960s and early 1970s, scientists at University of Tübingen and at the Meiji Seika Kaisha Company independently discovered that species of Streptomyces bacteria produce a tripeptide they called bialaphos that inhibits bacteria; it consists of two alanine residues and a unique amino acid that is an analog of glutamate that they named "phosphinothricin". The inactivation of the gltT gene indeed allowed B. subtilis to tolerate glufosinate (Figures 4B and 4C)! Moreover, the observation that the expression of two copies of the gltT gene in strain BP236 (amyE::Palf4-gltT) increased the sensitivity of the bacteria toward glufosinate further supports the idea that GltT is involved in glufosinate uptake by B. subtilis (Figures 4B and 4C). In contrast to glyphosate, however, the simultaneous deletion of the gltT and gltP genes did not increase glufosinate tolerance of B. subtilis (Figures 4B and 4C). To conclude, under the tested growth conditions the high-affinity glutamate transporter GltT is the major entryway of glyphosate into B. subtilis and GltT is also involved in Glufosinate uptake!
A novel nechanism conferring resistance to glyphosate
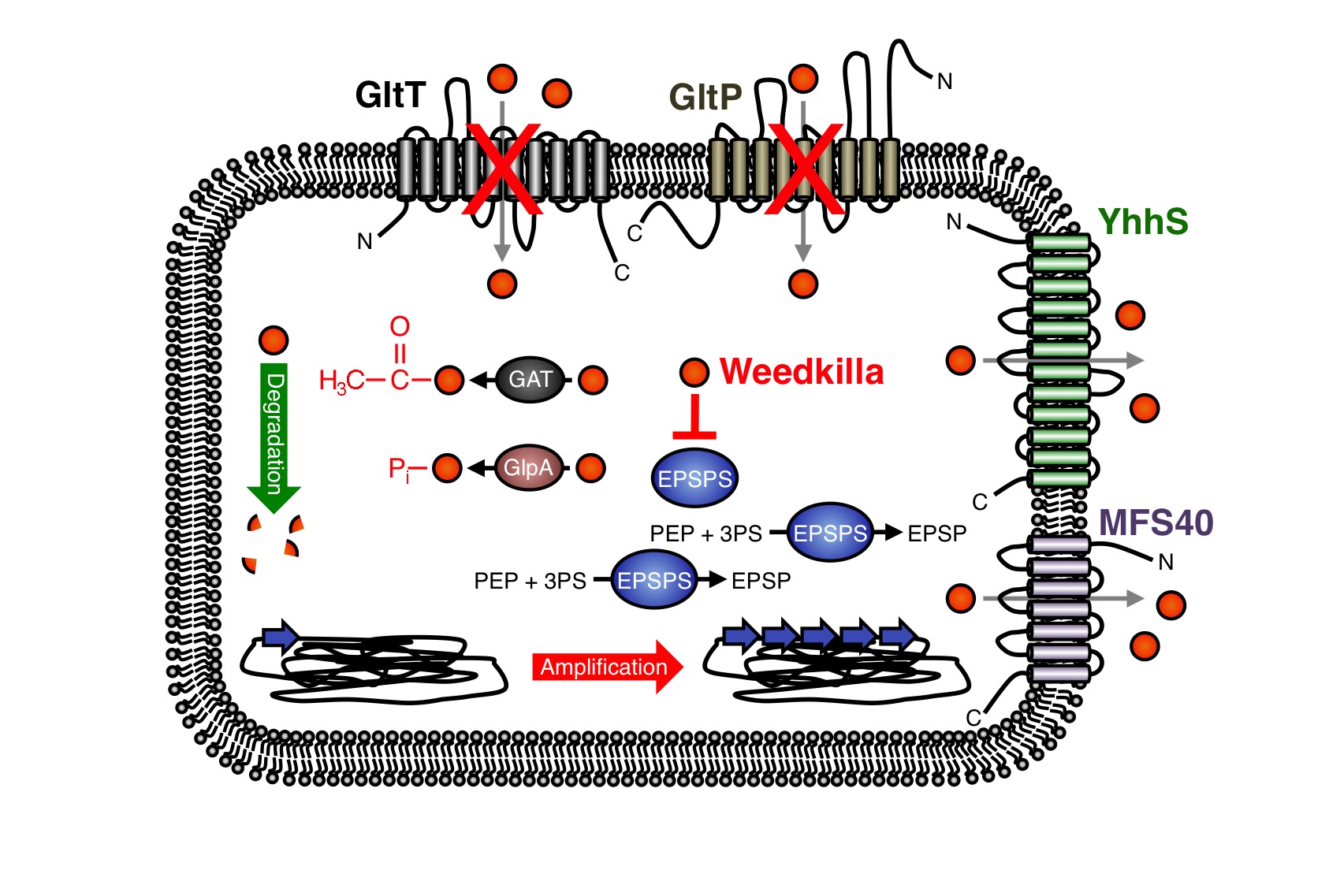
In the past years, the underlying molecular mechanisms conferring resistance to glyphosate have been intensively studied in bacteria and plants. In many cases glyphosate resistance is directly linked to the target of the herbicide. For instance, bacteria like S. aureus are a priori resistant to glyphosate because this organism synthesizes an insensitive EPSP synthase (13-16). Moreover, increased cellular levels of the EPSP synthase, which can be achieved either by overexpression of the coding gene or by gene amplification, can confer resistance to glyphosate (Figure 5) (9, 17-21). Due to the increased cellular levels of the EPSP synthase, the glyphosate is probably titrated away and sufficient amounts of the precursor for aromatic amino acid biosynthesis can be produced.
As mentioned in the design section, several glyphosate-insensitive EPSP synthase mutant variants have been isolated and engineered (11, 22-35). Often, a single amino acid exchange is sufficient to render the EPSP synthase insensitive to glyphosate. However, although glyphosate resistance is frequently linked to the target of the herbicide, resistance against