Part:BBa_K1033002:Experience
This experience page is provided so that any user may enter their experience using this part.
Please enter
how you used this part and how it worked out.
Applications of BBa_K1033002
User Reviews
UNIQe95c913fe84e6ac1-partinfo-00000000-QINU UNIQe95c913fe84e6ac1-partinfo-00000001-QINU
The STS-gene has been used by team UNIK copenhagen 2015 as a part of larger DNA construct that was transformed into another chassis organism moss Physcomitrella patens. P. patens has been shown to produce enzymes similar to 4CL. These enzymes from the Pp4CL family (P. patens) have been shown to have similar function as enzymes from the 4CL family of higher plants. This means that P. Patens only lack the production of STS to produce resveratrol.
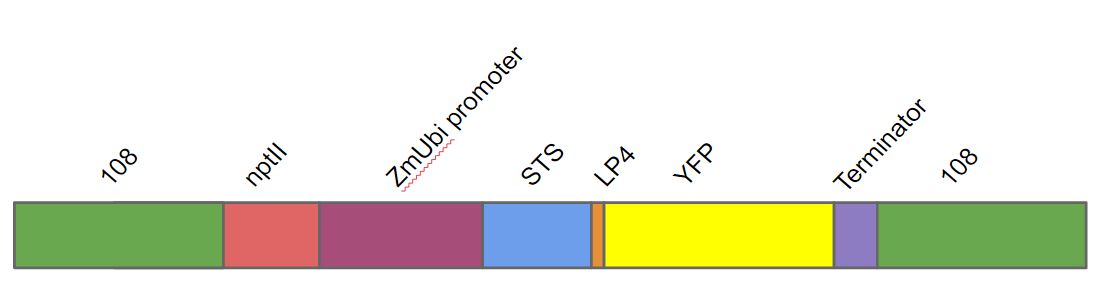
The DNA construct we made contained in the following order. A homologous region to the 108 locus on the moss genome (to ensure stable integration into P. patens genome), a nptII-resistance cassette, the Zea mays ubiquitin promoter driving the stilbene synthase gene (STS) linked to yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) with the LP4 linker sequence, terminator and lastly another 108 region. The STS-gene used has a different sequence than BBa_K1033002. This gene was available to us when the project started and has been added to the registry as BBa_K1825008.
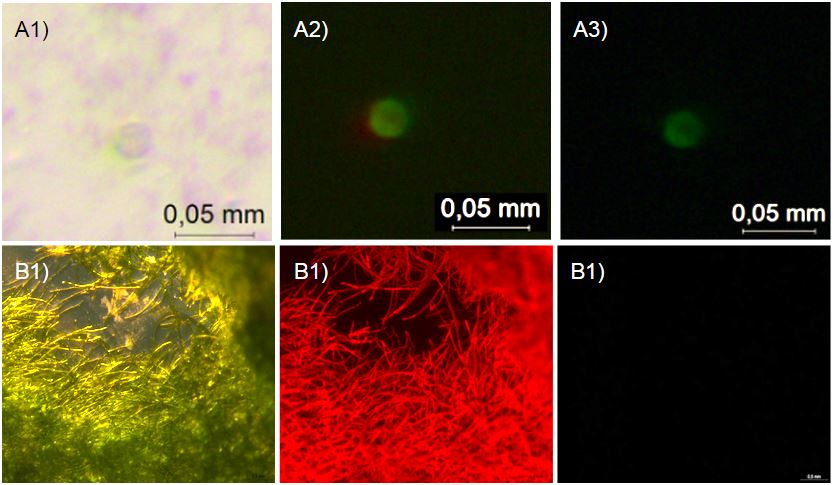
A few days after transforming this gene construct into P. patens protoplasts we observed YFP expression in several moss protoplasts. This confirms that the transformation was successful and highly suggests that the STS enzyme is expressed.
