Part:BBa_K1499200
Deinococcus radiodurans UV DNA damage endonuclease - uvsE
This part encodes uvsE, a putative UV damage endonuclease found in D. radiodurans that protects cells from radiation-induced DNA damage.
Usage and Biology
Deinococcus radiodurans is a highly radiation-resistant bacterium that can survive after up to 12,000 Gy (absorbed radiation dose, Gray). The unique genes that allow it to better handle radiation exposure may provide ways to make E. coli and other organisms more resistant for applications of synthetic biology in tough environmental conditions, like space. In addition to resistance against ionizing radiation, this bacterium is also known to resist UV radiation. One gene that contributes to this phenotype is a UV DNA damage endonuclease, uvsE, which catalyzes the excision and repair of pyridine dimers following UV exposure [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11807060 (1)]. E. coli possess a copy of this gene, but it is not as effective as the gene from D. radiodurans.
We have observed that this coding part imparts radiation resistance when expressed under a strong constitutive promoter and medium RBS. Although we have not tried inducible or weaker promoters, we expect the part to work under these conditions.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Characterization
Verification of Part
The part was sequence verified in the pSB1C3 backbone before submission to the registry. Two reads, forward and reverse, were obtained using VF2 and VR (Figure 1).
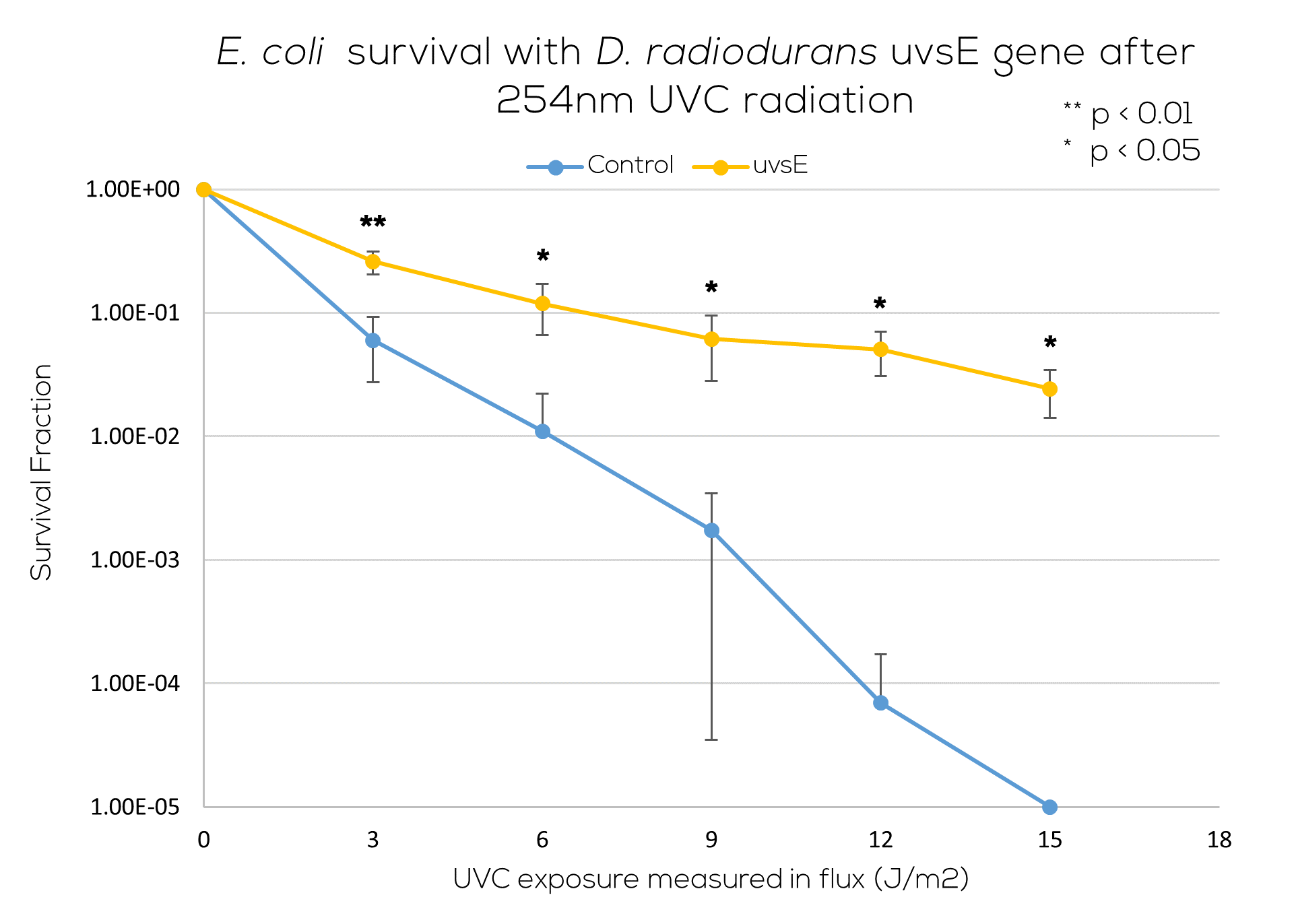
Results
The part has been confirmed to work as expected (Figure 2). The part expressed constitutively under a strong promoter and medium-strength RBS confers significant radiation resistance to E. coli. We have successfully isolated and characterized a new radiation resistance gene to use with the [http://2012.igem.org/Team:Stanford-Brown/Parts Hell Cell toolkit].
References
1. Earl, AM et al. (2002) Genetic evidence that the uvsE gene product of Deinococcus radiodurans R1 is a UV damage endonuclease. J. Bacteriol. 184(4):1003-9. PMID: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11807060 11807060].
//chassis/prokaryote/ecoli
| biology | Deinococcus radiodurans |
| protein | uvsE |