the herbicide may occur by other means. Several studies have demonstrated that glyphosate can be detoxified by covalent modification. For instance, the Gat glyphosate N-acetyltransferase from Bacillus licheniformis, which was subjected to directed evolution for creating an enzyme with higher efficiency and increased specificity for the herbicide, converts glyphosate to N-acetylglyphosate, which is not herbicidal and is not an effective inhibitor of EPSP synthases (Figure 9) (36-39). Moreover, the hygromycin phosphotransferases Hph and GlpA from E. coli and Pseudomonas pseudomallei, respectively, phosphorylate glyphosate and thus confer tolerance to the herbicide (Fig. 3) (40,41). Interestingly, the gat gene has also been used as a selection marker for genetic engineering of bacteria (39). The enzymes that covalently modify glyphosate have been successfully introduced into crops to increase herbicide resistance (42).
Recently, it has been also demonstrated that enhanced export of glyphosate can reduce toxicity of the herbicide. For instance, the overexpression of the uncharacterized membrane proteins MFS40 and YhhS from Aspergillus oryzae and E. coli, respectively, with similarity to the major facilitator secondary transporter superfamily, enhance glyphosate tolerance of E. coli (Figure 5) (43,44). It will be interesting to test whether these transporters are suitable for engineering crops to enhance glyphosate tolerance. Proteins of unknown function can also increase glyphosate tolerance. For instance, the overexpression of the igrA gene product from the Pseudomonas sp. strain PG2982 increases glyphosate tolerance in transgenic rice (45-47). Finally, many bacteria can survive in the presence of glyphosate because they are able to degrade the herbicide (Figure 5) (48-57). To conclude, several mechanisms of glyphosate resistance have been described over the past years and novel mechanisms allowing survival with the herbicide are certainly identified in the future. We have observed that the deletion of the gltT gene in B. subtilis confers high-level glyphosate resistance to the bacteria. The B. subtilis gltT mutant strain could be a suitable host to identify glyphosate uptake systems from plants by expressing cDNA libraries and by screening for transformants that are unable to grow with glyphosate.