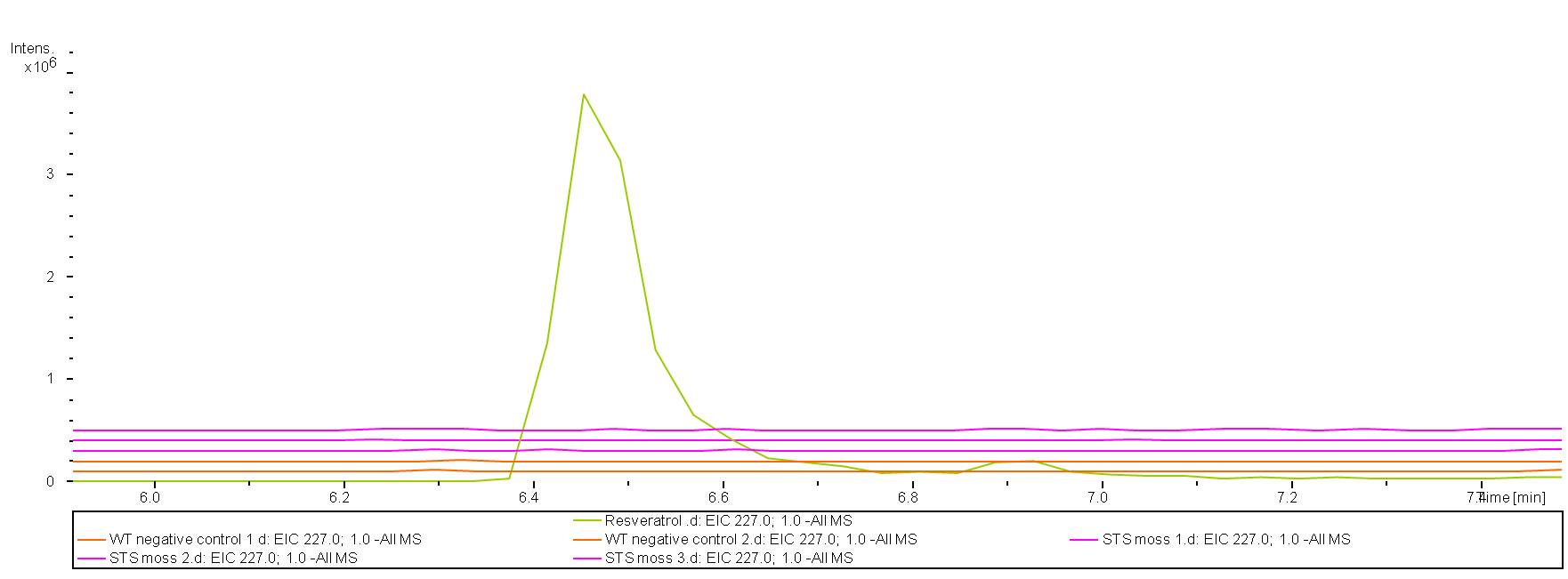
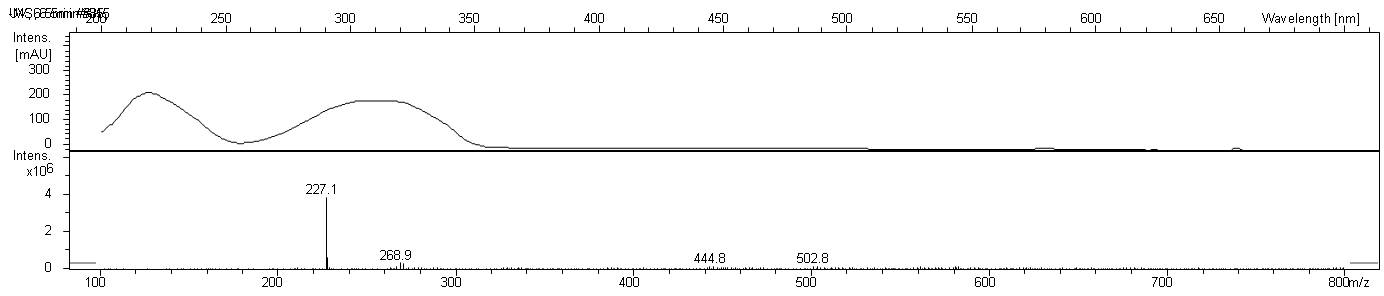
The moss protoplasts transformed with the STS-construct were left to grow for 6 weeks. After 6 weeks the protoplasts had grown into small moss clumps. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) was then used for the purpose of detecting resveratrol. 100% methanol was used for extraction and both WT moss as a negative control and transformed moss was extracted. Pure resveratrol dissolved in 100% methanol was used as a postive standard. However, the LC-MS machine was not able to detect resveratrol in the transformed moss. This suggests that resveratrol is not produced in the transformed moss. It may also be that the amounts of resveratrol was simply to small to be detected or the amount of transformed moss sample was too small.
In conclusion, the presence of YFP suggest that stilbene synthase is expressed in the moss cells, but the expression levels may be too low to produce resveratrol or the enzyme may be dysfunctional.