References
1. Fischer et al. (1986) J. Bacteriol. 168: 1147-1154
2. Zeigler et al. (2008) J. Bacteriol. 190: 6983-6995.
3. Barbe et al. (2009) Microbiology 155: 1758-1775
4. Kearse et al. (2012) Bioinformatics 28: 1647-1649.
5. Omasits et al. (2014) Bioinformatics. 30: 884-886.
6. Michna et al. (2014) Nucleic Acids Res. 42: D692–D698.
7. Zaprasis et al. (2015) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81: 250-259.
8. Tolner et al. (1995) J. Bacteriol. 177: 2863-2869.
9. Amrhein et al. (1980) Naturwissenschaften 67: 356-357.
10. Comai et al. (1983) Science 221: 370-371.
11. Stalker et al. (1985) J. Biol. Chem. 260: 4724-4728.
12. Gundlach et al. (2017) Sci. Signal. 10: eaal3011.
13. Priestmann et al., (2005) FEBS Lett. 579: 728-732.
14. Cao et al. (2012) PLoS One. 7: e38718.
15. Light et al. (2016) Biochemistry 55: 1239-1245.
16. Liu & Cao, (2018) Biotechnol Lett. 40: 855-864.
17. Rogers et al. (1983) Appl. Envrion. Microbiol. 46: 37-43.
18. Gaines et al. (2011) J Agric Food Chem. 59: 5886-5889.
19. Juglam et al. (2014) Plant Physiol. 166: 1200-1207.
20. Sammons & Gaines (2014) Pest. Manag. Sci. 70: 1367-1377.
21. Dillon et al. (2017) Plant Physiol. 173: 1226-1234.
22. Sost & Amrhein (1990) Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 282: 433-436.
23. Padgette et al. (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266: 22364-22369.
24. He et al. (2001) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1568: 1-6.
25. He et al. (2003) Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 67: 1405-1409.
26. Bearson et al. (2002) Plant Physiol. 129: 1265-1275.
27. Eschenburg et al. (2002) Planta 216: 129-135.
28. Sun et al. (2005) Appl. Envrion. Microbiol. 71: 4771-4776.
29. Zhou et al. (2006) Plant Physiol. 140: 184-195.
30. Healy-Fried et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282: 32949-32955.
31. Vande Berg et al. (2008) Pest. Manag. Sci. 64: 340-345.
32. Funke et al. (2009) J. Biol. Chem. 284: 9854-9860.
33. Tian et al. (2010) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76: 6001-6005.
34. Pollegioni et al. (2011) FEBS J. 278: 2753-2766.
35. Chekan et al. (2016) MedChemComm. 7: 28-36.
36. Castle et al. (2004) Science 304: 1151-1154.
37. Siehl et al. (2005) Pest. Manag. Sci. 61: 235-240.
38. Siehl et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282: 11446-11455.
39. Norris et al. (2009) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75: 6062-6075.
40. Rao et al. (1983) Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 24: 689-695.
41. Penaloza-Vazquez et al. (1995) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 538-543.
42. Liu et al. (2015) Transgenic Res. 24: 753-763.
43. Staub et al. (2012) J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 39: 641-647.
44. Tao et al. (2017) Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 140: 65-68.
45. Fitzgibbon & Braymer, (1988) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54: 1886-1888.
46. Fitzgibbon & Braymer, (1990) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56: 3382-3388.
47. Fartyal et al. (2018) Front. Plant. Sci. 13: 144.
48. Pipke et al. (1980) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53: 974-978.
49. Shinabarger et al. (1986) J. Bacteriol. 168: 702-707.
50. Liu et al. (1991) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57: 1799-1804.
51. Dick & Quinn, (1995) Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 43: 545-550.
52. Singh & Walker, (2006) FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 30: 428-471.
53. Castro et al. (2007) J. Environ. Sci. Health B. 42: 883-886.
54. Hove-Jensen et al. (2014) Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 78: 176-197.
55. Kryuchkova et al. (2014) Microbiol. Res. 169: 99-105.
56. Sviridov et al., (2011) Biochemistry (Mosc). 76: 720-725.
57. Sviridov et al. (2015) Prikl. Biokhim. Mikrobiol. 51: 183-190.
| control | |
| resistance |